Arm
®
CoreLink™ GIC-600AE Generic Interrupt Controller
Technical Reference Manual
Document ID: 101206_0003_04_en
Issue: 04
Functional Safety
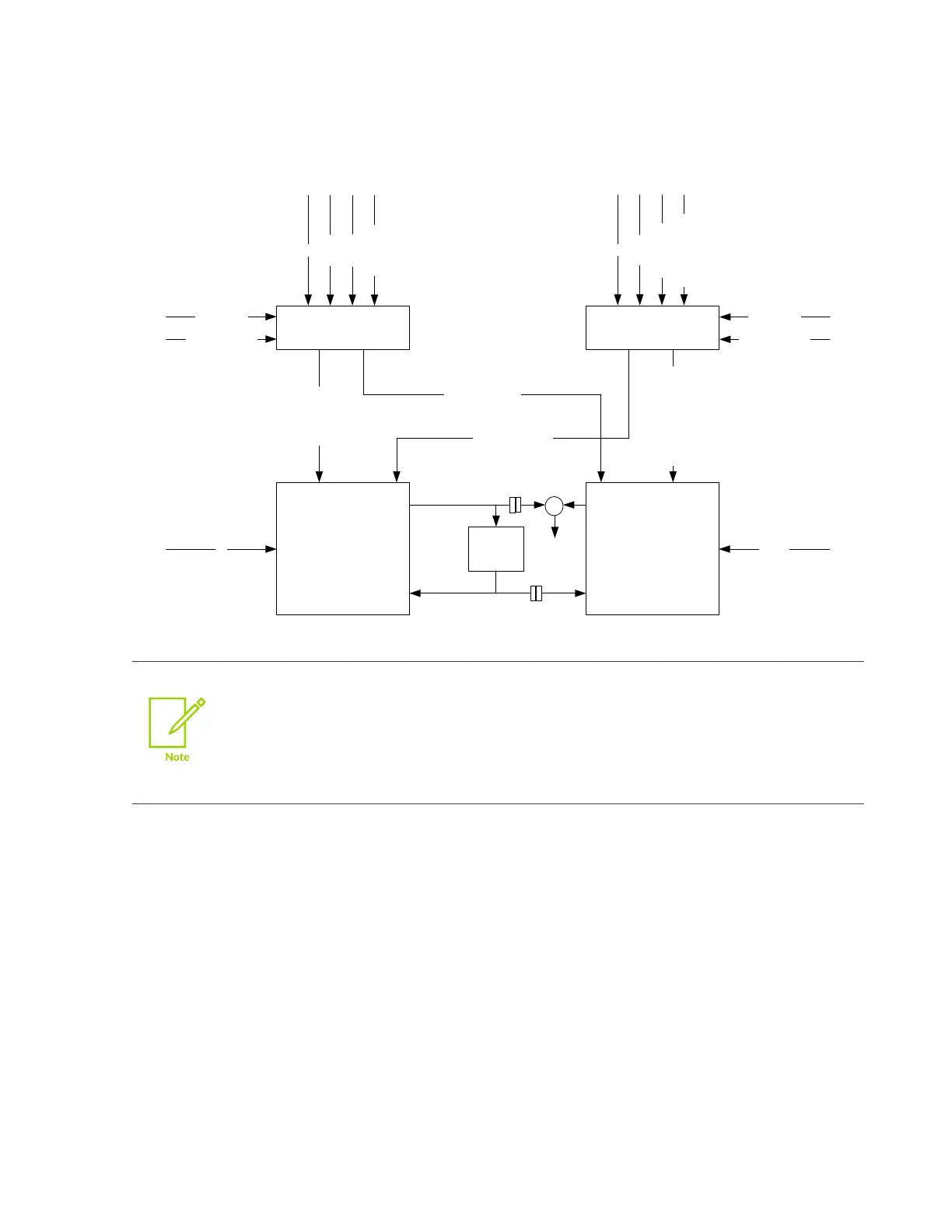
Figure 6-4: GIC clocks and resets
GIC block
no_ram
GIC block
no_ram
(duplicated)
reset_sync_prot
(main reset)
reset_sync_prot
(dbg reset)
Shared
RAM
dftrstdisable
dftrstdisable_fdc
dftrstdisable
dftrstdisable_fdc
clk clk_fdc
+
reset_n_sync
clk
clk_fdc
reset_n
reset_n_fdc
clk
clk_fdc
dbg_reset_n
dbg_reset_n_fdc
reset_n_fdc_sync
dbg_reset_n_sync
dbg_reset_n_fdc_sync
fault
ram inputs
ram inputs
ram outputs
ram outputs
•
Internal _sync reset signals are asynchronous-assert and synchronous-deassert.
•
The reset_n_fdc_sync and dbg_reset_n_fdc_sync signals are deasserted two
cycles after the non-FDC signals.
•
The reset qualification with the nmbistreset signal is not shown before the
reset_sync_prot block.
The extra reset_n_fdc and clk_fdc signals provide redundancy in the clock and reset trees to guard
against faults on the tree branches. If a fault occurs on a branch in the primary or FDC clock trees,
the Dual Lock-Step (DLS) comparators detect it.
6.5.1 Clocks
The GIC-600AE has two global clocks for each stitched level.
The clocks that are used for wrap components are:
clk This signal clocks the primary mission-critical logic
clk_fdc This signal clocks the Fault Detection and Control (FDC) redundant logic
Copyright © 2018–2020, 2022 Arm Limited (or its affiliates). All rights reserved.
Non-Confidential
Page 212 of 268
 Loading...
Loading...