32. Layer 3 Switching
ROX™ v2.2 User Guide 356 RuggedBackbone™ RX1500
32. Layer 3 Switching
32.1. Layer 3 Switching Fundamentals
32.1.1. What is a Layer 3 Switch?
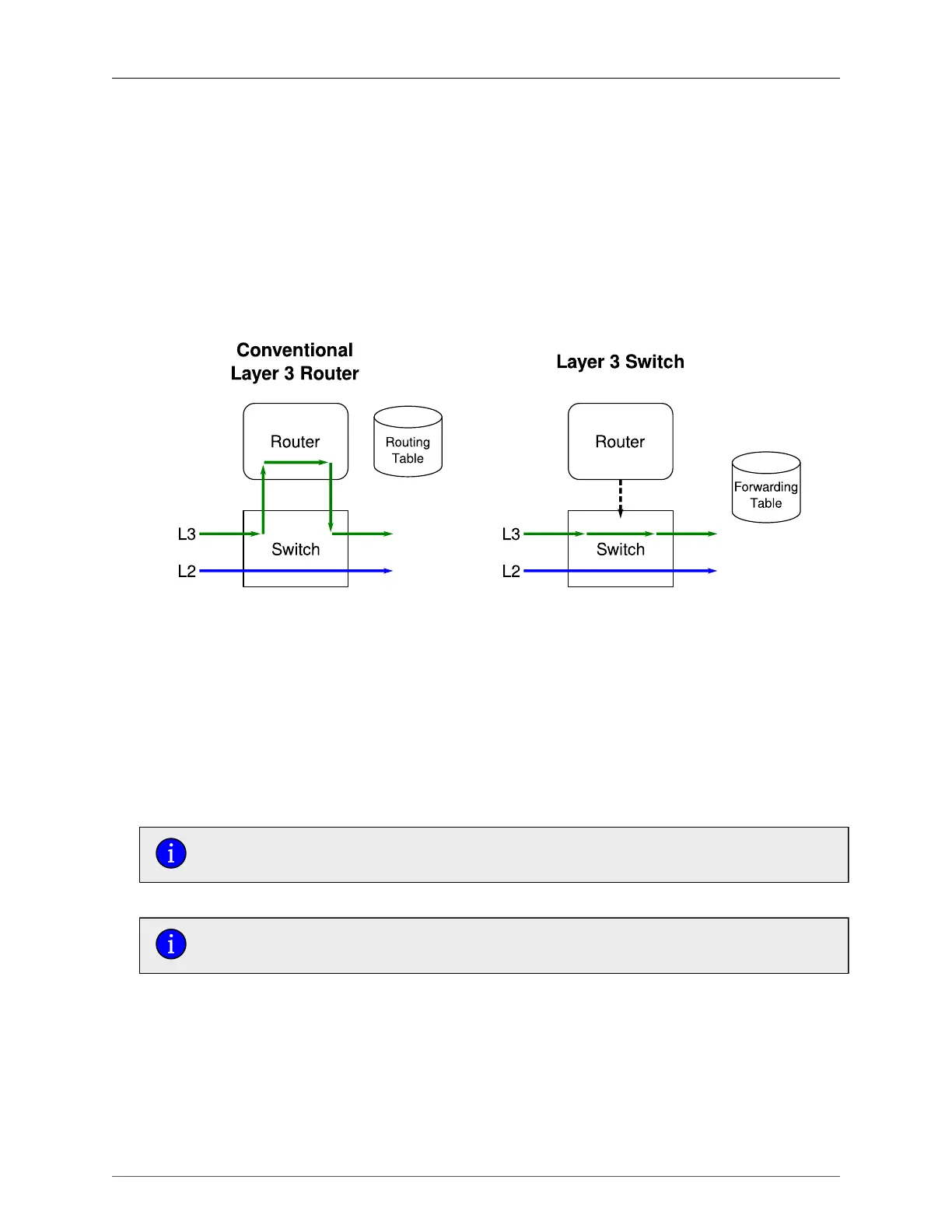
A switch is an internetwork device that makes frame forwarding decisions in hardware. A Layer 3 switch,
sometimes called a multilayer switch, is one which makes hardware-based decisions for IP packets
as well as Layer 2 frames. Traditionally, routers are used to make routing decisions using software. A
Layer 3 switch will make the same decisions in hardware, which means that packet forwarding will be
much faster than in a conventional router.
Figure 32.1. Layer 3 Switch
The RuggedBackbone™ Layer 3 Switch combines the rich feature set of a software router and the wire-
speed performance of a Layer 3 switch. It offers flexible configuration, allowing you to control which
routed traffic flows are hardware-accelerated and which flows are subject to software processing. This
allows the device to satisfy sophisticated firewall rules, which are not normally not supported by Layer
3 switches.
32.1.2. Layer 3 Switch Forwarding table
To route a packet with a specific destination IP address, a router needs the following information:
• Egress interface (subnet): this information is stored in the router’s Routing Table.
In a Layer 2 switched network segment, a VLAN constitutes an IP subnet.
• Next-hop gateway MAC address: this information is stored in the router’s ARP Table.
If the next hop is the destination subnet itself, then the destination host MAC address
is required.
A Layer 3 Switch uses the routing information listed above and translates it into Layer 3 switching rules.
These rules are known as the Layer 3 Switch Forwarding Information Base (FIB) or the Layer 3 Switch
Forwarding Table. A Layer 3 switching rule is actually a set of parameters identifying a traffic flow to be
switched and determining how to perform the switching.
Layer 3 switching application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) store Layer 3 switching rules in
a Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) table. Layer 3 switching rules can be statically
configured or dynamically learned (also known as auto-learned).
 Loading...
Loading...