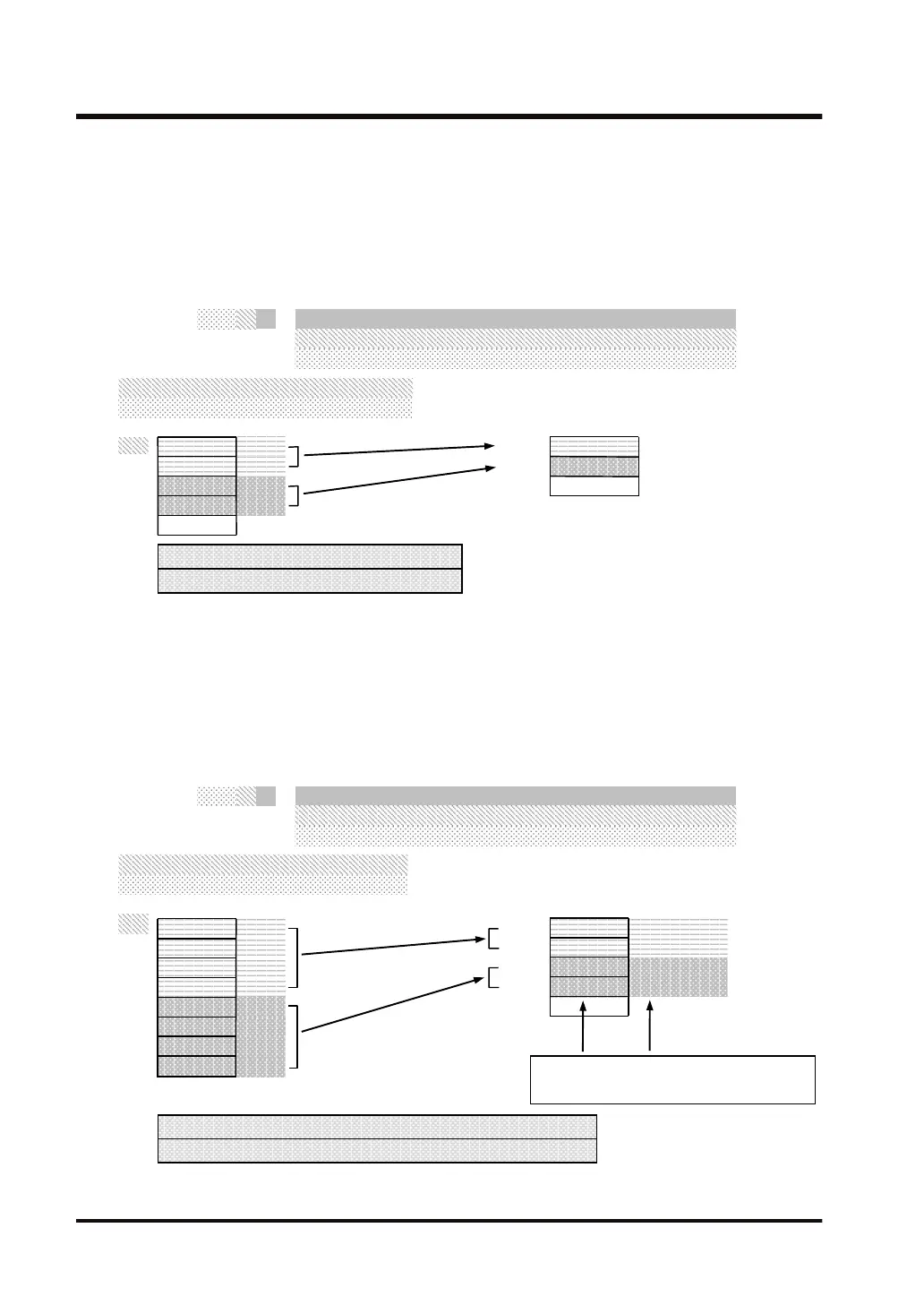
Example 13) Converting two hexadecimal ASCII data (4 digits) to two 16-bit binary
data (hexadecimal)
The conversion starts from the low byte of DT0. It is converted in forward direction (the high
word side of [S2] is considered as high-order numerical data).
B A
9 8
3 2
1 0
H 3938
H 4241
H 3130
H 3332
H 89AB
H 0123
DT0
DT101
DT1
DT2
DT3
(characters)
[S2]…DT0
[D]…DT100
[S2]
DT4
[i]…US
[S1]…"%4x"
[N]…H
DT100
DT102
Converts hexadecimal ASCII data (4-digit) to 16-bit data
① ASCII data (forward direction)
:
:
00020000
② Conversion starting position (0) → [S2]+0 byte
[D]
② Conversion starting position = +0 byte
③ Amount of data to be converted = 2
DT0 to DT1: "0123" → DT100: H 0123
DT2 to DT3: "89AB" → DT101: H 89AB
③ Amount of conversion data (2) → two 4-digit data
Example 14) Converting two decimal ASCII data (8 digits) to two 32-bit BCD data
The conversion starts from the low byte of DT0. It is converted in forward direction (the high
word side of [S2] is considered as high-order numerical data). For empty digits of the storage
area, zeros (0) are inserted.
2 1
H 3231
H 3030 0 0
H 3635
6 5
8 7
4 3
3 2
1 0
0 0
H 3433
H 3332
H 3837
H 3030
H 3130
DT0
DT1
DT2
DT3
(characters)
[S2]…DT0
[D]…DT100
[S2]
DT4
[i]…UL
[S1]…"%8b"
[N]…H
DT5
Converts decimal ASCII data (8-digit) to 32-bit BCD data
① ASCII data (forward direction)
:
:
00020000
② Conversion starting position (0) → [S2]+0 byte
② Conversion starting position = +0 byte
③ Amount of data to be converted = 2
DT0 to DT3 : "00000123" → DT100 to DT101 : H 0000 0123
DT4 to DT7 : "12345678" → DT102 to DT103 : H 1234 5678
DT6
DT100
[D]
DT101
DT102
DT103
DT104
H 0000
H 5678
H 1234 5678
H 0000 0123
H 1234
H 0123
* When the number of characters is smaller than
the number of converted bits, the portions that are
lacking are padded with “0”.
DT7
③ Amount of conversion data (2) → two 8-digit data
14.11 ATOB (Conversion: ASCII → BIN)
14-56 WUME-FP7CPUPGR-12

 Loading...
Loading...











