Arm
®
CoreLink™ GIC-600AE Generic Interrupt Controller
Technical Reference Manual
Document ID: 101206_0003_04_en
Issue: 04
Programmers model
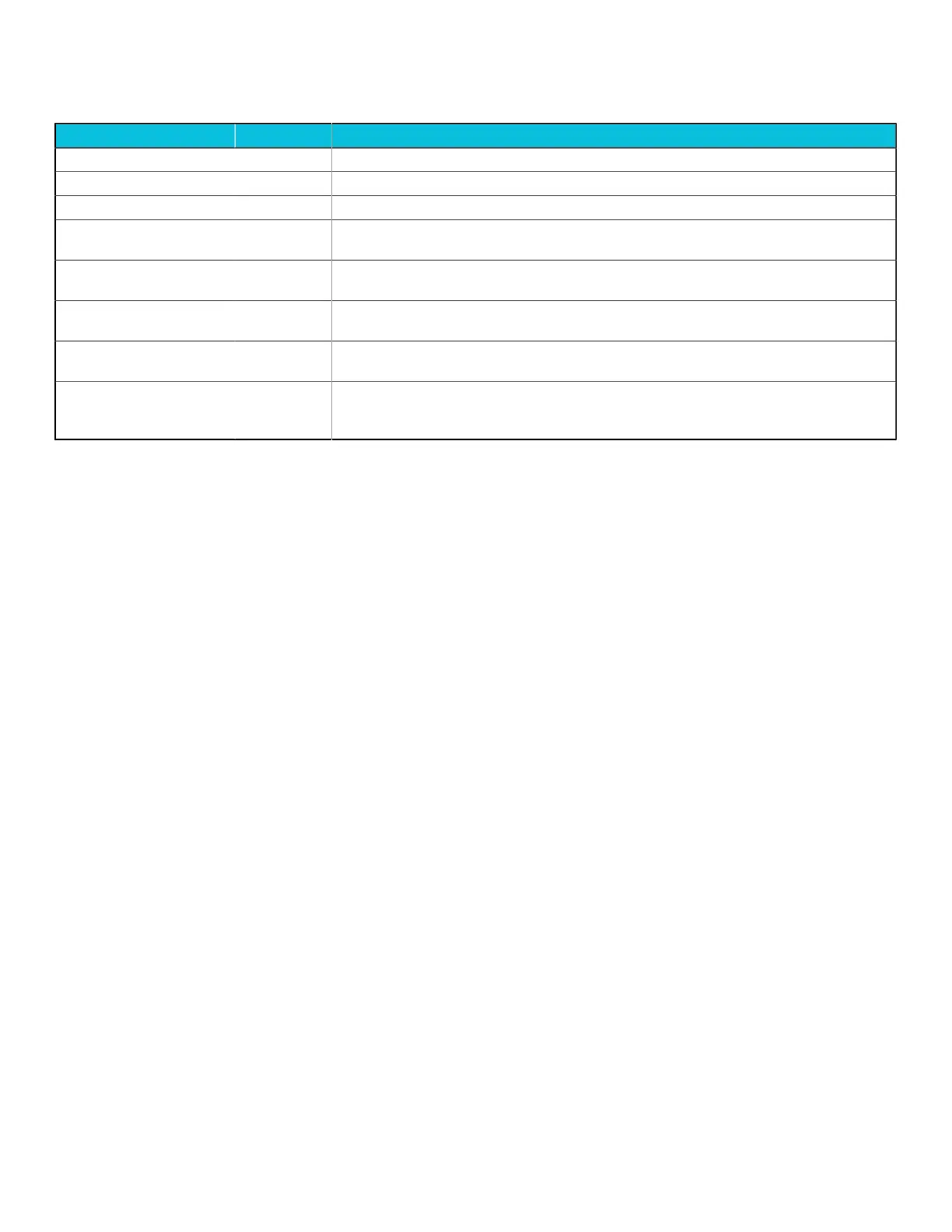
Page offset Page Description
1 GICA 5.3 Distributor registers (GICM) for message-based SPIs summary on page 117
2 GICT 5.8 GICT register summary on page 147
3 GICP 5.9 GICP register summary on page 163
4 + 2×ITSnum GITSn 5.6 ITS control register summary on page 136.
ITSnum is the serial number of each ITS, which is from 0 to ITScount−1.
5 + 2×ITSnum GITSn
translate
5.7 ITS translation register summary on page 147
4 + 2×ITScount +
2×RDnum
GICR (LPI) 5.4 Redistributor registers for control and physical LPIs summary on page 121.
ITScount is the total number of ITS.
5 + 2×ITScount +
2×RDnum
GICR (SGI) 5.5 Redistributor registers for SGIs and PPIs summary on page 130.
RDnum is the serial number of each “internal Redistributor”, which is from 0 to RDcount−1.
4 + 2×ITScount +
2×RDcount
GICDA Alias to GICD (page after last GICR page).
RDcount is the total number of “internal Redistributor”, which equals total number of CPU
cores.
For more information, see the Arm
®
Generic Interrupt Controller Architecture Specification, GIC
architecture version 3 and version 4.
You must set up the system address map so that each core accesses the GICD page on its local
chip at the same address. All other pages must be globally accessible, although access of pages on
a remote chip by a core is expected to be rare. Allowing the GIC pages to be globally accessible
might require the system interconnect to alias the page addresses.
The registers in the previous table are accessible through the ACE-Lite interface. The Fault
Management Unit (FMU) registers are accessible through the APB interface. See:
•
5.10 FMU register summary on page 179
•
6.2.1 FMU APB4 interface on page 196
Page offset
The ACE-Lite address bits[x:16] control which GIC register page is accessed in Table 5-1: Register
map pages on page 95. The value of x depends on the axis_addr_width GICD configuration
parameter.
In non-monolithic configurations, the GIC-600AE ignores address bits above ceil[log
2
(page_count)]
+ 15. For example, a configuration that uses 11 pages ignores address bits above 19, so any
address bits of the form 0xXXXXX00000 is accepted and it accesses the GICD page.
In monolithic configurations, where the Distributor and ITS share the ACE-Lite subordinate
port, there are two address tie-off signals that control the full page address of the GICD and
GITS_TRANSLATER pages. The page address comprises address bits[x:16]. For example, if the
GICD page is at 32-bit address 0xFFFF0000, the tie-off is 16-bit 0xFFFF. See A.6 Miscellaneous
signals on page 258 for information about the gicd_page_offset and its_transr_page_offset tie-off
signals.
Copyright © 2018–2020, 2022 Arm Limited (or its affiliates). All rights reserved.
Non-Confidential
Page 96 of 268
 Loading...
Loading...