Rev. 1.50, 10/04, page 180 of 448
3. OC address array write (associative)
When a write is performed with the A bit in the address field set to 1, the tag in each way
stored in the entry specified in the address field is compared with the tag specified in the data
field. The way numbers of bits [14:13] in the address field are not used. If the MMU is enabled
at this time, comparison is performed after the virtual address specified by data field bits
[31:10] has been translated to a physical address using the UTLB. If the addresses match and
the V bit in the way is 1, the U bit and V bit specified in the data field are written into the OC
entry. In other cases, no operation is performed. This operation is used to invalidate a specific
OC entry. If the OC entry U bit is 1, and 0 is written to the V bit or to the U bit, write-back is
performed. If a UTLB miss occurs during address translation, or the comparison shows a
mismatch, an exception is not generated, no operation is performed, and the write is not
executed.
Note: This function may not be supported in the future SuperH Series. Therefore, it is
recommended that the OCBI, OCBP, or OCBWB instruction should be used to operate the
OC definitely by reporting data TLB miss exception.
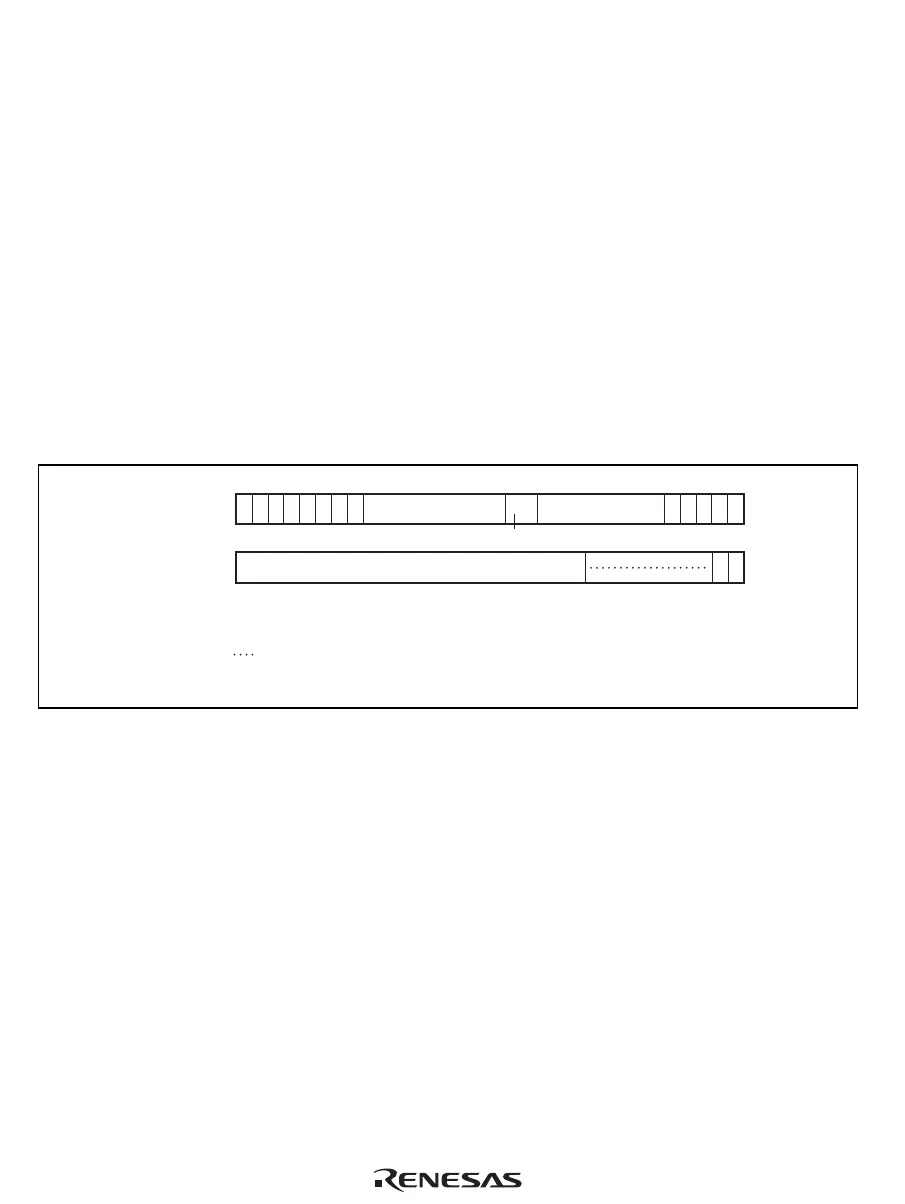
Address field
31 23 543210
11110100 Entry A
Data field
31 10 9 1 0
V
Tag
24 13
121415
2
U
V
U
A
: Validity bit
: Dirty bit
: Association bit
:
Reserved bits
(write value should be 0 and read value is undefined )
: Don't care
Way
0000
*********
*
Figure 8.7 Memory-Mapped OC Address Array
 Loading...
Loading...











