K3: Compensations
4.2 Temperature compensation
Extended Functions
Function Manual, 03/2013, 6FC5397-1BP40-3BA1
225
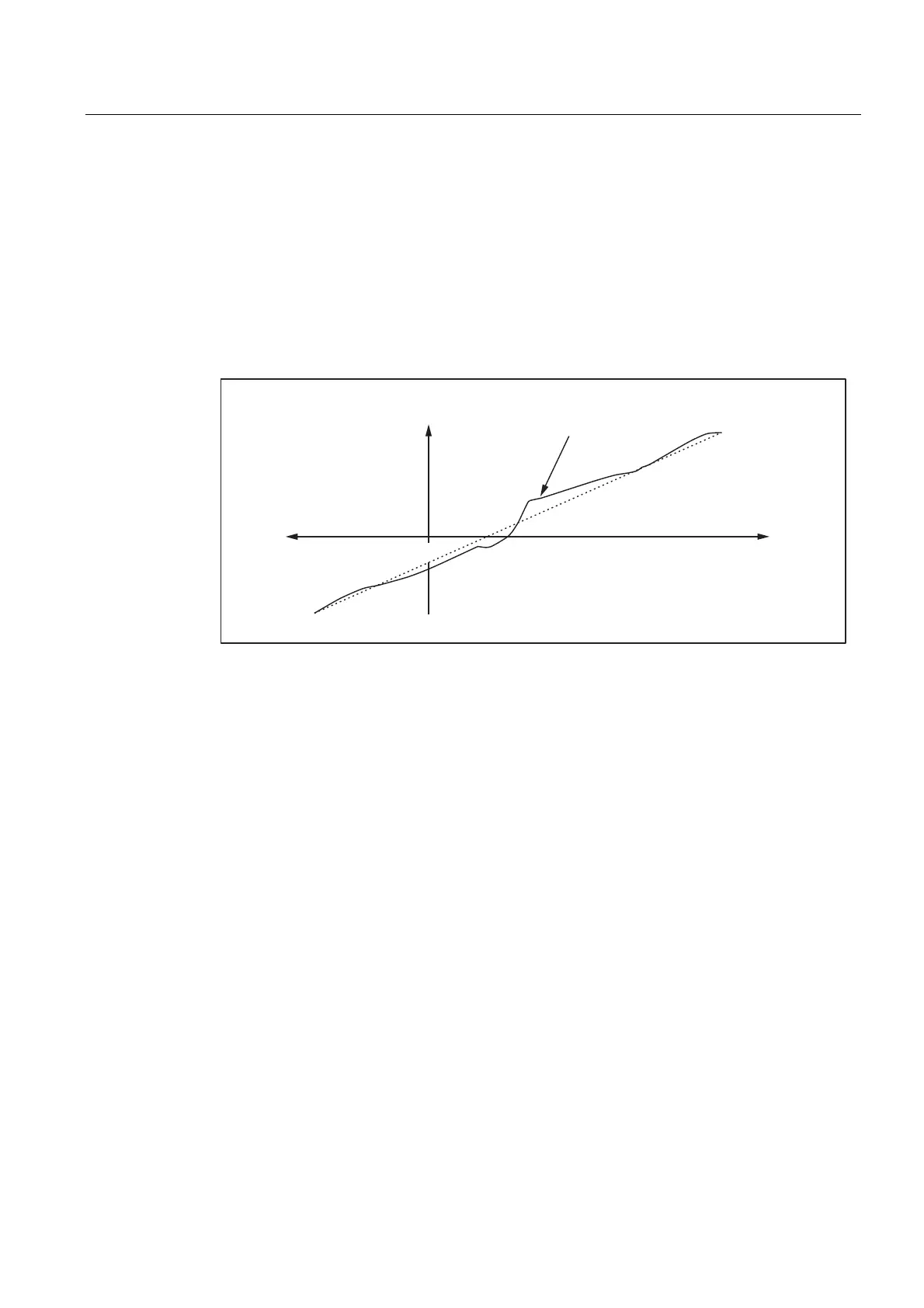
Error curve characteristic
If an axis position reference point P
0
is selected, an offset in the reference point
(corresponds to the "position-independent component" of the temperature compensation)
can be observed as the temperature changes, and because of the change in length an
additional offset in the other position points, which increases with the distance to the
reference point (corresponds to the "position-dependent component" of the temperature
compensation).
The error curve for a given temperature T can generally be represented with sufficient
accuracy by a straight line with a temperature dependent gradient and reference position.
(UURUGHYLDWLRQ
(UURUFXUYHIRUWHPSHUDWXUH7
[ [
Compensation equation
The compensation value ∆K
x
is calculated on the basis of current actual position P
x
of this
axis and temperature T according to the following equation:
ΔK
x
= K
0
(T) + tanβ (T) * (P
x
- P
0
)
The meaning is as follows:
ΔK
x
: Temperature compensation value of axis at position P
x
K
0
: Position-independent temperature compensation value of axis
P
x
: Actual position of axis
P
0
Reference position of axis
tanβ Coefficient for the position-dependent temperature compensation (corresponds
to the gradient of the approximated error line)

 Loading...
Loading...











