Remote control - status reporting system
R&S
®
RTM3000
826User Manual 1335.9090.02 ─ 09
B.4.3 Query of an instrument status
Each part of any status register can be read using queries. There are two types of
commands:
●
The common commands *ESR?, *IDN?, *IST?, *STB? query the higher-level
registers.
●
The commands of the STATus system query the SCPI registers
(STATus:QUEStionable...)
The returned value is always a decimal number that represents the bit pattern of the
queried register. This number is evaluated by the controller program.
Queries are usually used after an SRQ in order to obtain more detailed information on
the cause of the SRQ.
B.4.3.1 Decimal representation of a bit pattern
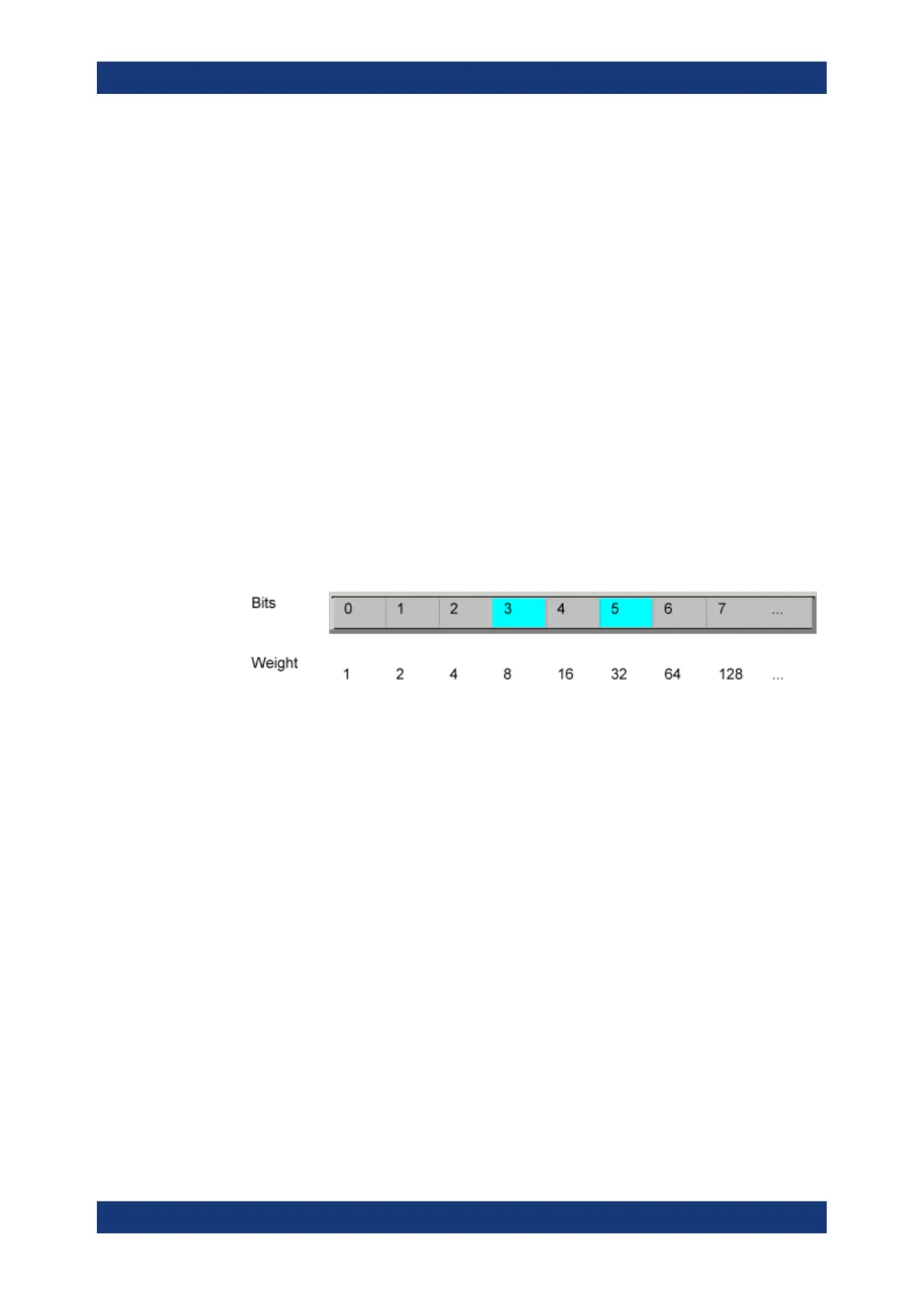
The STB and ESR registers contain 8 bits, the SCPI registers 16 bits. The contents of
a status register are specified and transferred as a single decimal number. To make
this possible, each bit is assigned a weighted value. The decimal number is calculated
as the sum of the weighted values of all bits in the register that are set to 1.
Example:
The decimal value 40 = 32 + 8 indicates that bits no. 3 and 5 in the status register (e.g.
the QUEStionable status summary bit and the ESB bit in the STatus Byte ) are set.
B.4.4 Error queue
Each error state in the instrument leads to an entry in the error queue. The entries of
the error queue are detailed plain text error messages that can be looked up in the
Error Log or queried via remote control using SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]?. Each call of
SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]? provides one entry from the error queue. If no error mes-
sages are stored there any more, the instrument responds with 0, "No error".
The error queue should be queried after every SRQ in the controller program as the
entries describe the cause of an error more precisely than the status registers. Espe-
cially in the test phase of a controller program the error queue should be queried regu-
larly since faulty commands from the controller to the instrument are recorded there as
well.
Application of the status reporting system
 Loading...
Loading...