Rev. 1.50, 10/04, page 115 of 448
MMU
MMU
Process 1
Physical
Memory
(1)
(0)
(2)
(3) (4)
Physical
Memory
Physical
Memory
Physical
Memory
Virtual
Memory
Virtual
Memory
Physical
Memory
Process 1
Process 1
Process 2
Process 3
Process 1
Process 1
Process 2
Process 3
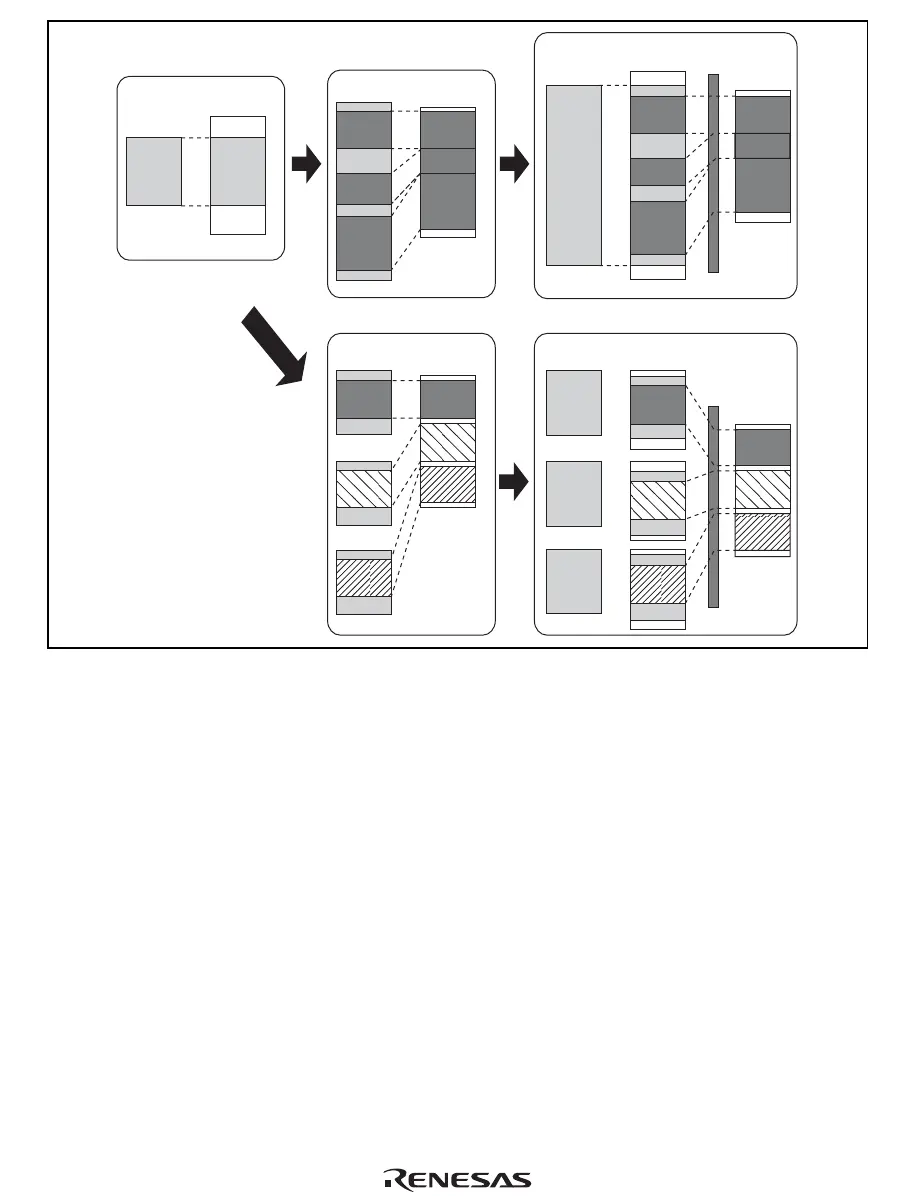
Figure 7.1 Role of MMU
7.1.1 Address Spaces
Virtual Address Space: The SH-4A supports a 32-bit virtual address space, and can access a 4-
Gbyte address space. The virtual address space is divided into a number of areas, as shown in
figures 7.2 and 7.3. In privileged mode, the 4-Gbyte space from the P0 area to the P4 area can be
accessed. In user mode, a 2-Gbyte space in the U0 area can be accessed. When the SQMD bit in
the MMU control register (MMUCR) is 0, a 64-Mbyte space in the store queue area can be
accessed. When the RMD bit in the on-chip memory control register (RAMCR) is 1, a 16-Mbyte
space in on-chip memory area can be accessed. Accessing areas other than the U0 area, store
queue area, and on-chip memory area in user mode will cause an address error.
When the AT bit in MMUCR is set to 1 and the MMU is enabled, the P0, P3, and U0 areas can be
mapped onto any physical address space in 1-, 4-, or 64-Kbyte, or 1-Mbyte page units. By using
an 8-bit address space identifier, the P0, P3, and U0 areas can be increased to a maximum of 256.
Mapping from the virtual address space to the 29-bit physical address space is carried out using
the TLB.
 Loading...
Loading...











