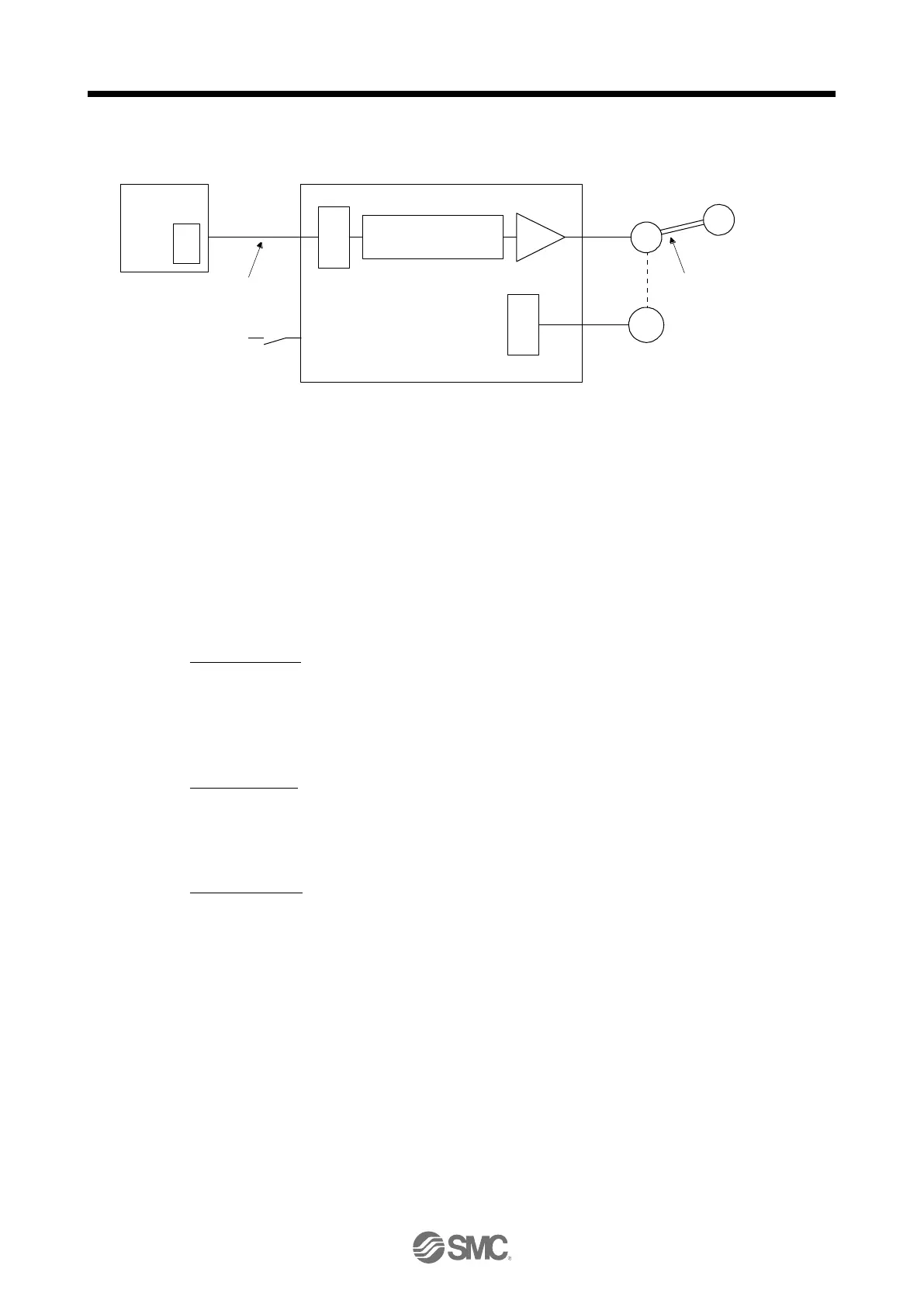
Encoder
Q
P
C
M
L
(b) Cumulative command pulses
(c) Cumulative feedback pulses
(d) Machine stop position M
Cause B
(a) Output pulse
counter
Cause A
SON (Servo-on) input
LSP/LSN (Stroke end) input
Servo amplifierController
Servo motor
Machine
Electronic gear
[Pr. PA05], [Pr. PA06],
[Pr. PA07], [Pr. PA21]
Cause C
When a position shift occurs, check (a) output pulse counter display Q, (b) cumulative command pulse P,
(c) cumulative feedback pulse C, and (d) machine stop position M in the above diagram.
Also, Causes A, B, and C indicate the causes of position mismatch. For example, Cause A indicates that
noise entered the wiring between the PC or PLC...etc and driver, causing command input pulses to be
miscounted.
In a normal status without position shift, there are the following relationships.
1) Q = P (Output counter = Cumulative command pulses)
2) When [Pr. PA21] is "0 _ _ _"
P •
= C (Cumulative command pulses × Electronic gear = Cumulative feedback
pulses)
3) When [Pr. PA21] is "1 _ _ _"
P •

 Loading...
Loading...