Call routing
168
System functions and features as of R4.1
syd-0570/1.2 – R4.1 – 08.2016
6. 3 Incoming traffic
6. 3. 1 Routing
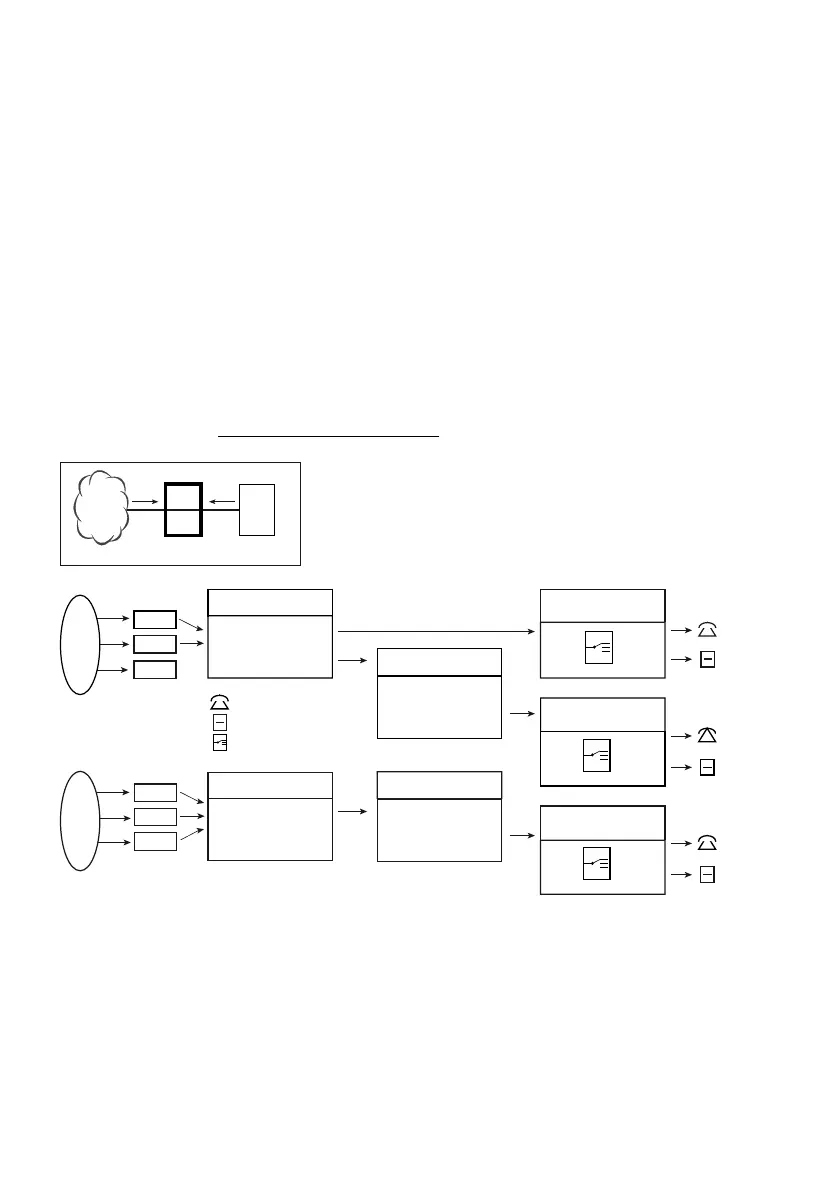
Network interfaces with the same network-specific characteristics are all grouped to-
gether in a trunk group. It is for example specified whether the network interfaces allo-
cated to a trunk group are connected to a private leased-line network or to the public
network.
A call is routed via a trunk group to a direct dialling plan, a call distribution element or a
destination with a number from the internal numbering plan.
Each direct dial number is allocated a call distribution element. Several direct dial num-
bers can be allocated to the same call distribution element.
A call distribution element is allocated destinations depending on the switch group and
switch position (see "Call destination", page 121
).
[1] One and the same trunk group cannot contain both analogue and digital network interfaces.
Fig. 82 Routing and destinations of an incoming call
Call routing depends in principle on whether a call originates
• from the public network or
220
1/n
220
2/n
220
3/n
[1]
PINX 1
PINX 2
PINX 1
PISN
Call Distribution
Element 3
Call Distribution
Element 2
Call Distribution
Element 1
Direct dialling plan 2
Direct dialling plan 1
Trunk group 2:
Trunk group 1:
-> Direct dialling plan 2
Network
interfaces
Ex-
change
Changeover switches
KT line
User
Sexternal
BRI-T
PRI
FXO
BRI-T
PRI
DDI no. 100
-> Call distribution 2
DDI no. 100
-> Call distribution 3
-> Call Distribution 1
-> Direct dialling plan 1
 Loading...
Loading...