14. COMMUNICATION FUNCTION
14 - 32
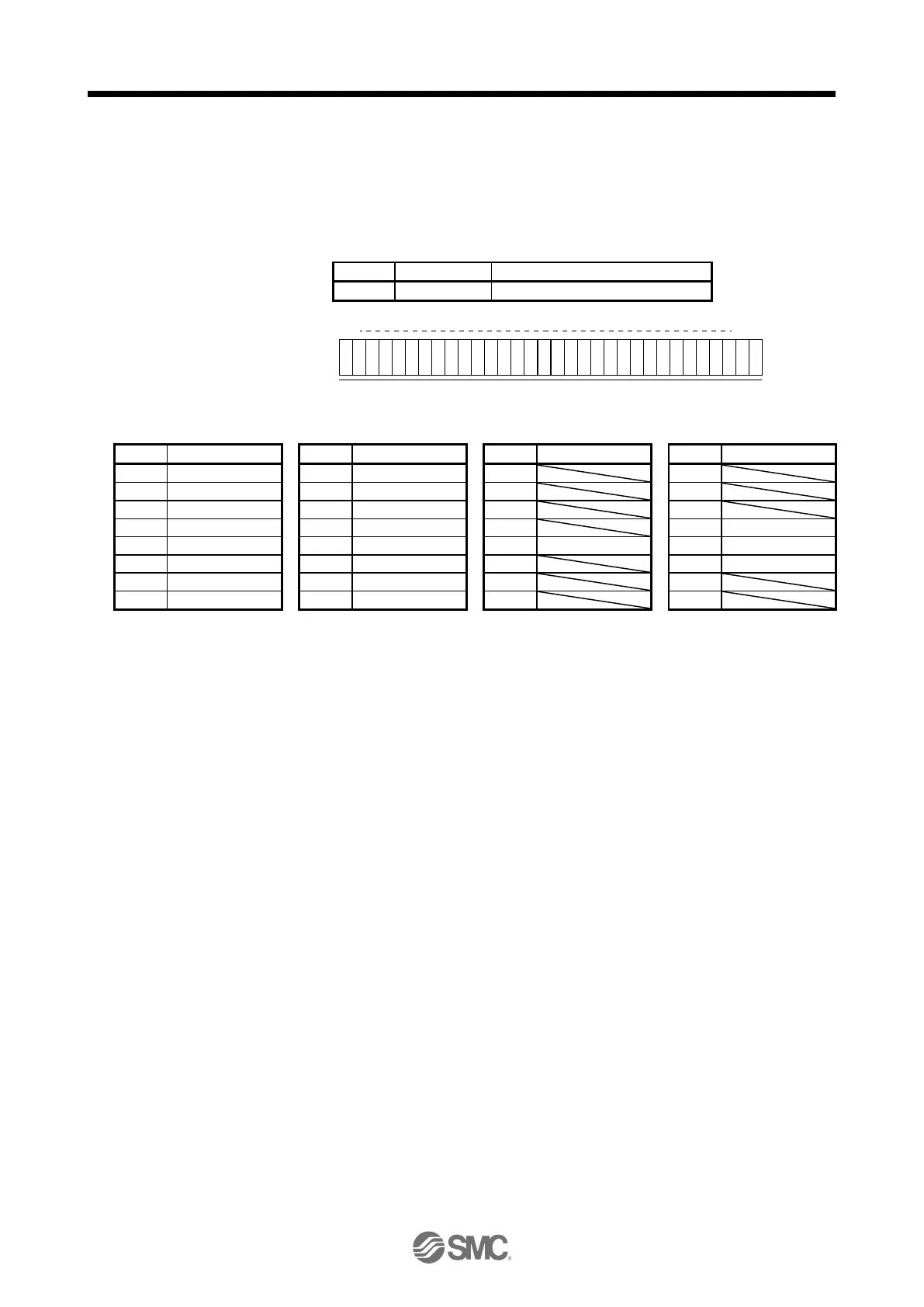
14.5.7 Input devices on/off (test operation)
Each input devices can be turned on/off for test operation. However, when the device to be switched off is in
the external input signal, also switch off the input signal.
Transmit command [9] [2], data No. [0] [0], and data.

 Loading...
Loading...