104 AMCC Proprietary
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
Setting ZPR[Zn] = 00 for a ZPR field is the only way to deny read access to a page defined by an otherwise valid
TLB entry. TLB_entry[EX] and TLB_entry[WR] do not support read protection. Note that the icbi instruction is
considered a load with respect to access protection; executed in user mode, it causes a data storage interrupt if
MSR[DR] = 1 and ZPR[Zn] = 00 is associated with the EA.
For a given ZPR field value, a program in supervisor state always has equal or greater access than a program in
the problem state. System software can never be denied read (load) access for a valid TLB entry.
5.7.2 Access Protection for Cache Control Instructions
Architecturally the instructions dcba, dcbi, and dcbz are treated as “stores” because they can change data, or
cause loss of data by invalidating a dirty line (a modified cache block).
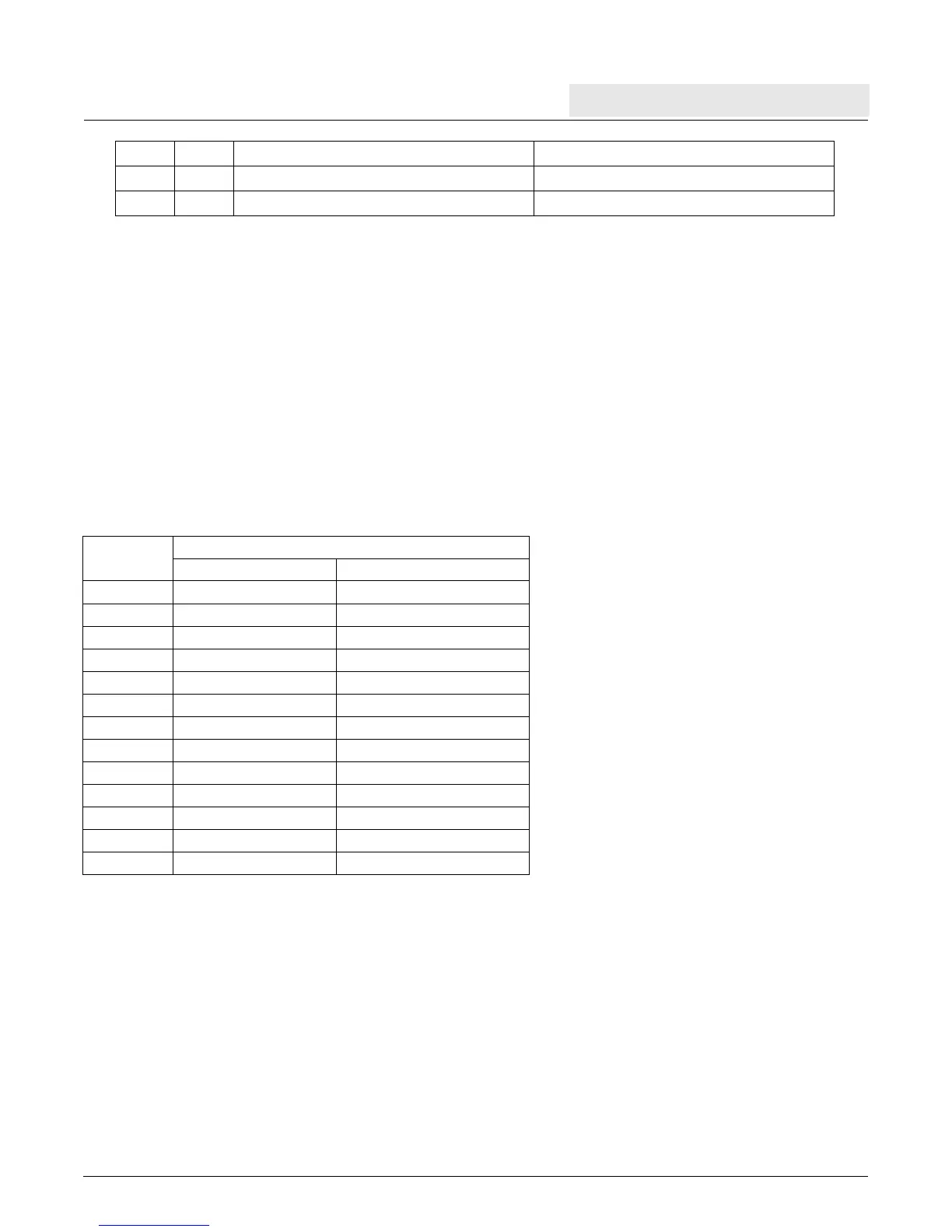
Table 5-2 summarizes the conditions under which the cache control instructions can cause data storage interrupts.
If data address translation is enabled, and write permission is denied (TLB_entry[WR] = 0), dcbi and dcbz can
cause data storage interrupts. dcbz can cause a data storage interrupt when executed in the problem state and all
access is denied (ZPR[Zn] = 00); dcbi cannot cause a data storage interrupt because it is a privileged instruction.
The dcba instruction enables “speculative” line establishment in the cache arrays; the established lines do not
cause a line fill. Because the effects of dcba are speculative, interrupts that would otherwise result when
ZPR[Zn] = 00 or TLB_entry[WR] = 0 do not occur. In such cases, dcba is treated as a no-op.
The dccci instruction can also be considered a “store” because it can change data by invalidating a dirty line;
however, dccci is not address-specific (it affects an entire congruence class regardless of the operand address of
the instruction). To restrict possible damage from an instruction which can change data and yet avoids the
protection mechanism, the dccci instruction is privileged.
26:27 Z13 See the description of Z0.
28:29 Z14 See the description of Z0.
30:31 Z15 See the description of Z0.
Table 5-2. Protection Applied to Cache Control Instructions
Instruction
Possible Data Storage interrupt
When ZPR[Zn] = 00 When TLB_entry[WR] = 0
dcba No (instruction no-ops) No (instruction no-ops)
dcbf Yes No
dcbi No Yes
dcbst Yes No
dcbt No (instruction no-ops) No
dcbtst No (instruction no-ops) No
dcbz Yes Yes
dccci No Yes
dcread No No
icbi Yes No
icbt No (instruction no-ops) No
iccci No No
icread No No
 Loading...
Loading...