T1: Indexing axes
15.6 Starting up indexing axes
Extended Functions
Function Manual, 03/2013, 6FC5397-1BP40-3BA1
789
Example 2: Indexing axis as linear axis
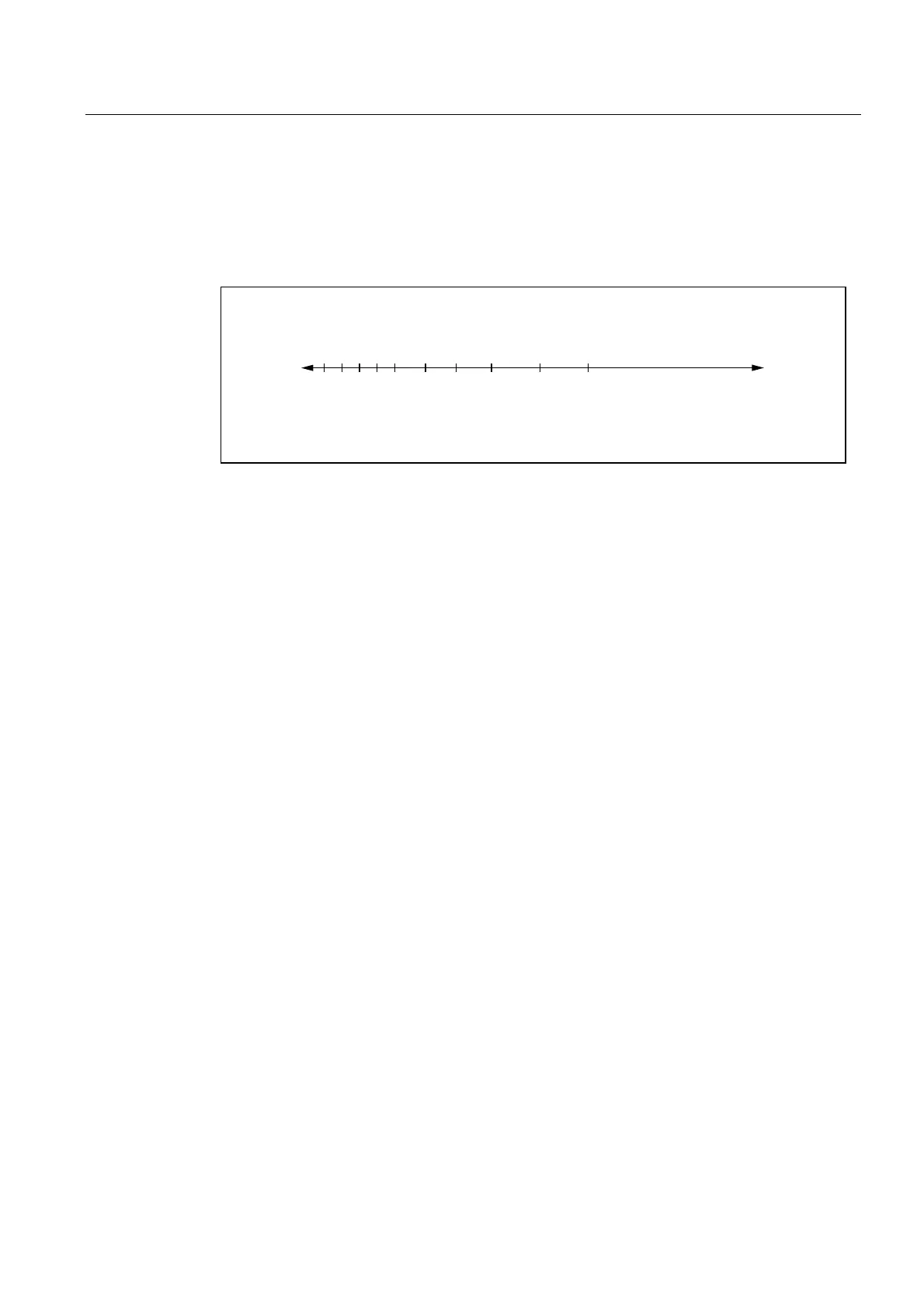
Workholder with 10 locations.
The distances between the 10 locations are different. The first location is at position -100
mm.
$[LVSRVLWLRQ>PP@
,QGH[LQJSRVLWLRQ
Figure 15-4 Example: Workholder as an indexing axis
The indexing positions for the workholder are entered in table 2:
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[0] = -100 ; 1. indexing position at -100
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[1] = 0 ; 2. indexing position at 0
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[2] = 100 ; 3. indexing position at 100
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[3] = 200 ; 4. indexing position at 200
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[4] = 300 ; 5. indexing position at 300
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[5] = 500 ; 6. indexing position at 500
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[6] = 700 ; 7. indexing position at 700
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[7] = 900 ; 8. indexing position at 900
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[8] = 1250 ; 9. indexing position at 1250
MD10930 $MN_INDEX_AX_POS_TAB_2[9] = 1650 ; 10. indexing position at 1650
Other machine data:
MD10920 $MN_INDEX_AX_LENGTH_POS_TAB_2=10 ; 10 indexing positions in table 2
MD30500 $MA_INDEX_AX_ASSIGN_POS_TAB [AX6] = 2; Axis 6 is defined as indexing
axis, indexing positions in table
2

 Loading...
Loading...











