7.3 Compensating Values to Match Reference Values (Load Compensation)
288
Compensate measurement values to match the element that will be the reference.
With load compensation it is possible to calculate the compensation coefficient by measuring a reference
sample with known data and perform the compensation for the test data obtained from the target sample.
The compensation coefficient can be acquired using up to five compensation conditions. The reference value
of each compensation condition can be set independently.
The following seven compensation conditions should be set for each measurement frequency:
The compensation coefficient is computed from the reference values of Z and obtained from the set values
and the actual data acquired from the reference sample at each of the compensation frequencies.
The measured values of Z and are first compensated using the following equations, and then individual
parameters from the compensated Z and Éý values are employed.
7.3 Compensating Values to Match Refer-
ence Values (Load Compensation)
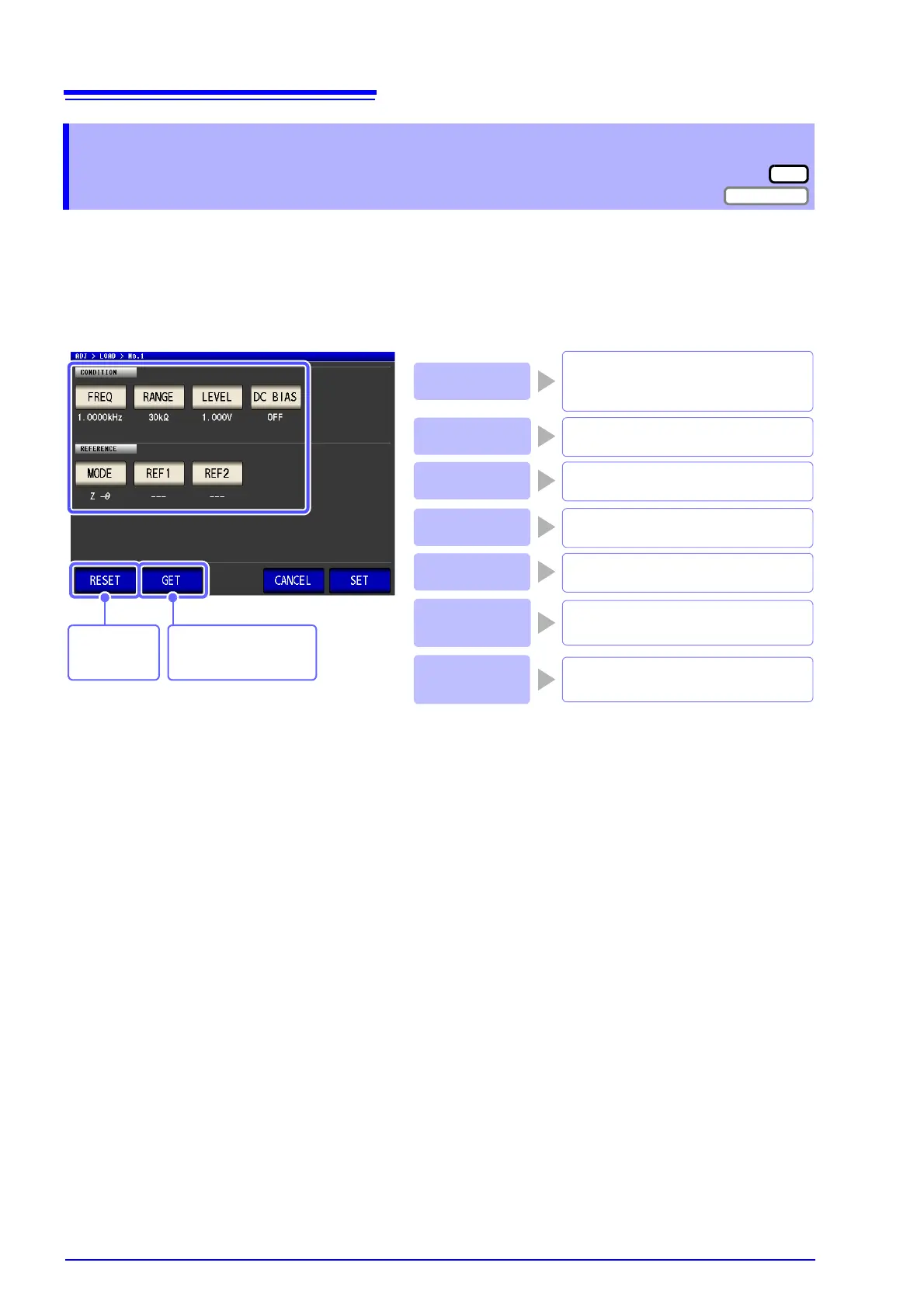
Set the Z/ Cs/ Cp/ Ls/ Lp/ Rs reference
value selected for the parameter type.
Compensation
frequency
Define the measurement frequency
used to measure and compensate the
reference sample.
Compensation
Range
Set the range to compensate.
Compensation
Signal Level
Set the type and value of the signal level
to compensate.
DC Bias
Enable or disable DC bias and set the
value.
Parameter Type
Set the parameter to use as the ref-
erence value.
Reference
Value 1
Reference
Value 2
Set the / D/ Rs/ Rp/ Q/ X reference
value selected for the parameter type.
Acquires the current
measurement conditions.
Deletes the
compensation
conditions.
Compensation coefficient of Z = (Reference value of Z) / (Actual data of Z)
Compensation value of = (Reference value of ) - (Actual data of )
Z = (Z before compensation) × (Compensation coefficient of Z)
= ( before compensation) + (Compensation value of )

 Loading...
Loading...