Arm
®
CoreLink™ GIC-600AE Generic Interrupt Controller
Technical Reference Manual
Document ID: 101206_0003_04_en
Issue: 04
Functional Safety
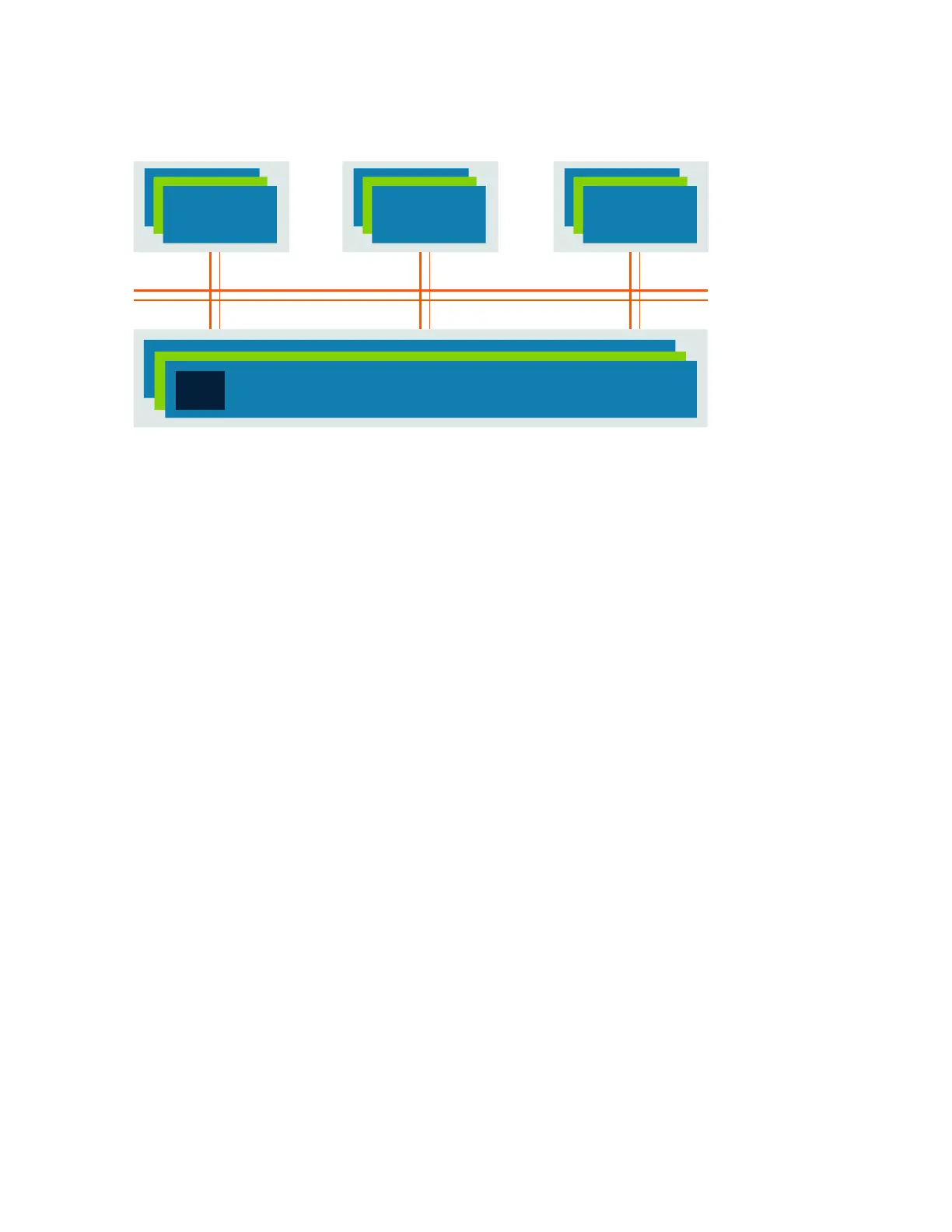
Figure 6-11: Partial duplication microarchitecture
Interfaces that use partial duplication do not invert their *_chk signals.
If a GIC-600AE configuration needs no interconnect components between two GIC blocks, the
GIC interconnect render engine automatically uses point-to-point (P2P) protection.
Example
Consider an interconnect with the following conditions:
•
One ITS block, with no ADB
•
No register slices between the ITS and Distributor
The connections are point-to-point, and AMBA parity extensions are used instead of partial
duplication with CRC. If any interconnect component lies between the ITS and Distributor, the
render engine chooses partial duplication.
6.9.1.1 AMBA Domain Bridge
To maintain lockstep operation between the primary and redundant interconnects, the SoC
integrator must use the GIC-600AE AMBA Domain Bridge (ADB).
To support partial duplication across asynchronous CDC, the ADB must also be partially duplicated.
The asynchronous nature of the CDC makes the arrival time at the subordinate indeterminate.
Assuming a temporal delay of two cycles between the primary and shadow, the nondeterminism
means that any of the following scenarios can occur. The primary can arrive:
•
One cycle ahead of the shadow, which is a fast shadow
•
Two cycles ahead of the shadow, which is the normal case
•
Three cycles ahead of the shadow, which is a slow shadow
Copyright © 2018–2020, 2022 Arm Limited (or its affiliates). All rights reserved.
Non-Confidential
Page 227 of 268
 Loading...
Loading...