3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3 - 5
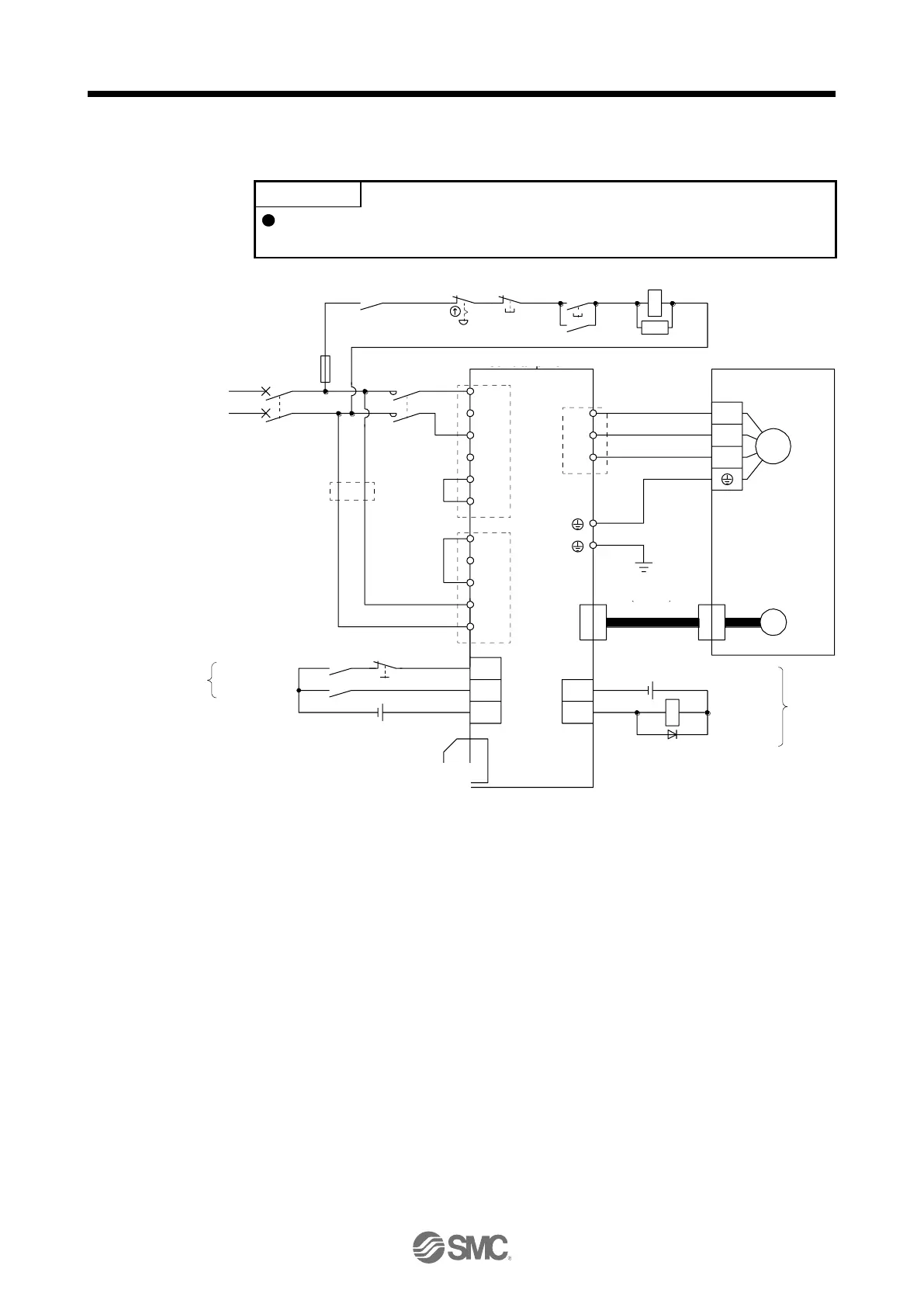
(2) Using 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply for LECSB2-T
□
Connect the 1-phase 200 V AC to 240 V AC power supply to L1 and L3. One of
the connecting destinations is different from LECSB
□
-S
□
Series Driver's.
L1
L2
L3
P3
P4
P+
L11
L21
N-
D
C
U
V
W
CNP1
CNP3
CNP2
U
V
W
M
CN2
MC
MC
SK
CN8
MCCB
ALM
DOCOM
CN1
RA1
CN1
EM2
SON
DICOM
(Note 6)
MC
(Note 4)
24 V DC (Note 11)
Malfunction
1-phase
200 V AC to
240 V AC
Servo amplifier
(Note 1)
(Note 9)
(Note 2)
Servo motor
Motor
Encoder
(Note 3)
Encoder cable
(Note 5)
Malfunction
RA1
OFF
ON
Emergency stop switch
Forced stop 2
Servo-on
(Note 4)
(Note 8)
Short-circuit connector
(Packed with the servo amplifier)
(Note 7)
Main circuit power supply
(Note 10)
(Note 10)
24 V DC (Note 11)
Between P3 and P4 is connected by default.
Always connect between P+ and D terminals (factory-wired). When using the regenerative option, refer to section 11.2.
This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.9.3.
Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of
contacts) of 80 ms or less. Depending on the main circuit voltage and operation pattern, bus voltage decreases, and that may
cause the forced stop deceleration to shift to the dynamic brake deceleration. When dynamic brake deceleration is not
required, slow the time to turn off the magnetic contactor.
Configure a circuit to turn off EM2 when the main circuit power is turned off to prevent an unexpected restart of the driver.
When not using the STO function, attach the short-circuit connector came with a driver.
When wires used for L11 and L21 are thinner than wires used for L1, and L3, use a molded-case circuit breaker. (Refer to
section 11.10.)
Connecting a servo motor of the wrong axis to U, V, W, or CN2 of the driver may cause a malfunction.
The illustration of the 24 V DC power supply is divided between input signal and output signal for convenience. However, they
can be configured by one.

 Loading...
Loading...