Rev. 1.50, 10/04, page 43 of 448
Section 4 Pipelining
The SH-4A is a 2-ILP (instruction-level-parallelism) superscalar pipelining microprocessor.
Instruction execution is pipelined, and two instructions can be executed in parallel.
4.1 Pipelines
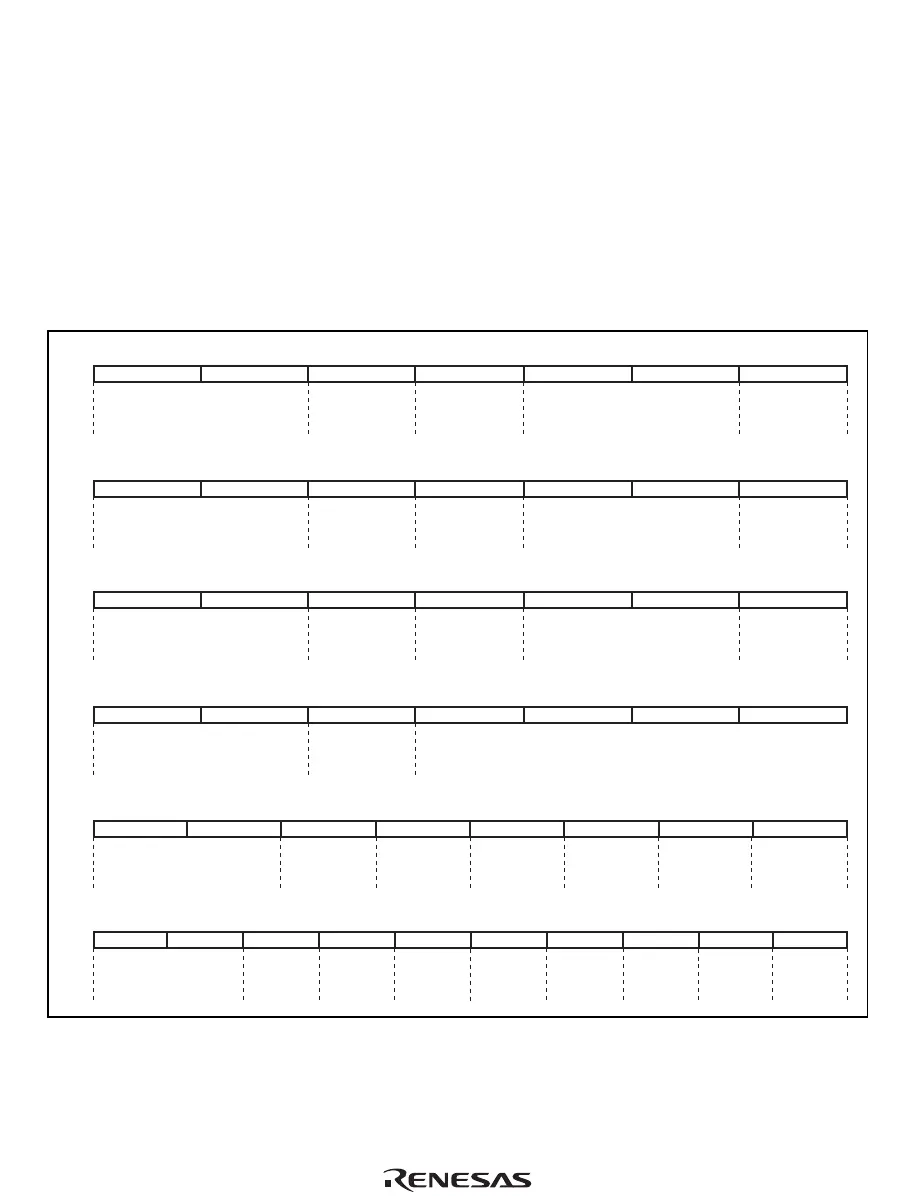
Figure 4.1 shows the basic pipelines. Normally, a pipeline consists of seven stages: instruction
fetch (I1/I2), decode and register read (ID), execution (E1/E2/E3), and write-back (WB). An
instruction is executed as a combination of basic pipelines.
1. General Pipeline
-
Instruction fetch
-
Instruction decode
-
Issue
-
Register read
-
Write-back
-
Operation
-
Forwarding
-
Address calculation
I1 I2 ID E1 E2 E3 WB
2. General Load/Store Pipeline
3. Special Pipeline
4. Special Load/Store Pipeline
5. Floating-Point Pipeline
6. Floating-Point Extended Pipeline
-
Instruction fetch
-
Instruction decode
-
Issue
-
Operation
-
Write-back
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Register read
-
Forwarding
I1 I2 ID FS1 FS2 FS4FS3 FS
-
Operation
-
Instruction fetch
-Instruction
decode
-Issue
-Register read
-Forwarding
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Operation
-
Write-back
I1 I2 ID FE1 FE2 FE3 FE4 FE5 FE6 FS
-
Instruction fetch
-
Instruction decode
-
Issue
-
Register read
-
Write-back
-
Memory data access
I1 I2 ID E1 E2 E3 WB
-
Forwarding
-
Instruction fetch
-
Instruction decode
-
Issue
-
Register read
-
Write-back
-
Operation
I1 I2 ID E1 E2 E3 WB
-
Instruction fetch
-
Instruction decode
-
Issue
-
Register read
I1 I2 ID E1 E2 E3 WB
Figure 4.1 Basic Pipelines
 Loading...
Loading...











