92 AMCC Proprietary
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
5.3 Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB)
The TLB is hardware that controls translation, protection, and storage attributes. The instruction and data units
share a unified fully-associative TLB, in which any page entry (TLB entry) can be placed anywhere in the TLB. TLB
entries are maintained under program control. System software determines the TLB entry replacement strategy
and the format and use of page state information. A TLB entry contains the information required to identify the
page, to specify translation and protection controls, and to specify the storage attributes.
5.3.1 Unified TLB
The unified TLB (UTLB) contains 64 entries; each has a TLBHI (tag) portion and a TLBLO (data) portion, as
described in Figure 5-2 on page 93. TLBHI contains 36 bits; TLBLO contains 32 bits. When translation is enabled,
the UTLB tag portion compares some or all of EA0:21 with some or all of the effective page number EPN0:21,
based on the size bits SIZE0:2. All 64 entries are simultaneously checked for a match. If an entry matches, the
corresponding data portion of the UTLB provides the real page number (RPN), access control bits (ZSEL, EX,
WR), and storage attributes (W, I, M, G, E, U0).
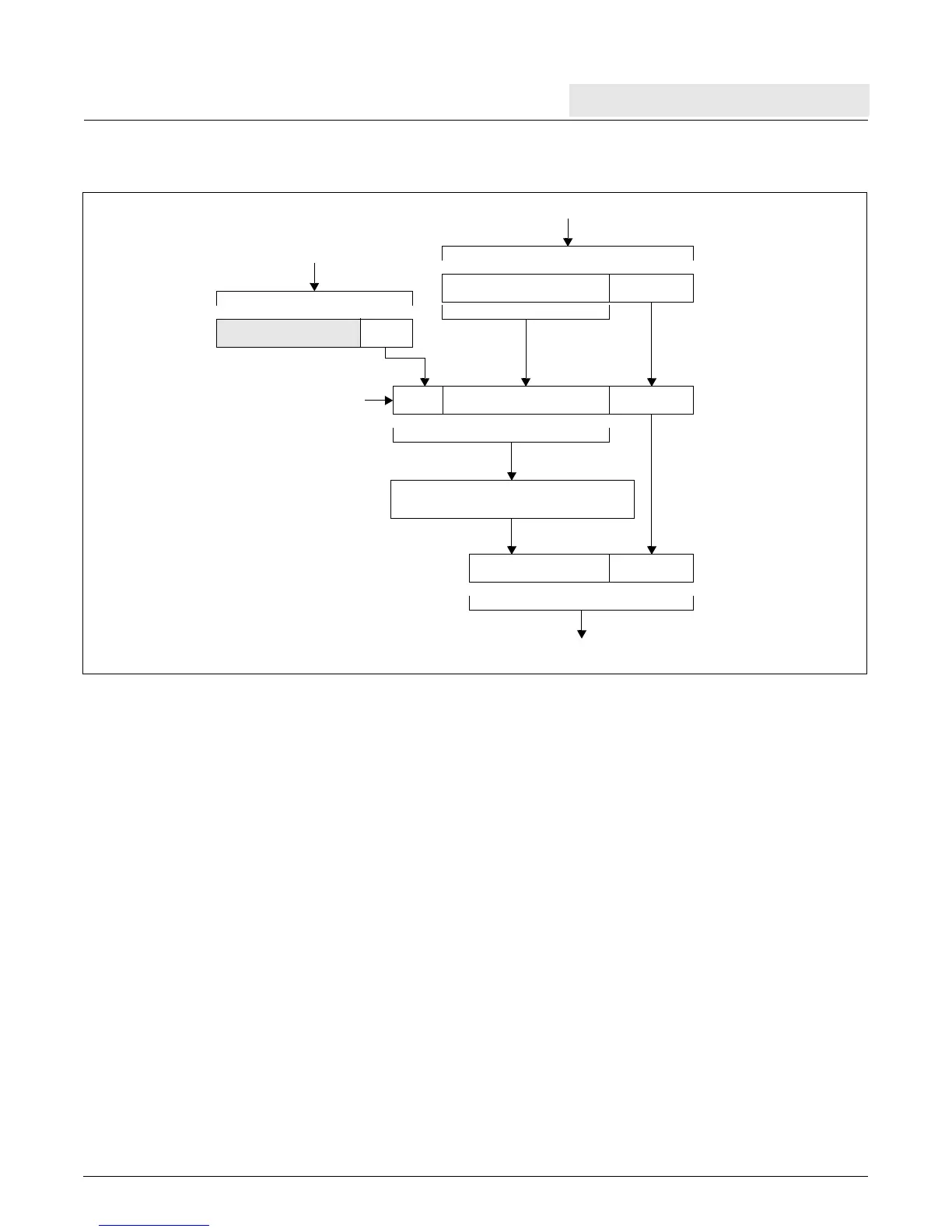
Figure 5-1. Effective-to-Real Address Translation Flow
[0:n–1] [n:31]
OffsetEffective Page Address
[0:7]
PID
Effective Page Address OffsetPID
32-bit EA
Unified TLB
64-entry Fully-associative Array
OffsetReal Page Number
32-bit Real Address
[8:n+7]
[0:n–1] [n:31]
[n+8:39]
[24:31]
[0:23]
40-bit Virtual Address
Note:n is determined by page size.
See Table 5-1, “TLB Fields Related to
Page Size,” on page -94.
PID Register
 Loading...
Loading...