Call routing
246
System functions and features as of R4.1
syd-0570/1.2 – R4.1 – 08.2016
6. 8 Testing overflow routing in the PISN
When a connection is setup the system checks the availability of the selected path. If it
is not available due to overloading or due to a defect, an attempt will be made to set up
the connection via an alternative route, depending on the configuration. There are two
types of overflow routing:
• Overflow routing within the private leased-line network:
Both the initial and the alternative connection path run via dedicated lines of the pri-
vate leased-line network.
• Overflow routing via the public network:
The initial connection path runs via dedicated lines of the private leased-line net-
work while the alternative connection path runs via the public network.
Transmission of the CLIP number depends on the CLIP settings. See also the overflow
situations illustrated in the example on page 93
.
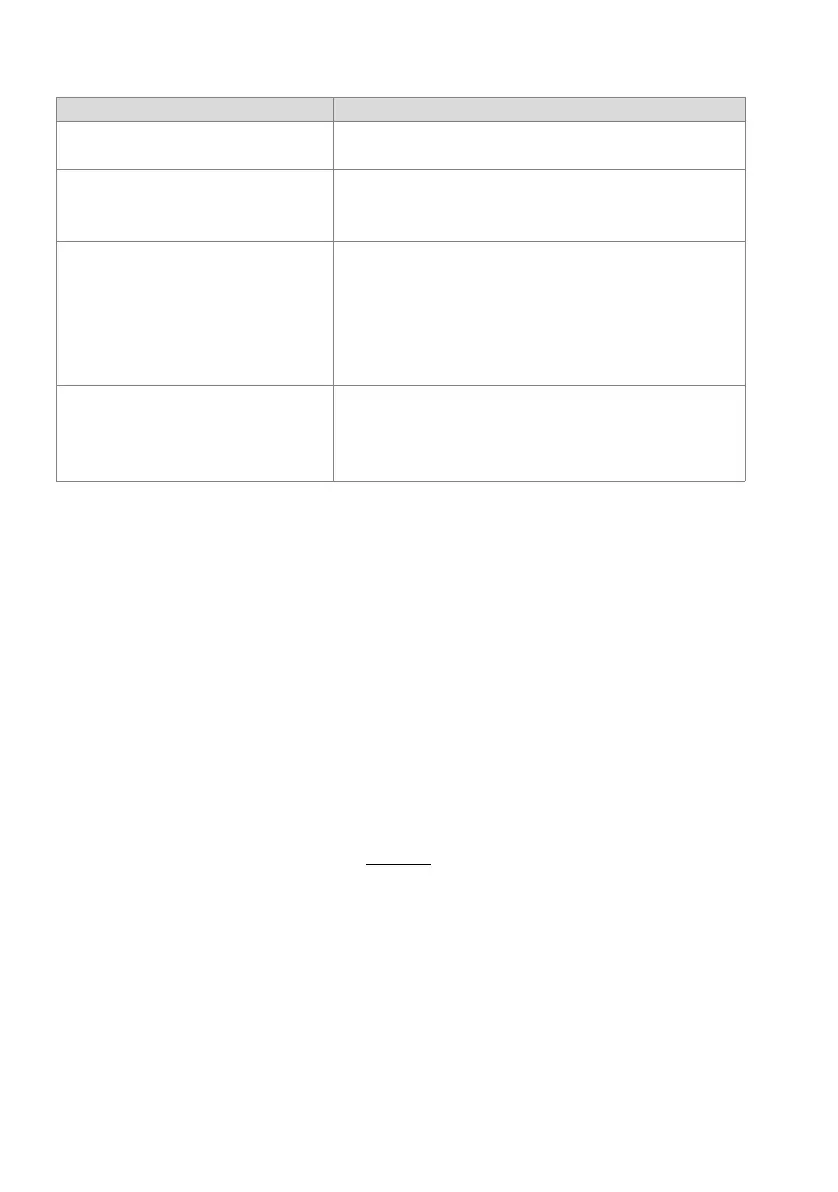
• DDI plan 1 (relevant only if a suitable DD number is found)
• Call Distribution Element Not relevant to this case
User configuration PISN-BN 330:
• Route 2 (route reference number)
• External call number Phone number to be dialled without exchange access prefix
Route 2:
• Trunk group 2 2 (reference number of one or more trunk group(s))
• Digit barring Use or do not use digit barring
• Max outgoing calls Number of calls going out simultaneously via this route
• Numbering plan identifier (NPI) PNP
• Type of number (TON) Unknown
Trunk group 2:
• Network interfaces Network interfaces of this trunk group
• Network type Private
• Protocol QSIG or QSIG / PSS1 ISO
Parameter Parameter value
 Loading...
Loading...