Acceleration time constant
Deceleration time constant
Absolute value travel command
Continuous travel command
Suspend the step until PI1 (Program input 1) is switched on.
2) Program example 2
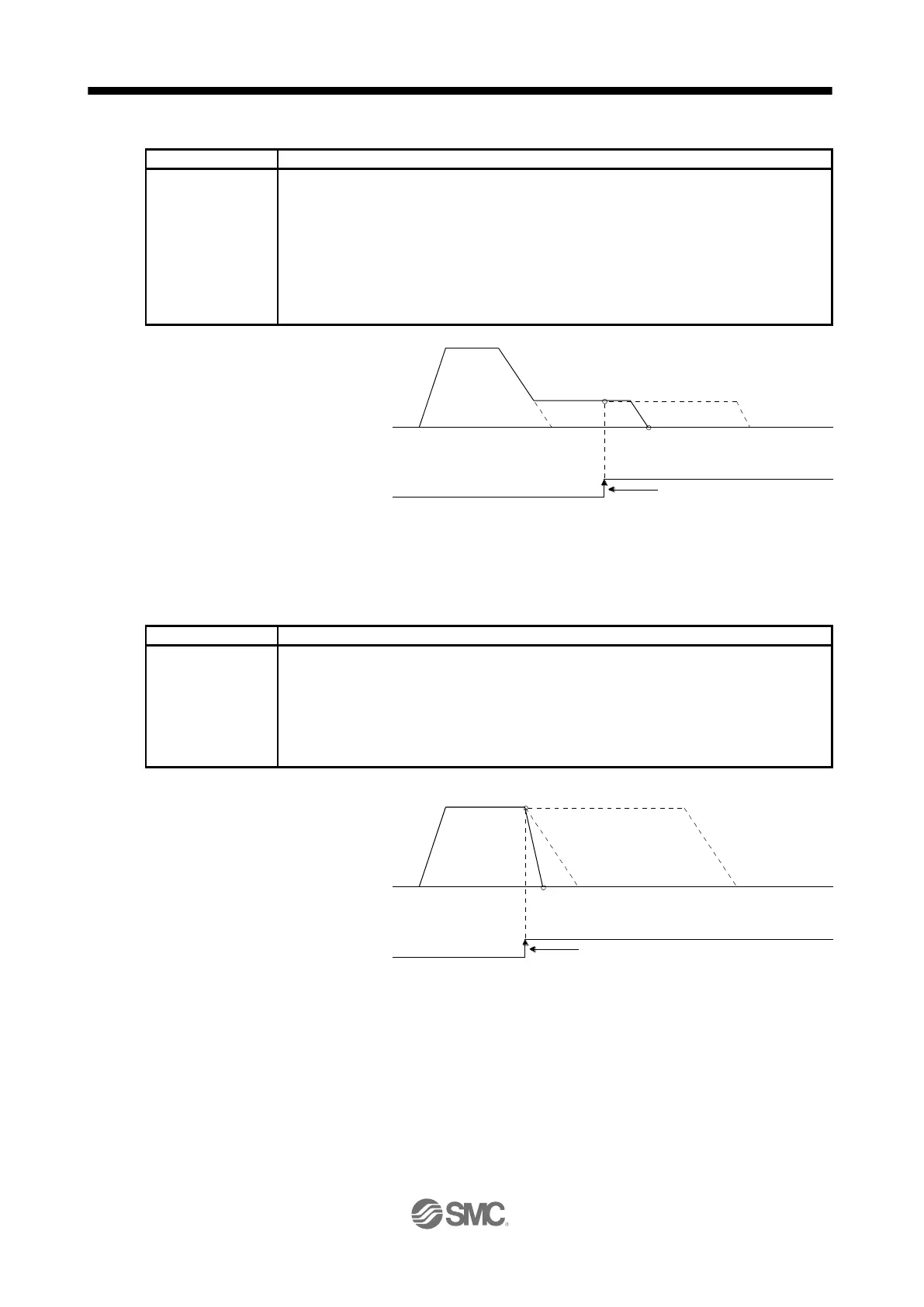
When the travel distance set by the "ITP" command is smaller than the travel distance required
for deceleration, the actual deceleration time constant becomes smaller than the setting value of
the "STB" command.
Acceleration time constant
Deceleration time constant
Absolute value travel command
Suspend the step until PI1 (Program input 1) is switched on.
Waiting for PI1 on (a))
by SYNC (1)
P1
ON
OFF
PI1
(Program input 1)
P1 + b) (200 × 10
STM
μ
m)
Servo motor speed
Forward rotation
0 r/min
Reverse rotation
Waiting for PI1 on (a))
by SYNC (1)
P1
ON
OFF
PI1
(Program input 1)
P1 + b) (50 × 10
STM
μ
m)
Servo motor speed
Forward rotation
0 r/min
Reverse rotation
 Loading...
Loading...