PROGRAMMING GUIDE
SINUS PENTA
259/486
33. CARRIER FREQUENCY MENU
33.1. Overview
The Carrier Frequency Menu makes it possible to set some of the PWM modulation characteristics based on the preset
type of control.
33.1.1. CARRIER FREQUENCY SETTING
It is possible to gain access to all the parameters included in the Carrier Frequency menu.
The user can set the minimum value and the maximum value of the switching carrier frequency and the number of
pulses per period used to produce the output frequency when switching from min. carrier frequency to max. carrier
frequency (synchronous modulation).
The silent modulation function can also be enabled (C004).
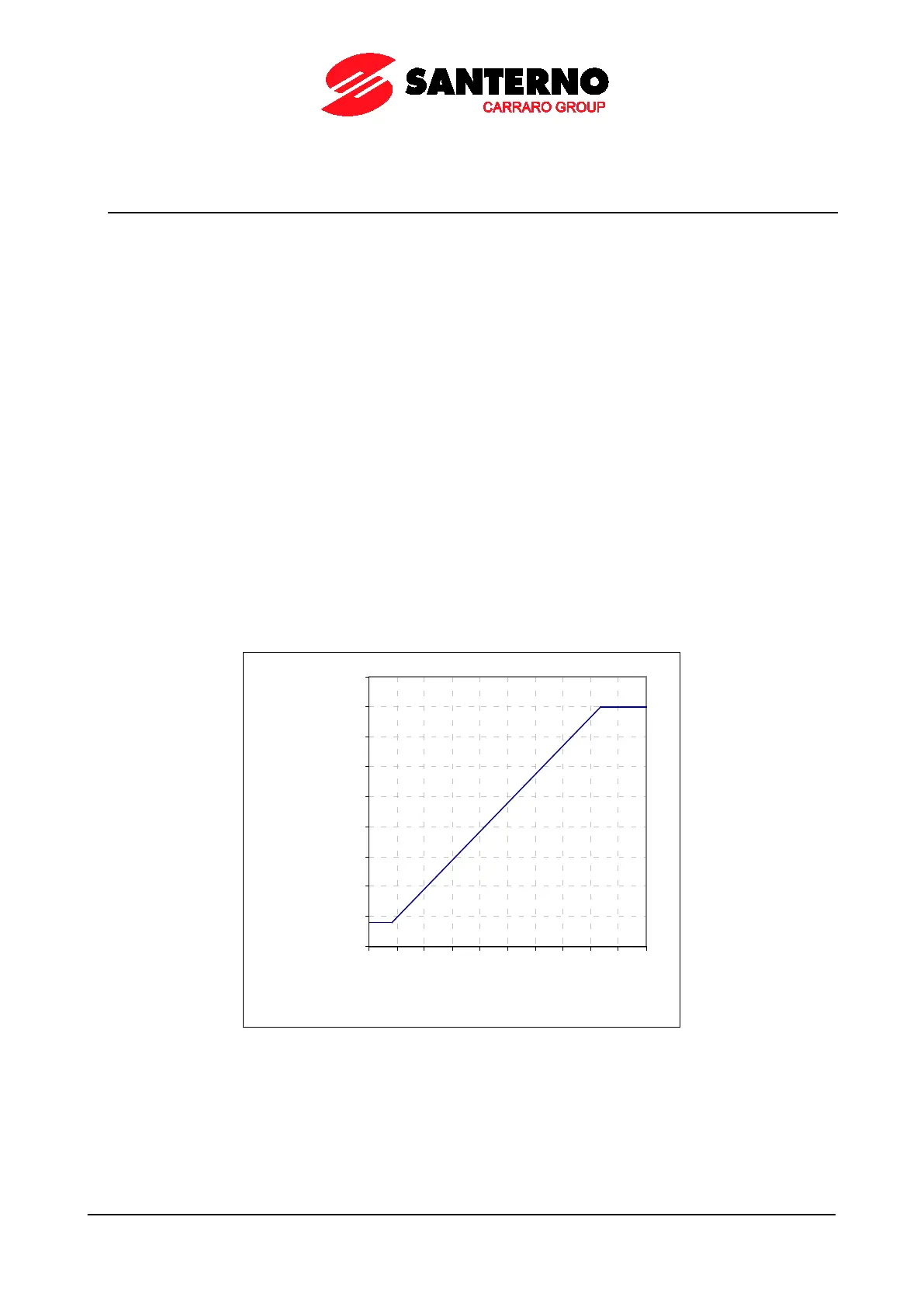
33.1.2. EXAMPLE
Setting two levels of carrier frequency and the number of pulses used for synchronous modulation.
A lower value for carrier frequency ensures a better performance of the motor in terms of output torque but implies
higher noise levels. Suppose that the connected motor has a rated speed equal to 1500rpm at 50Hz and that you need
the best performance up to 200rpm and a “noiseless” carrier frequency at max. speed (3000rpm).
In this case, the max. speed of the drive will produce an output voltage with a frequency value equal to 100Hz; in
proximity to this speed the carrier frequency should be at its maximum level. Suppose that a model implementing max.
16kHz carrier frequency is used.
Assign the following:
C001 = 1600Hz
C002 = 16000Hz
C003 ≥ (C002/100Hz) = (160 pulses per period)
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
14000
16000
18000
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
70 80 90 100
Figure 41: Carrier frequency (example)
Suppose that C003 = 192np, so that C002/C003 = 16000/192 = 83.33Hz. The max. carrier frequency is obtained with
this output frequency. The min. frequency is kept constant until frequency C001/C003 = 8.33 Hz is attained,
corresponding to 250 rpm of the motor speed. In the output frequency range, ranging from 8.33 to 83.33Hz,
synchronous modulation is obtained and the carrier frequency applied results from: f carrier = fout * C003 [Hz].

 Loading...
Loading...