R2: Rotary axes
12.3 Programming rotary axes
Extended Functions
690 Function Manual, 03/2013, 6FC5397-1BP40-3BA1
5RWDU\D[LV&
3RVLWLYH
URWDWLRQ
1HJDWLYH
URWDWLRQ
r
r
r
r
r r
r
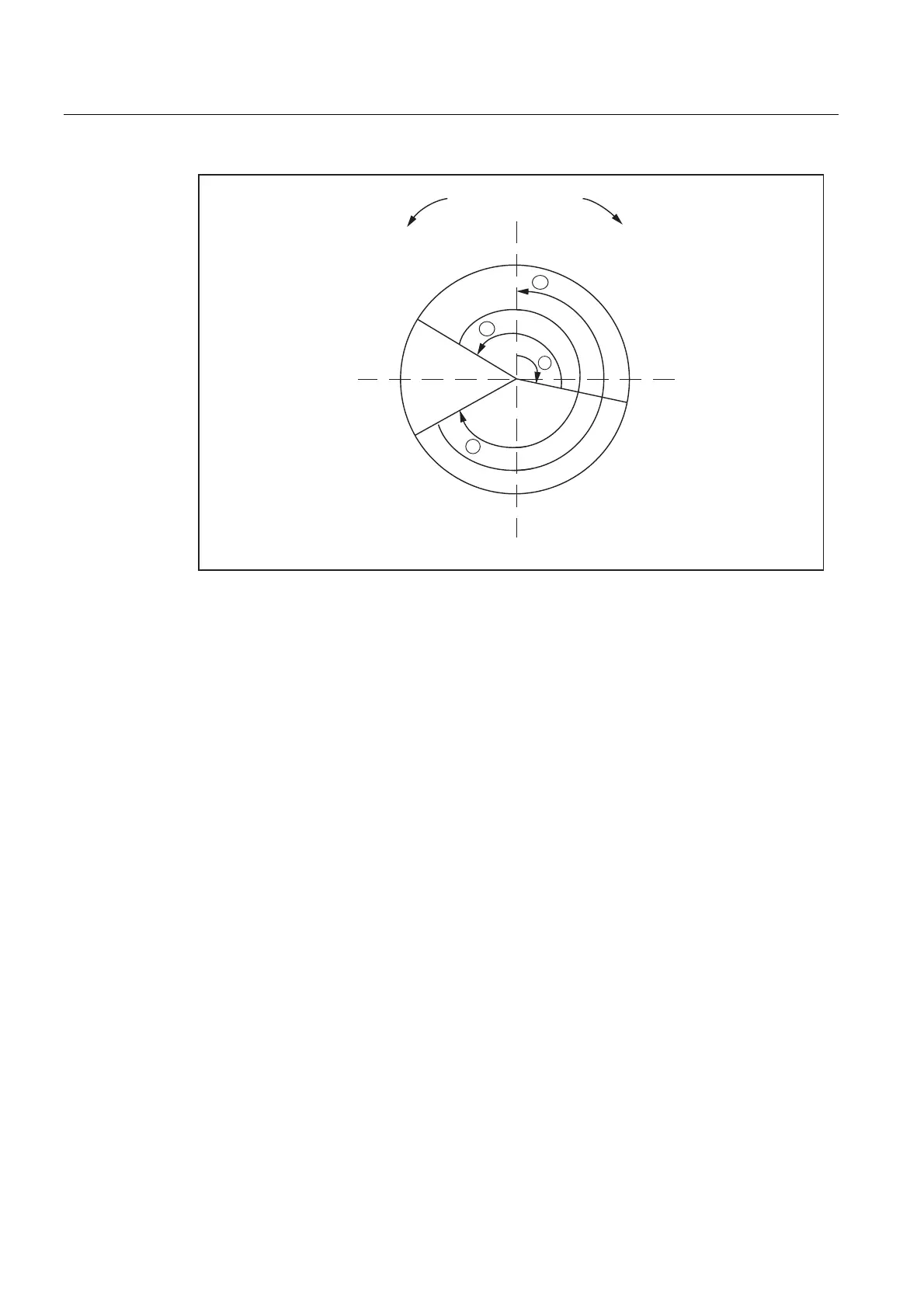
Figure 12-5 Examples of absolute programming for modulo axes
Absolute programming along the shortest path (DC)
POS[axis name] = DC(value)
● The value identifies the rotary-axis target position in a range from 0° to 359.999°. Alarm
16830, "Incorrect modulo position programmed", is output for values with a negative sign
or ≥ 360°.
● With
DC (Direct Control), the rotary axis approaches the programmed absolute position
within one revolution along the shortest path (traversing movement max. ∓ 180°).
● The control calculates the direction of rotation and the traverse path according to the
current actual position. If the path to be traversed is the same in both directions (180°),
the positive direction of rotation receives preference.
●
DC application example: the rotary table is required to approach the changeover position
in the shortest time (and, therefore, via the shortest path) possible.
● If
DC is programmed with a linear axis, alarm 16800, "DC traverse instruction cannot be
used", is output.

 Loading...
Loading...











