AMCC Proprietary 113
Revision 1.02 - September 10, 2007
PPC405 Processor
Preliminary User’s Manual
Save/Restore Register 1 (SRR1) is written with the contents of the MSR; the MSR is then updated to reflect the
new machine context. The new MSR contents take effect beginning with the first instruction of the interrupt
handling routine.
Interrupt handling routine instructions are fetched at an address determined by the interrupt type. The address of
the interrupt handling routine is formed by concatenating the 16 high-order bits of the EVPR and the interrupt
vector offset. (A user must initialize the EVPR contents at power-up using an mtspr instruction.)
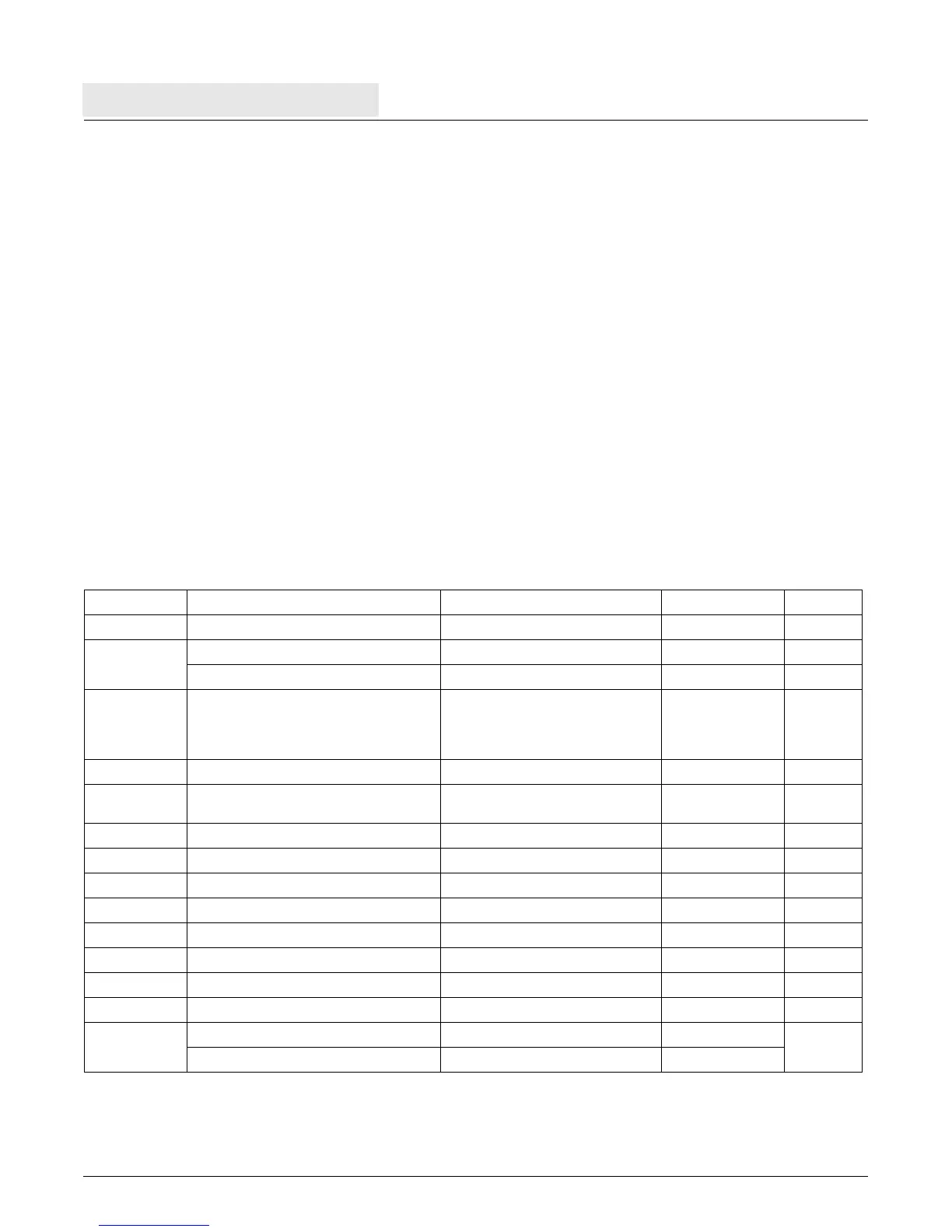
Table 6-2 on page 113 shows the interrupt vector offsets for the interrupt types. Note that there can be multiple
sources of the same interrupt type; interrupts of the same type are mapped to the same interrupt vector, regardless
of source. In such cases, the interrupt handling routine must examine status registers to determine the exact
source of the interrupt.
At the end of the interrupt handling routine, execution of an rfi instruction forces the contents of SRR0 and SRR1 to
be written to the program counter and the MSR, respectively. Execution then begins at the address in the program
counter.
Critical interrupts are processed similarly. When a critical interrupt is taken, Save/Restore Register 2 (SRR2) and
Save/Restore Register 3 (SRR3) hold the next sequential address to be processed when returning from the
interrupt, and the contents of the MSR, respectively. At the end of the critical interrupt handling routine, execution
of an rfci instruction writes the contents of SRR2 and SRR3 into the program counter and the MSR, respectively.
Table 6-2. Interrupt Vector Offsets
Offset Interrupt Type Interrupt Class Category Page
0x0100 Critical input interrupt Asynchronous precise Critical 118
0x0200 Machine check—data — Critical 118
Machine check—instruction — Critical 118
0x0300 Data storage interrupt—
MSR[DR]=1 and ZPR[Z
n] = 0 or
TLB_entry[WR] = 0 or TLB_entry[U0] = 1
or SU0R[U
n]=1
Synchronous precise Noncritical
120
0x0400 Instruction storage interrupt Synchronous precise Noncritical 121
0x0500 External interrupt (external to the
processor core)
Asynchronous precise Noncritical
122
0x0600 Alignment Synchronous precise Noncritical 123
0x0700 Program Synchronous precise Noncritical 123
0x0C00 System Call Synchronous precise Noncritical 124
0x1000 PIT Asynchronous precise Noncritical 125
0x1010 FIT Asynchronous precise Noncritical 125
0x1020 Watchdog timer Asynchronous precise Critical 126
0x1100 Data TLB miss Synchronous precise Noncritical 127
0x1200 Instruction TLB miss Synchronous precise Noncritical 127
0x2000 Debug—BT, DAC, DVC, IAC, IC, TIE Synchronous precise Critical
128
Debug—EXC, UDE Asynchronous precise Critical
 Loading...
Loading...