AMCC Proprietary 61
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
eieio was necessary, because the read and write addresses are different, but affect each other
The PPC405 implements both sync and eieio identically, in the manner described above for sync. In the PowerPC
Architecture, sync can function across all processors in a multiprocessor environment; eieio functions only within
its executing processor. The PPC405 does not provide hardware support for multiprocessor memory coherency, so
sync does not guarantee memory ordering across multiple processors.
2.11 Implemented Instruction Set Summary
This section provides an overview of the various types and categories of instructions implemented within the
PPC405. In addition, Instruction Set on page 157 provides a complete alphabetical listing of every implemented
instruction.
Appendix A Instruction Summary on page 357 alphabetically lists each instruction and extended mnemonic and
provides a short-form description. Appendix B Instructions by Category on page 395 provides short-form
descriptions of instructions, grouped by the instruction categories listed in Table 2-12.
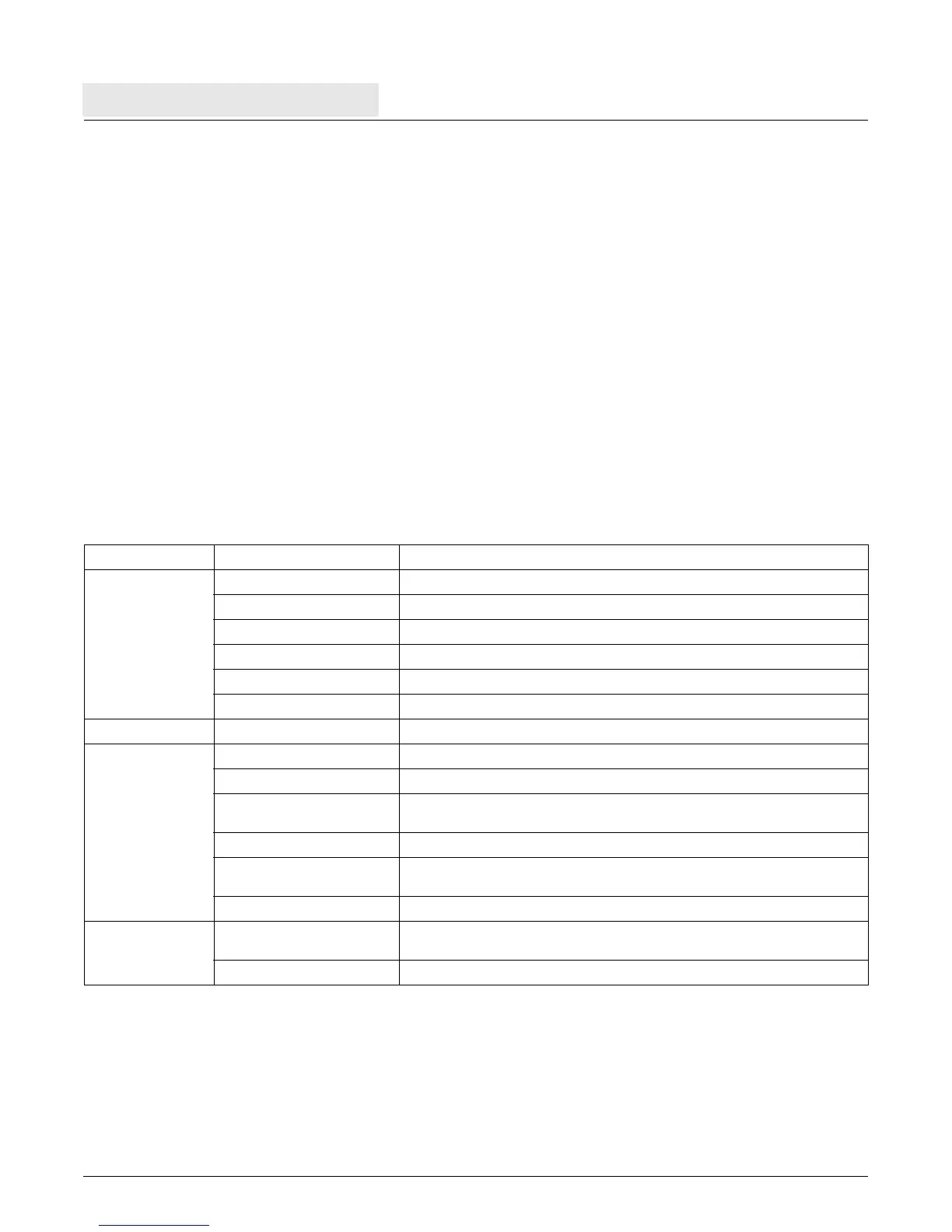
Table 2-12 summarizes the PPC405 instruction set functions by categories. Instructions within each category are
described in subsequent sections.
Table 2-12. PPC405 Instruction Set Summary
Category Subcategory Instruction Types
Integer
Integer Storage Access load, store
Integer Arithmetic add, subtract, negate, multiply, multiply-accumulate, multiply halfword, divide
Integer Logical and, andc, or, orc, xor, nand, nor, xnor, extend sign, count leading zeros
Integer Compare compare, compare logical, compare immediate
Integer Rotate rotate and insert, rotate and mask
Integer Shift shift left, shift right, shift right algebraic
Branch branch, branch conditional, branch to LR, branch to CTR
Processor Control
Condition Register Logical crand, crandc, cror, crorc, crnand, crnor, crxor, crxnor, move CR field
Register Management move to/from SPR, move to/from DCR, move to/from CR
System Linkage
system call, return from interrupt, return from critical interrupt, return from machine
check interrupt
Trap trap
Interrupt Control
move to/from MSR, return from interrupt, return from critical interrupt, return from
machine check interrupt, write to external interrupt enable bit
Processor Synchronization synchronize
Storage Control
Cache Management
data allocate, data invalidate, data touch, data zero, data flush, data store, data
read, instruction invalidate, instruction touch
TLB Management read, write, search, synchronize
 Loading...
Loading...