General purpose timer (TIMx) UM0306
256/519
counters are aligned, Timer 1 must be configured in Master/Slave mode (slave with respect
to TI1, master with respect to Timer 2):
● Configure Timer 1 master mode to send its Enable as trigger output (MMS=001 in the
TIM1_CR2 register).
● Configure Timer 1 slave mode to get the input trigger from TI1 (TS=100 in the
TIM1_SMCR register).
● Configure Timer 1 in trigger mode (SMS=110 in the TIM1_SMCR register).
● Configure the Timer 1 in Master/Slave mode by writing MSM=’1’ (TIM1_SMCR
register).
● Configure Timer 2 to get the input trigger from Timer 1 (TS=001 in the TIM2_SMCR
register).
● Configure Timer 2 in trigger mode (SMS=110 in the TIM2_SMCR register).
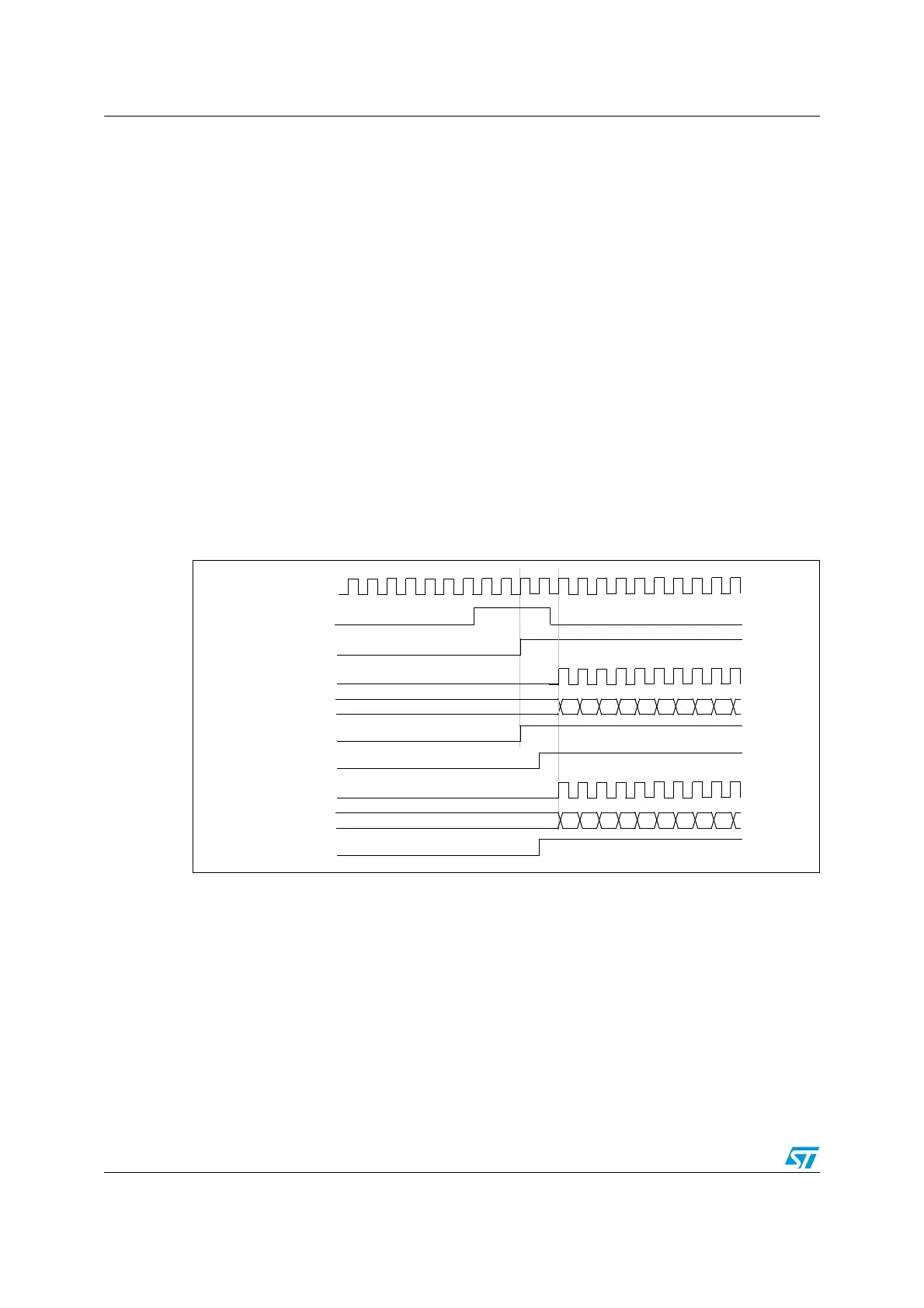
When a rising edge occurs on TI1 (Timer 1), both counters starts counting synchronously on
the internal clock and both TIF flags are set.
Note: In this example both timers are initialized before starting (by setting their respective UG
bits). Both counters starts from 0, but you can easily insert an offset between them by
writing any of the counter registers (TIMx_CNT). You can see that the master/slave mode
insert a delay between CNT_EN and CK_PSC on timer 1.
Figure 117. Triggering Timer 1 and 2 with Timer 1 TI1 input.
13.4.16 Debug mode
When the microcontroller enters debug mode (Cortex-M3 core - halted), the TIMx counter
either continues to work normally or stops, depending on DBG_TIMx_STOP configuration
bit in DBG module. For more details, refer to Section 20.15.2: Debug support for timers and
watchdog and bxCAN.
00 01
CK_INT
TIMER1-CEN=cnt_en
TIMER1-CNT
TIMER 1-TI1
TIMER 1-ck_psc
02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09
TIMER1-TIF
00 01
TIMER2-CEN=cnt_en
TIMER2-CNT
TIMER 2-ck_psc
02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09
TIMER2-TIF

 Loading...
Loading...