3.15 OPEN CONDUCTOR WITH SINGLE LINE-TO-GROUND FAULT
Most open-conductor (OC) conditions also involve SLG faults at both sides of the open. (See Figure 3-22.) This
is called an "OC/2-SLG" fault (open conductor with two single-line-to-ground). The SLG faults are usually high
resistance, since the broken conductor may touch only dry or frozen earth, or dry pavement. However, this con-
dition is easier
to relay than a high-resistance SLG fault without a broken conductor. This is because the
through-load current that tends to mask the internal fault current on some relay schemes is interrupted by the
broken conductor.
(OPEN)
SLG
SLG
Figure 3-22. Open conductor with two single-line-to-ground faults (OC/2-SLG)
Because of its "rainbow" characteristic, the RFL 9300 is not affected by the through-load component. It can han-
dle OC/2-SLG and high-resistance SLG faults equally well.
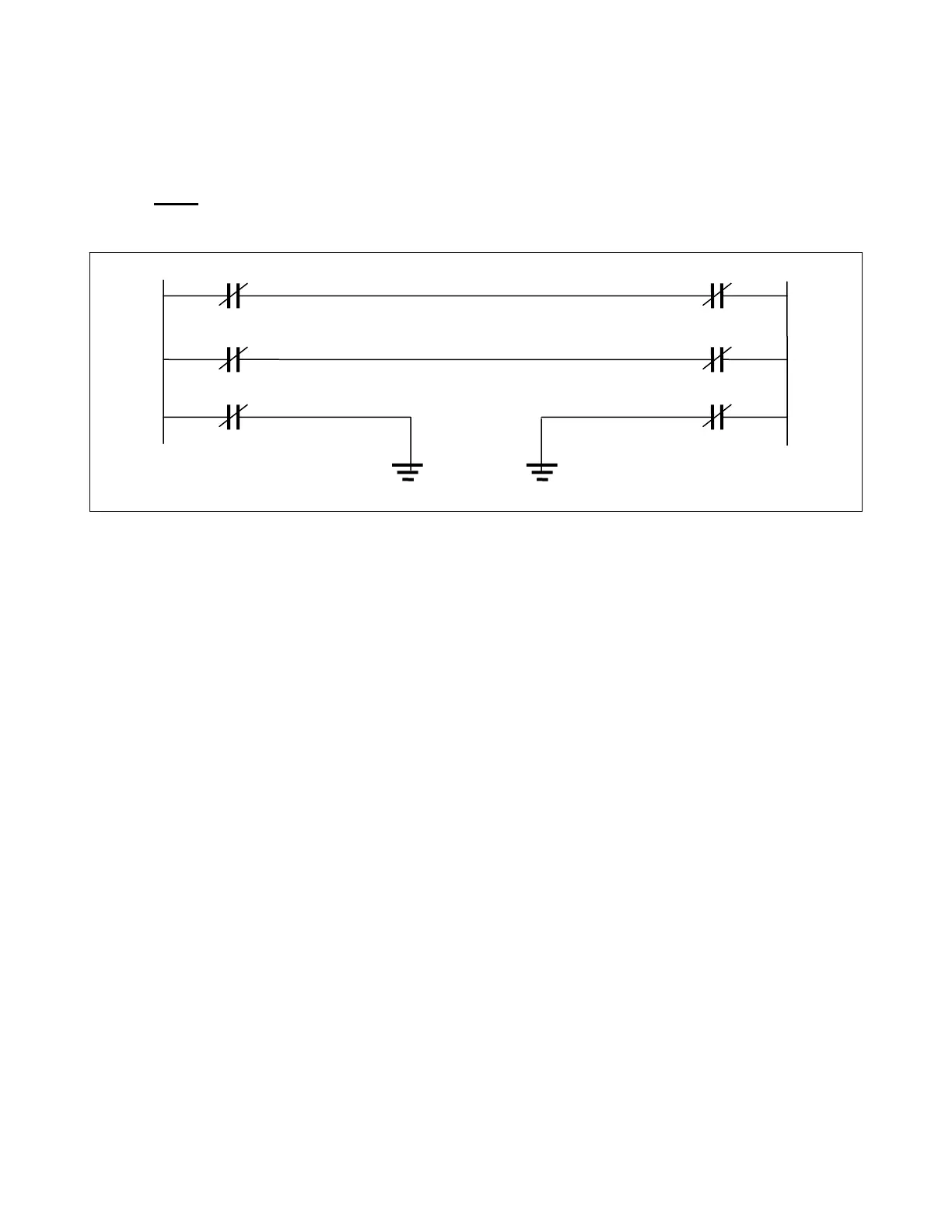
If the open conductor occurs near a tower, it is possible to have an open conductor with an SLG fault on only
one side of the open conductor. (See Figure 3-23.) This is called an "OC/SLG" fault (open conductor with one
single-line-to-ground). This is a common occurrence if the line opens at the supporting insulator.
The RFL 9300 has three modes it can use to clear an OC/SLG condition: phase weak-feed, ground weak-feed,
and ground strong-feed. Phase weak-feed and ground weak-feed are not very sensitive, since they require a
minumum of 2.5 amperes at the remote terminal. This is equivalent to a fault current caused by about 130 ohms
of fault resistance @ 138 kV, using 1200:5 CT's. Ground strong-feed normally provides much more sensitive
protection.
3.15.1 PHASE WEAK-FEED
In phase weak-feed, the faulted phase current at the open conductor side (the local terminal in Figure 3-23) is
zero or very small, if there is no tapped load. This current will be caused by the capacitive charging current of the
portion of the line to the left of the open. This is less than 0.5 amperes for all overhead lines less than 100 miles
long (160 km).
The faulted phase current at the right terminal is equal to the total fault current. If this current is above
1.5amperes plus phase bias, a weak-feed trip is established at the local terminal. (This happens because the
local current is less than 1.5 amperes and it receives 1.5 amperes plus phase bias or more from the remote ter-
minal.) As a result, high-speed tripping will occur at both terminals.
3.15.2 GROUND WEAK-FEED
If there is a small load current flowing during the OC/SLG condition (less than 1.5 amperes), the 3I
0
current at
the local terminal will be less than 1.5 amperes. The ground phase controller also will trip on weak-feed, assum-
ing the total 3I
0
current at the remote terminal is 1.5 amperes plus phase bias or more.
RFL 9300 RFL Electronics Inc.
August 25, 2000 3 - 25 (973) 334-3100

 Loading...
Loading...