Cryptographic processor (CRYP) RM0033
516/1381 RM0033 Rev 9
ECB decryption, AES-CBC encryption and AES-CBC decryption.This reference manual
only gives a brief explanation of each mode.
AES Electronic codebook (AES-ECB) mode
• AES-ECB mode encryption
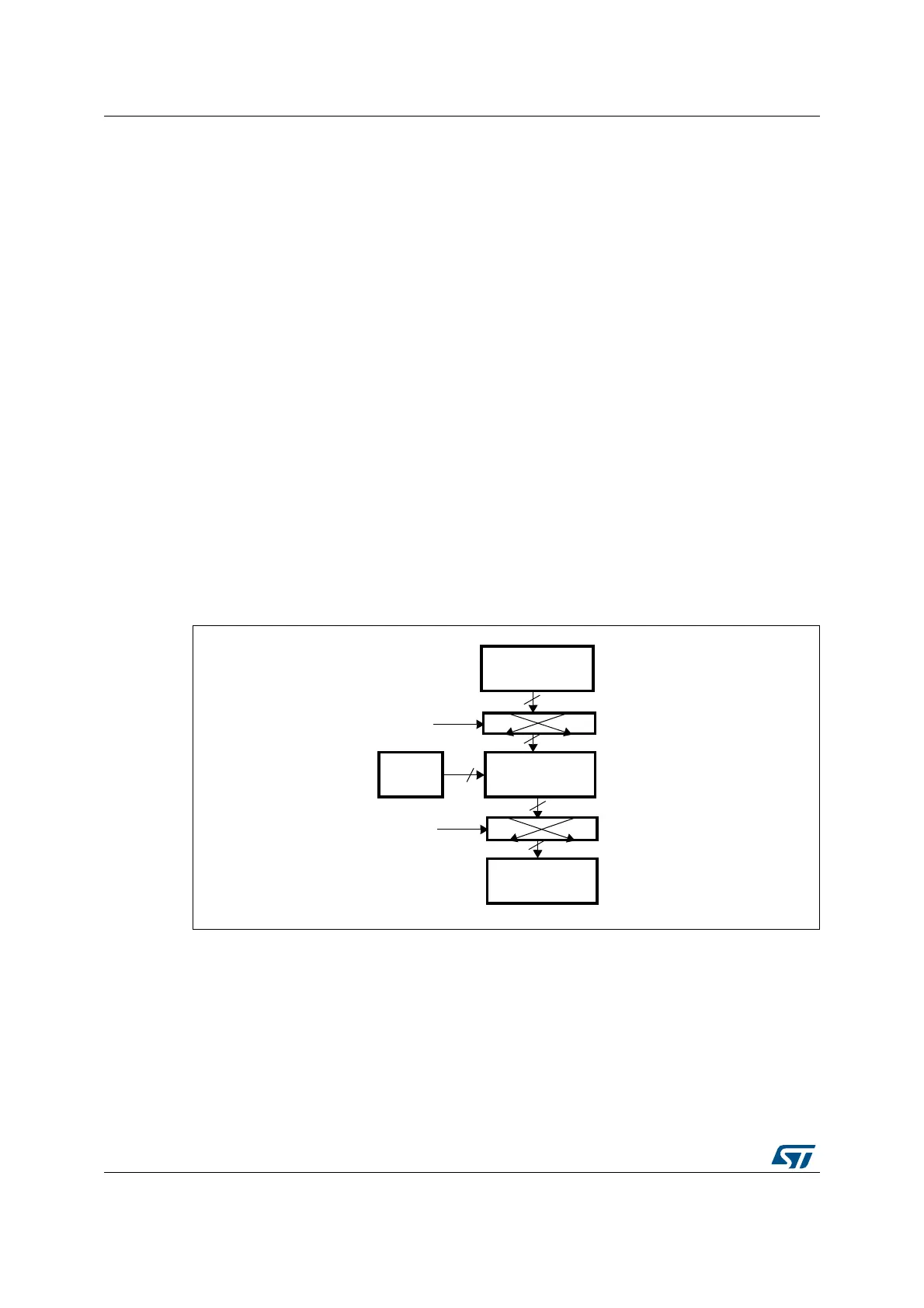
Figure 200 illustrates the AES Electronic codebook (AES-ECB) mode encryption.
In AES-ECB encryption, a 128- bit plaintext data block (P) is used after bit/byte/half-
word swapping (refer to Section 19.3.3: Data type on page 522) as the input block (I).
The input block is processed through the AEA in the encrypt state using the 128, 192 or
256-bit key. The resultant 128-bit output block (O) is used after bit/byte/half-word
swapping as ciphertext (C). It is then pushed into the OUT FIFO.
• AES-ECB mode decryption
Figure 201 illustrates the AES Electronic codebook (AES-ECB) mode encryption.
To perform an AES decryption in the ECB mode, the secret key has to be prepared (it is
necessary to execute the complete key schedule for encryption) by collecting the last
round key, and using it as the first round key for the decryption of the ciphertext. This
preparation function is computed by the AES core. Refer to Section 19.3.6: Procedure
to perform an encryption or a decryption for more details on how to prepare the key.
In AES-ECB decryption, a 128-bit ciphertext block (C) is used after bit/byte/half-word
swapping as the input block (I). The keying sequence is reversed compared to that of
the encryption process. The resultant 128-bit output block (O), after bit/byte or half-
word swapping, produces the plaintext (P).
Figure 200. AES-ECB mode encryption
1. K: key; C: cipher text; I: input block; O: output block; P: plain text.
2. If Key size = 128: Key = [K3 K2].
If Key size = 192: Key = [K3 K2 K1]
If Key size = 256: Key = [K3 K2 K1 K0].
IN FIFO
AEA, encrypt
K0...3
(1)
P, 1 2 8 b i t s
OUT FIFO
plaintext P
ciphertext C
128/192
I, 128 bits
swapping
C, 128 bits
swapping
DATATYPE
DATATYPE
or 256
ai16071b

 Loading...
Loading...