118 AMCC Proprietary
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
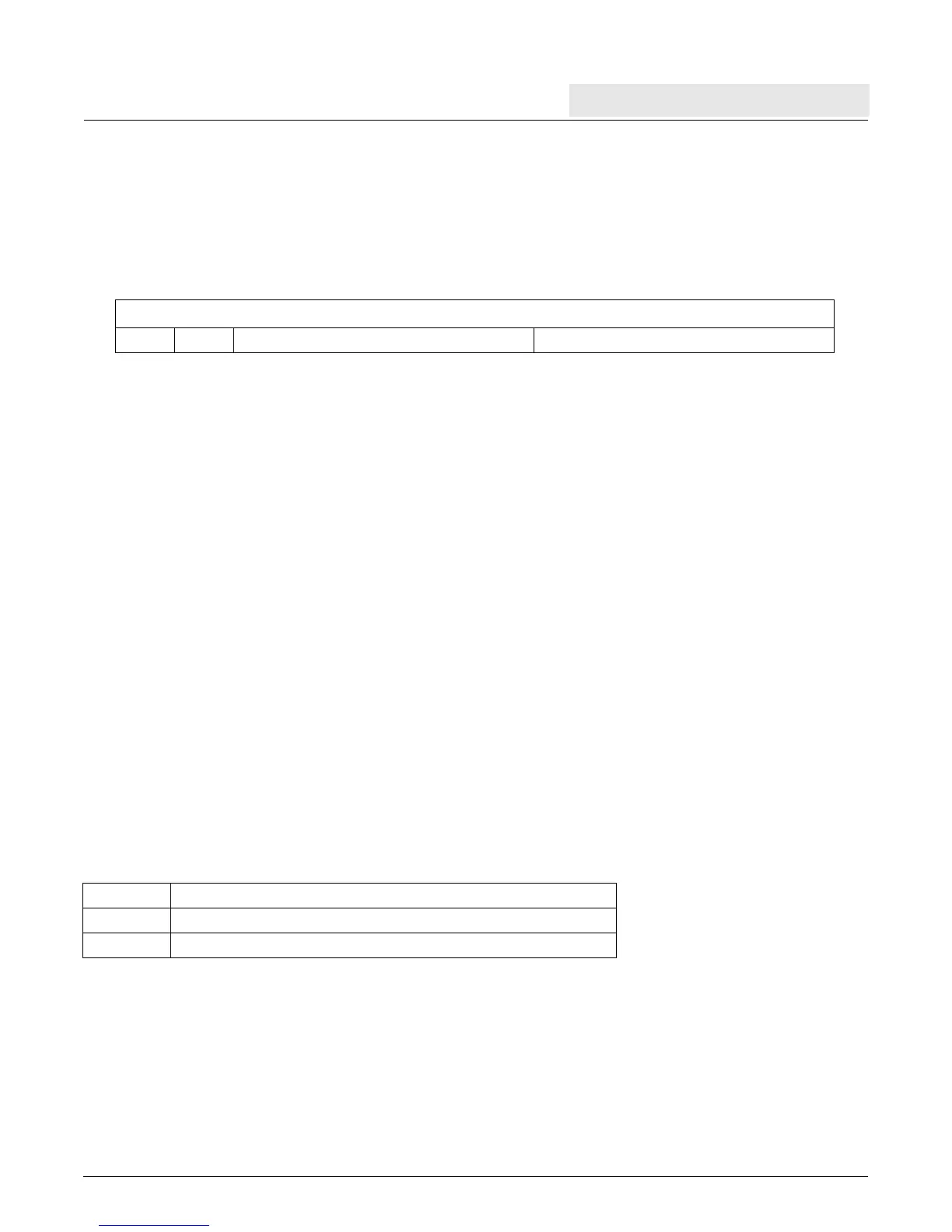
6.5.6 Data Exception Address Register (DEAR)
The DEAR is a 32-bit register that contains the address of the access for which one of the following synchronous
precise errors occurred: alignment error, data TLB miss, or data storage interrupt. The contents of the DEAR can
be written to a GPR using the mfspr instruction. The contents of a GPR can be written to the DEAR using the
mtspr instruction.
6.6 Critical Input Interrupts
The UICCR can be programmed so that any UIC interrupt can be presented as a critical interrupt input to the
processor core. Critical interrupts are recognized only if enabled by MSR[CE].
MSR[CE] also enables the watchdog timer first-time-out interrupt. However, the watchdog interrupt has a different
interrupt vector than the critical pin interrupt. See Watchdog Timer Interrupt on page 126.
After detecting a critical interrupt, if no synchronous precise interrupts are outstanding, the PPC405 immediately
takes the critical interrupt and writes the address of the next instruction to be executed in SRR2. Simultaneously,
the contents of the MSR are saved in SRR3. MSR[CE] is reset to 0 to prevent another critical interrupt or the
watchdog timer first time-out interrupt from interrupting the critical interrupt handler before SRR2 and SRR3 get
saved. MSR[DE] is reset to 0 to disable debug interrupts during the critical interrupt handler.
The MSR is also written with the values shown in Table 6-4. The high-order 16 bits of the program counter are then
loaded with the contents of the EVPR and the low-order 16 bits of the program counter are loaded with 0x0100.
Interrupt processing begins at the address in the program counter.
Inside the interrupt handling routine, after the contents of SRR2/SRR3 are saved, critical interrupts can be enabled
again by setting MSR[CE] = 1.
Executing an rfci instruction restores the program counter from SRR2 and the MSR from SRR3, and execution
resumes at the address in the program counter.
6.7 Machine Check Interrupts
When an external bus error occurs on an instruction fetch, and execution of that instruction is subsequently
attempted, a machine check—instruction interrupt occurs.
When an external bus error occurs while attempting data accesses, a machine check—data interrupt occurs.
Figure 6-8. Data Exception Address Register (DEAR)
0:31 Address of Data Error (synchronous)
Table 6-4. Register Settings during Critical Input Interrupts
SRR2 Written with the address of the next instruction to be executed
SRR3 Written with the contents of the MSR
PC EVPR[0:15] || 0x0100
 Loading...
Loading...