SINUS PENTA
PROGRAMMING GUIDE
268/486
34.1.6. EXAMPLE 2 - V/F PATTERN PARAMETERIZATION
The voltage/frequency pattern is to be programmed for an asynchronous motor (400V/50Hz) having a rated power of 7.5
kW and a rated speed of 1420 rpm with a voltage compensation depending on the motor torque:
depending on the starting torque
Voltage compensation (AutoBoost) results from the formula below:
∆V = C019 x (C038/100) x (T/Tn)
Where T is the estimated motor torque and Tn is the rated motor torque.
Tn is calculated as follows:
Tn = (Pn x pole pairs/2πf = (C017 x pole pairs)/(2π x C015)
“Pole pairs” is the integer number obtained by rounding down (60* C015/C016).
The programmable parameters relating to the AutoBoost functions are the following:
C038 (AutoBoost): variable torque compensation expressed as a percentage of the motor rated voltage (C019). The
value set in C038 is the voltage increase when the motor is running at its rated torque.
C017 (Pn): rated power of the connected motor.
34.1.7. SLIP COMPENSATION (IFD ONLY)
This function allows compensating the speed decrease of the asynchronous motor when the mechanical load increases
(slip compensation). This is available for IFD control only.
The parameters relating to this function are included in the Motor Control Menu (Configuration Menu).
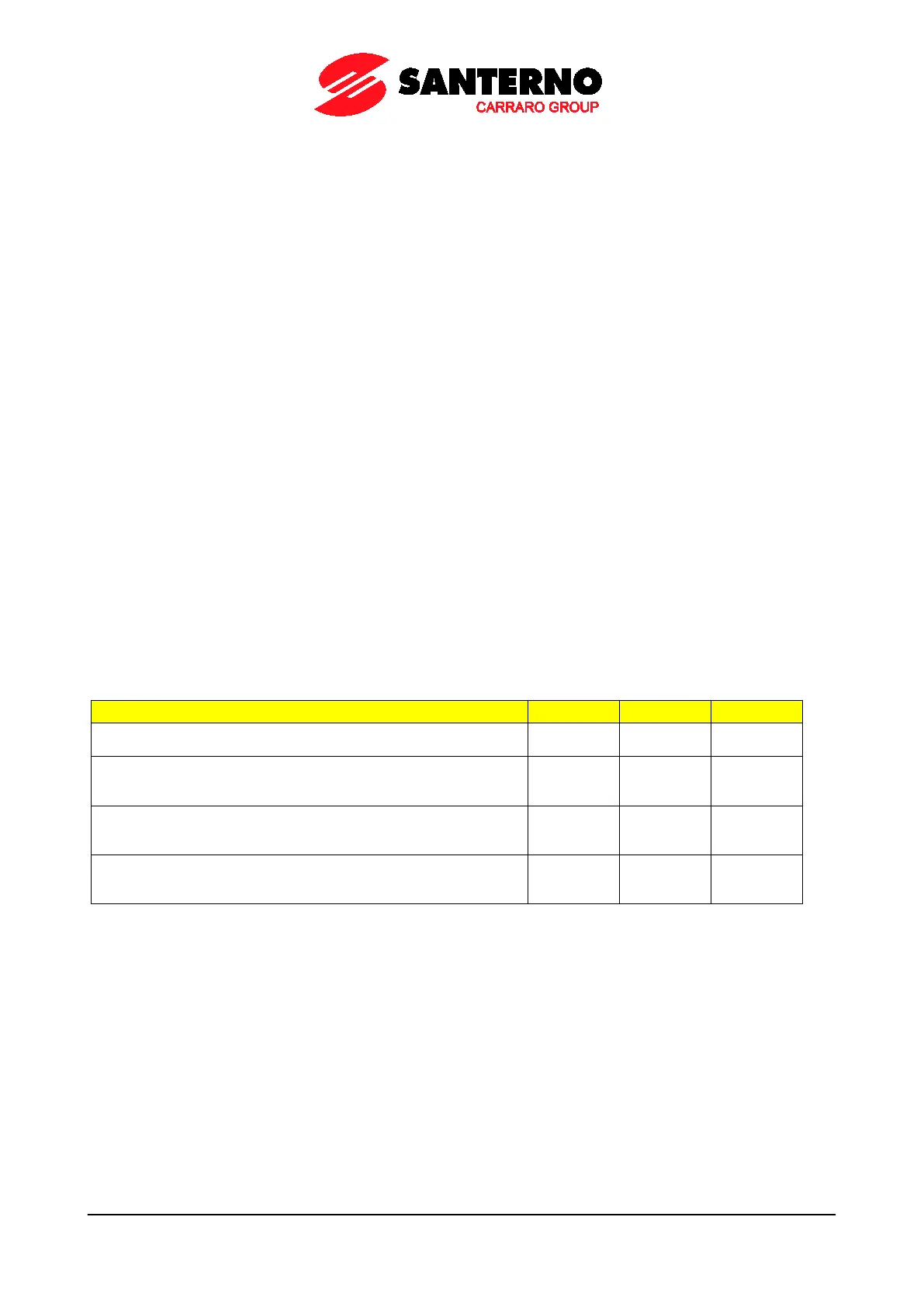
Table 77: Parameters setting Slip Compensation (IFD Control)
Parameter Motor 1 Motor 2 Motor 3
Rated voltage:
Rated voltage of the connected motor (voltage rating).
C019 C062 C105
No-load power:
Power absorbed by the motor when no load is connected to the
motor; it is expressed as a percentage of the motor rated power.
C020 C063 C106
Stator resistance:
Determines the resistance of the stator phases used to compute the
power consumption due to Joule effect.
C022 C065 C108
Activation of slip compensation:
If other than zero, this parameter enables slip compensation and
defines its relevant value.
C039 C082 C125
Once the drive output power has been estimated and the power losses due to the Joule effect and to the mechanical
parts (depending on output voltage and no-load power) have been subtracted, mechanical power is obtained. Starting
from mechanical power and the value set for slip compensation (C039 for motor 1), you can obtain the increase of the
output frequency limiting the error between the desired speed value and the actual speed value of the connected motor.
 Loading...
Loading...