10.5. Brake energy management
When braking electrical motors, the kinetic energy of the drive train is fed back
regeneratively to the DC bus. This energy causes a DC-bus voltage boost. If the energy fed
back is too high, the inverter reports an error.
Several different strategies can serve to avoid DC-bus overvoltage:
• Stopping the deceleration ramp function generator when the active voltage threshold
for the brake operation is exceeded
• Use of the "Inverter motor brake" function
• Combination of the above named options
Details
The voltage threshold for braking operation results on the basis of the rated mains voltage
set:
Voltage thresholds for braking operation
230 V
DC 390 V
DC 380 V
The voltage threshold for braking operation can be reduced by 0 ... 100 V. The reduction
required must be set in 0x2541:003 (P706.03). However, the reduction must be made to
such an extent that the reduced voltage threshold is still above the normal stationary DC-
bus voltage.The active voltage threshold for the braking operation is displayed in
0x2541:002 (P706.02).
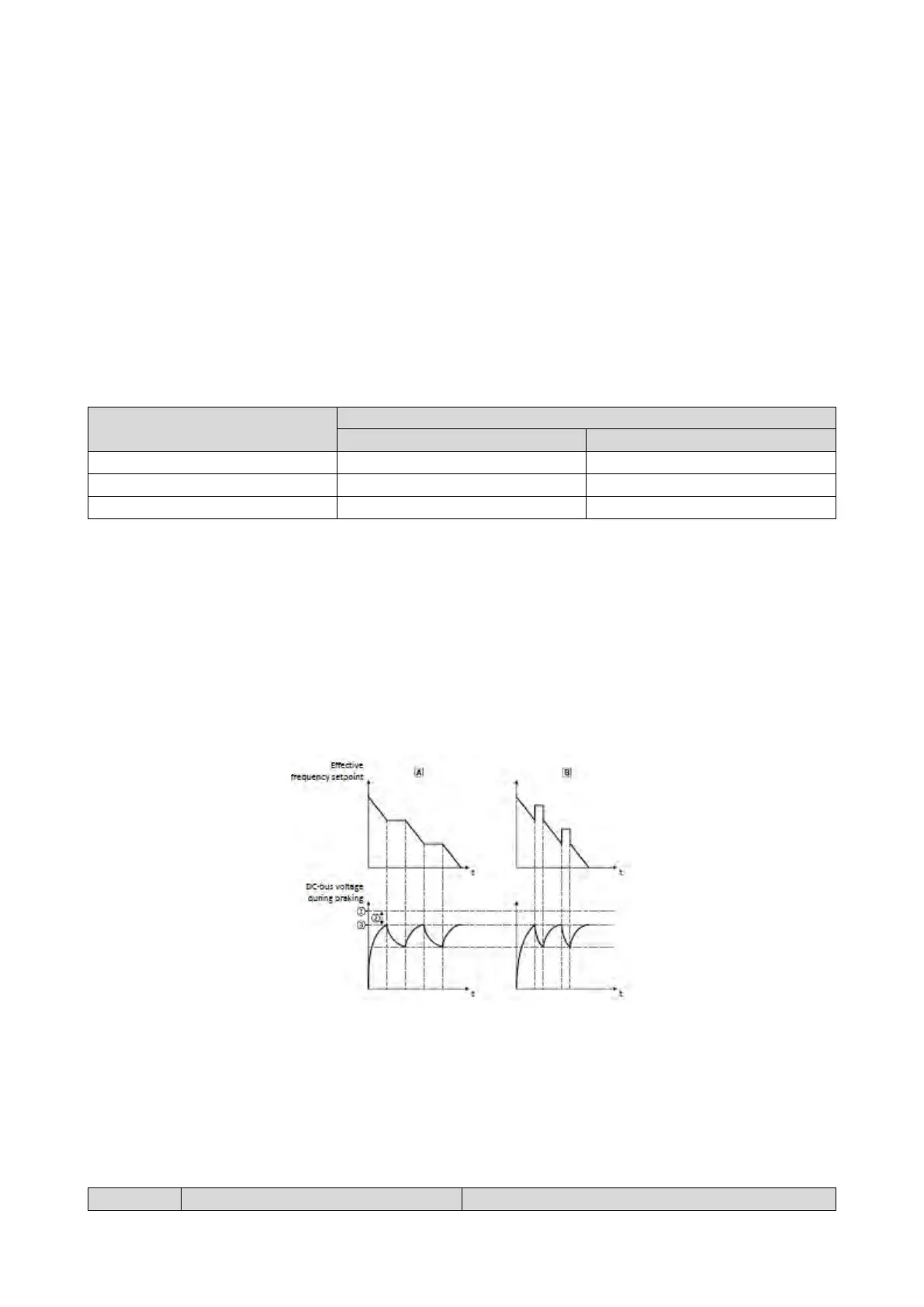
If the DC-bus voltage exceeds the voltage threshold for braking operation, the braking
method selected in 0x2541:001 (P706.01) is applied.
• Stopping the deceleration ramp function generator enables smoother deceleration
with lower torque oscillation.
• The "Inverter motor brake" function allows for quick braking. For process-related
reasons, torque oscillations may occur.
① Voltage threshold for braking operation A Stopping the deceleration ramp function generator
268
② Reduced threshold0x2541:003 (P706.03) B Inverter motor brake 269
③ Active threshold0x2541:002 (P706.02)
Name / value range / [default setting]
 Loading...
Loading...