6 – 4
Chapter 6 Principles of Operation
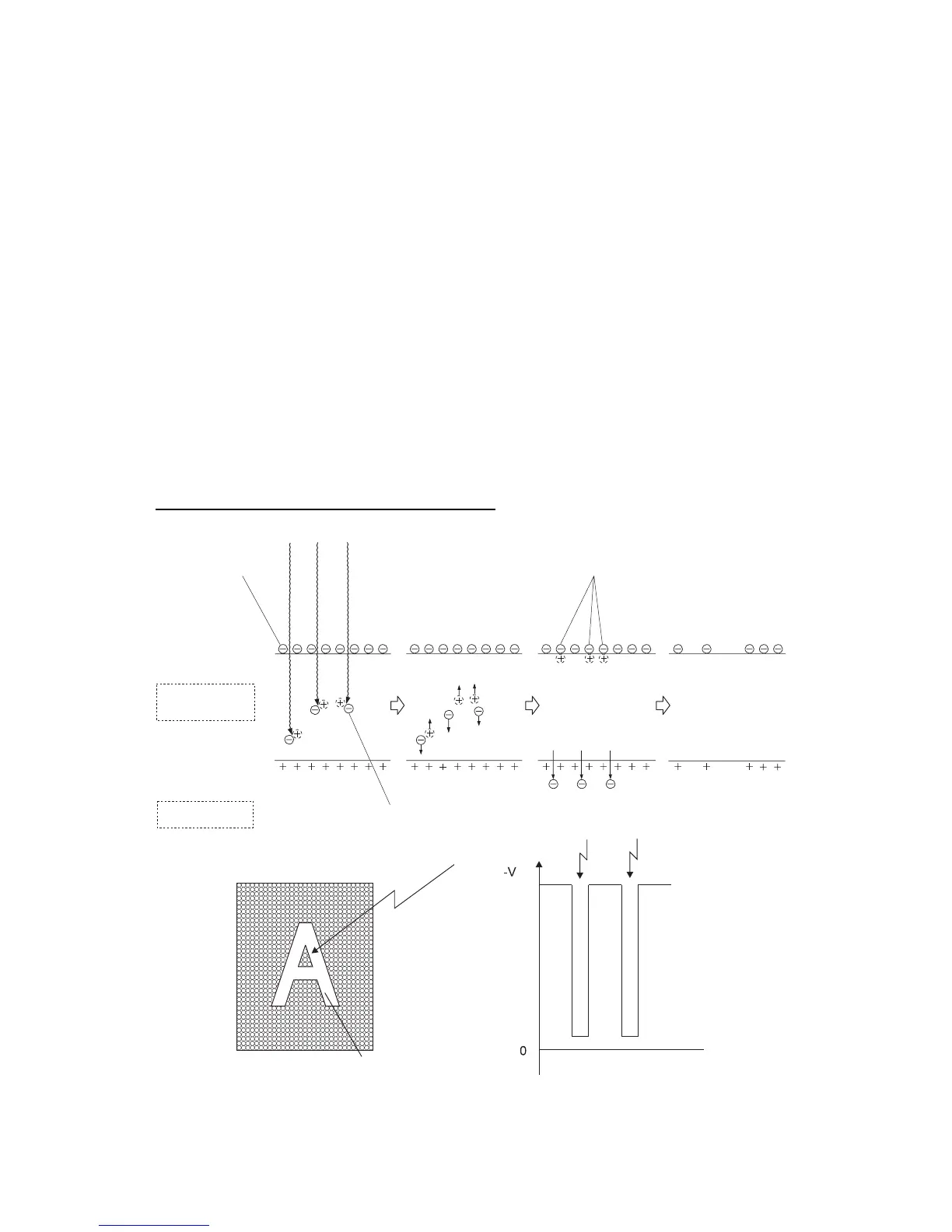
In the exposure step, the surface of the drum negatively charged by the previous
charging step is scanned by a thin laser beam. The light radiated from the laser diode
of the ROS (Raster Output Scanner) scans the drum from one end to the other. The
light passes via a rotating polygon mirror (12 facets) and also via a lens.
The radiation of the laser beam is adjusted according to a video signal from the PWBA
ESS.
The laser beam shot at the drum excites electrons directed to the photoconductor. As
a result, electron hole pairs are induced in the photoconductive layer. Since electrons
are moved toward the body inside the drum by the electric field, the electron-hole pairs
move to the surface of the photoconductive layer. Negative charges in this portion
decrease, thus creating an invisible electrostatic latent image there.
Toner particles are adsorbed onto this electrostatic latent image in the next step. Thus,
the image is developed. The toner particles adsorbed to the drum are attracted to
positive charges supplied by the BTR, and are transferred to the paper. The drum is
sent for peeling and cleaning steps.
Electrostatic latent image formed on drum:
JG6104AA

 Loading...
Loading...









