AMCC Proprietary 42
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
2.3.5 Machine State Register (MSR)
The Machine State Register (MSR) controls processor core functions, such as the enabling or disabling of
interrupts and address translation.
The MSR is written from a GPR using the mtmsr instruction. The contents of the MSR can be read into a GPR
using the mfmsr instruction. MSR[EE] is set or cleared using the wrtee or wrteei instructions.
The MSR contents are automatically saved, altered, and restored by the interrupt-handling mechanism. See
Machine State Register (MSR) on page 114.
2.3.6 Device Control Registers
Device Control Registers (DCRs) are used to control various on-chip system functions such as the operation of on-
chip buses, peripherals, and certain processor behaviors. The DCR access instructions are mtdcr (move-to-device
control register) and mfdcr (move-from-device control register), which move data between GPRs and the DCRs.
Some DCRs are directly accessed, that is, they are accessed using their DCR numbers. Other DCRs are indirectly
accessed. Such DCRs are accessed by writing an offset to a directly accessed DCR and then reading the data at
the offset in another directly accessed DCR.
2.4 Data Types and Alignment
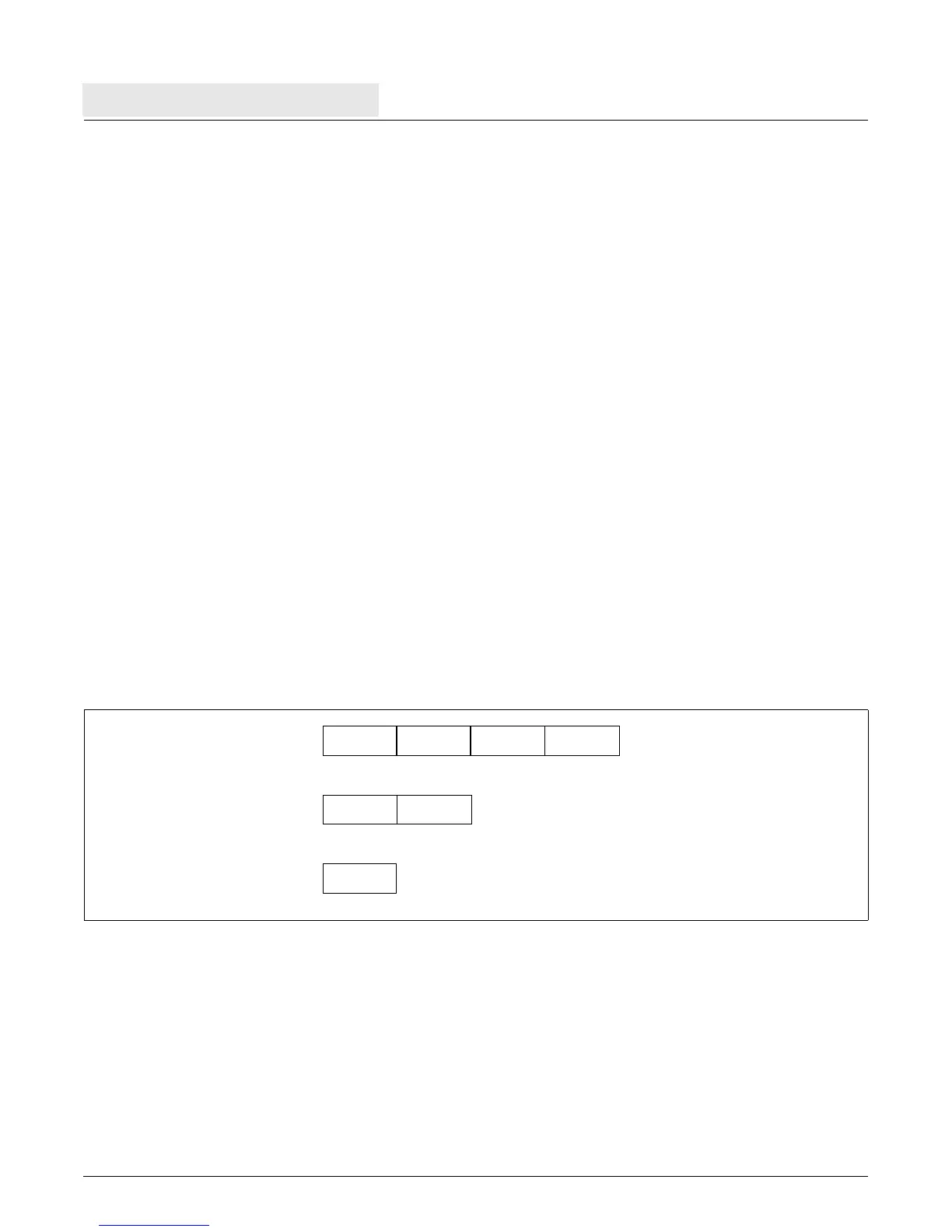
The data types consist of bytes (eight bits), halfwords (two bytes), words (four bytes), and strings (1 to 128 bytes).
Figure 2-10 shows the byte, halfword, and word data types and their bit and byte definitions for big endian
representations of values. Note that PowerPC bit numbering is reversed from industry conventions; bit 0
represents the most significant bit of a value.
Data is represented in either twos-complement notation or in an unsigned integer format; data representation is
independent of alignment issues.
The address of a data object is always the lowest address of any byte comprising the object.
All instructions are words, and are word-aligned (the lowest byte address is divisible by 4).
Figure 2-10. PPC405 Data Types
Byte
Halfword
Word
Bit
3
2
1
0
0
31
Byte
0
15
1
0
0
0
7
Bit
Bit
Byte
Byte
 Loading...
Loading...