Arm
®
CoreLink™ GIC-600AE Generic Interrupt Controller
Technical Reference Manual
Document ID: 101206_0003_04_en
Issue: 04
Functional Safety
6.2.6 Ping mechanisms
The FMU provides background ping and directed ping mechanisms.
Background ping
The background ping mechanism can help identify the following issues:
•
Connectivity issue between remote GIC blocks and the GICD
•
Systematic issue in the network that is causing misrouting of messages
•
Congestion in the network that exceeds the programmed ping_timeout_value
•
Permanent deadlock caused by valid and ready signals that are stuck LOW
The GICD sends a ping message over the AXI4-Stream network to a remote GIC block, one at a
time. It starts a timer and waits for the PING_ACK message from the GIC block. If the PING_ACK
message is not received within the expected interval, the FMU indicates a PING_ACK timeout
error. The FMU repeats this process for each GIC block.
The FMU sends ping messages in the following sequence, which repeats until background pings are
disabled:
1.
PPI0 through PPI<ppi_count−1>
2.
ITS0 through ITS<its_count−1>
3.
SPI Collator
4.
Wake Request
To skip a particular GIC block in the sequence, write to the FMU_PINGMASK
register.
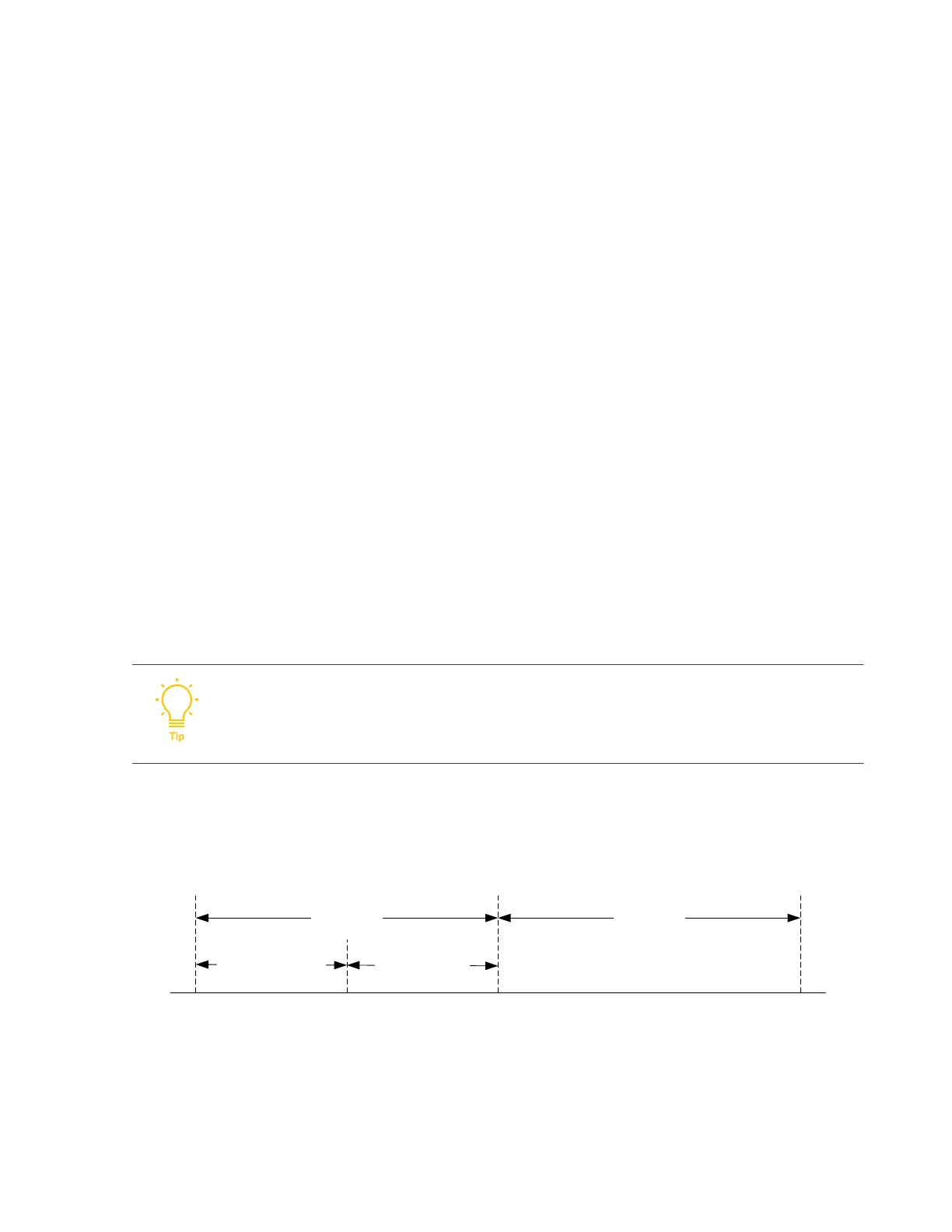
The following figure shows the relationship between the ping mechanism parameters.
Figure 6-3: Ping mechanism parameters
Ping sent
to PPI0
Ping sent
to PPI1
Ping sent
to ITS0
ping_timeout_value ping_interval_diff
ping_interval ping_interval
Copyright © 2018–2020, 2022 Arm Limited (or its affiliates). All rights reserved.
Non-Confidential
Page 203 of 268
 Loading...
Loading...