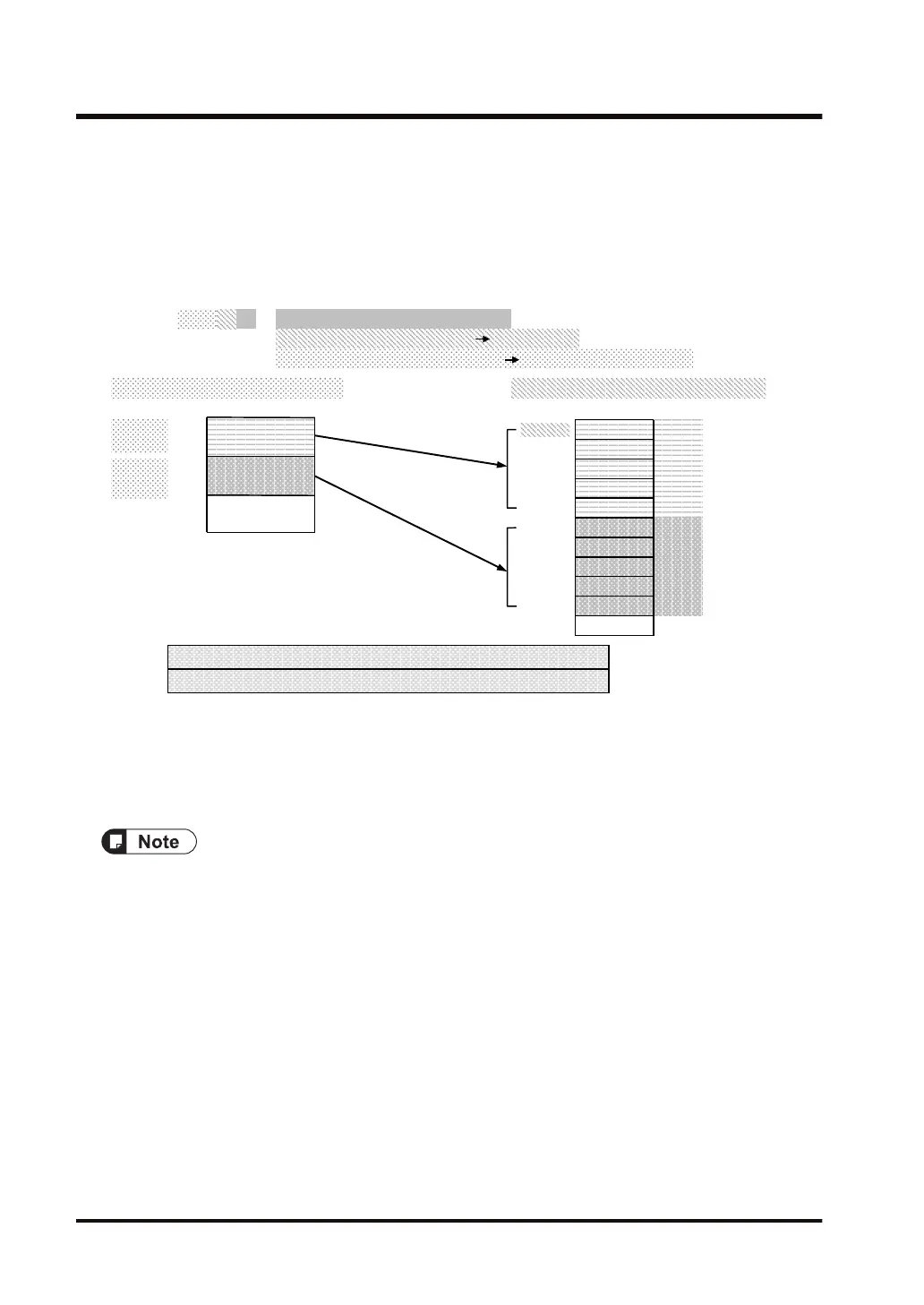
Example 12) Converting 32-bit single-precision floating point real number data (2
data) to exponential notation ASCII data (10 digits x 2)
The low byte of DT100 is set as the beginning of the storage area. 2 digits after the decimal
point. Exponential notation is used. For a positive number, a space is inserted.
H 2031
␣ 1
H 2032
␣ ␣
H 312D
1 -
H 322E
H 3120
2 0
2 .
e 3
. 1
3 2
+ e
H 6533
H 322E
H 302B
H 6533
123.4567
DT100
DT101
DT102
DT103
(characters)
[S2]…DT0
[D]…DT100
[D]
DT104
[i]…SF
[S1]…"%-10.2e"
[N]…H
DT0
DT105
DT106
DT107
Convert 32-bit single precision real number data into exponential ASCII data (10 digits)
① ASCII data (reverse direction)
:
:
00020001
② Storage start position (0) [D]+0 bytes
③ Conversion data amount (2) Convert [S2] and [S2]+2
[S2]
② Storage start position = +0 bytes③ Conversion data amount = 2
DT0 to DT3: 123.4567 → DT100 to DT104: "1.23e+02␣ ␣ "
DT4 to DT7: -12.34567 → DT105 to DT109: "-1.23e+01␣ "
0 +
H 302B
DT108
DT109
-12.34567
DT2
DT4
DT110
DT1
DT3
[S2]
[S2+1]
[S2+2]
[S2+3]
Example 13) Converting 32-bit single-precision floating point real number data (2
data) to floating point ASCII data or exponential notation ASCII data (9 digits x 2)
The high byte of DT100 is set as the beginning of the storage area. It is stored left-aligned (low
word side). The data is converted to 7 significant figure floating point ASCII data before storing.
● The conversion is either to floating point ASCII data or to exponential notation ASCII data,
whichever is shorter.
14.9 BTOA (Conversion: BIN → ASCII)
14-42 WUME-FP7CPUPGR-12

 Loading...
Loading...











