14. COMMUNICATION FUNCTION
14 - 38
14.5.10 Alarm history
(1) Alarm No. reading
The following shows how to read alarm Nos. which occurred in the past. Alarm Nos. and occurrence
times of No. 0 (last alarm) to No. 15 (sixteenth alarm in the past) are read.
(a) Transmission
Transmit command [3] [3] + data No. [1] [0] to [1] [F]. Refer to section 14.4.1.
(b) Return
Alarm Nos. corresponding to the data No. is provided.
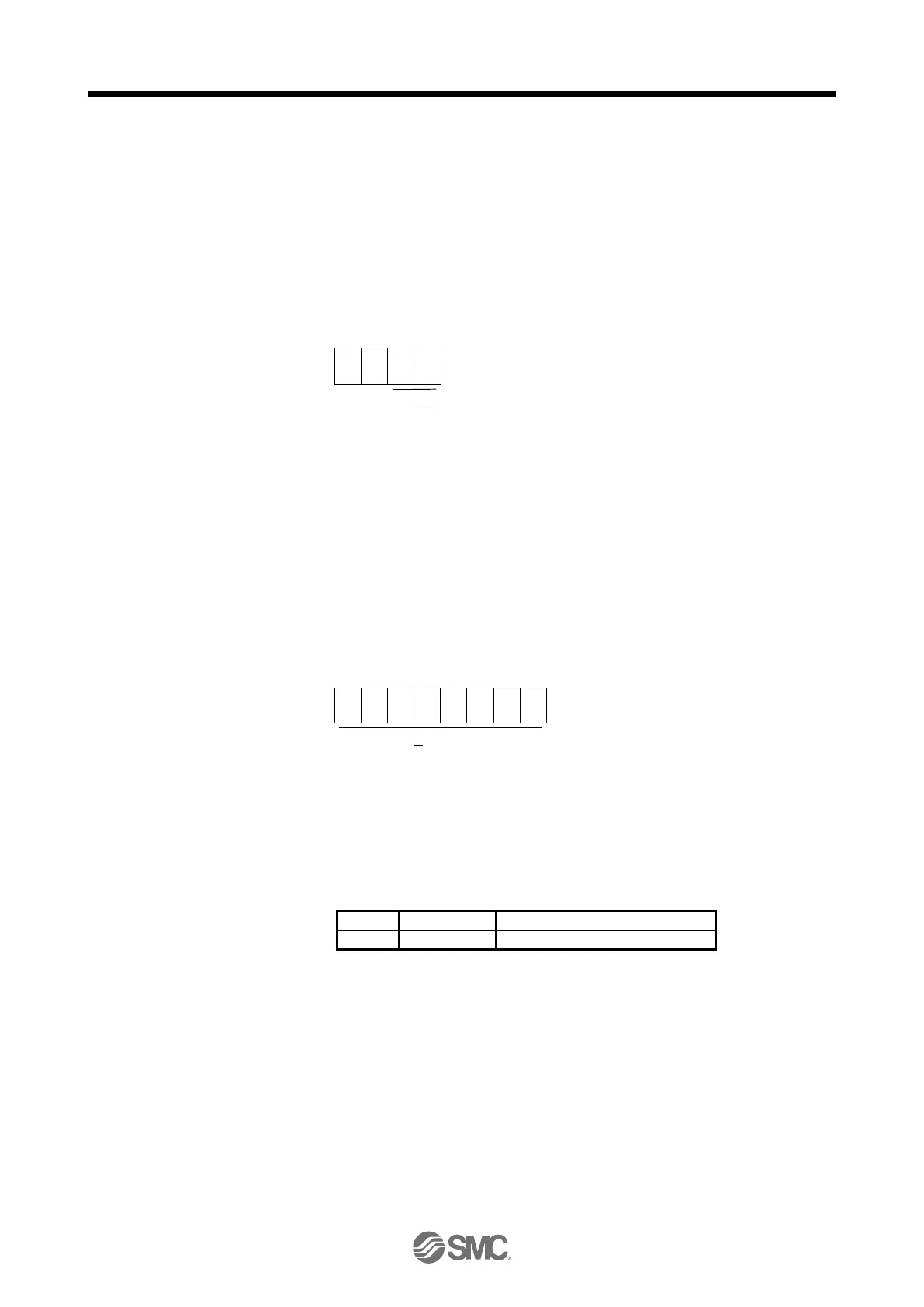
0 0
Alarm No. is transferred in hexadecimal.
For example, "0032" means [AL. 32] and "00FF" means [AL. _ _ ] (no alarm).
(2) Alarm occurrence time reading
The following shows how to read alarm occurrence times which occurred in the past.
Alarm occurrence time corresponding to the data No. is provided in terms of the total time beginning with
operation start, with the minute unit omitted.
(a) Transmission
Transmit command [3] [3] + data No. [2] [0] to [2] [F].
Refer to section 14.4.1.
(b) Return
The alarm occurrence time is transferred in hexadecimal.
Hexadecimal must be converted into decimal.
For example, data "01F5" means that the alarm occurred in 501 hours after starting operation.
(3) Clearing the alarm history
Alarm history is cleared.
Transmit command [8] [2] and data No. [2] [0].

 Loading...
Loading...