Refer to the 2600B specifications for details on source settling times. For the latest specifications, go
to tek.com/keithley.
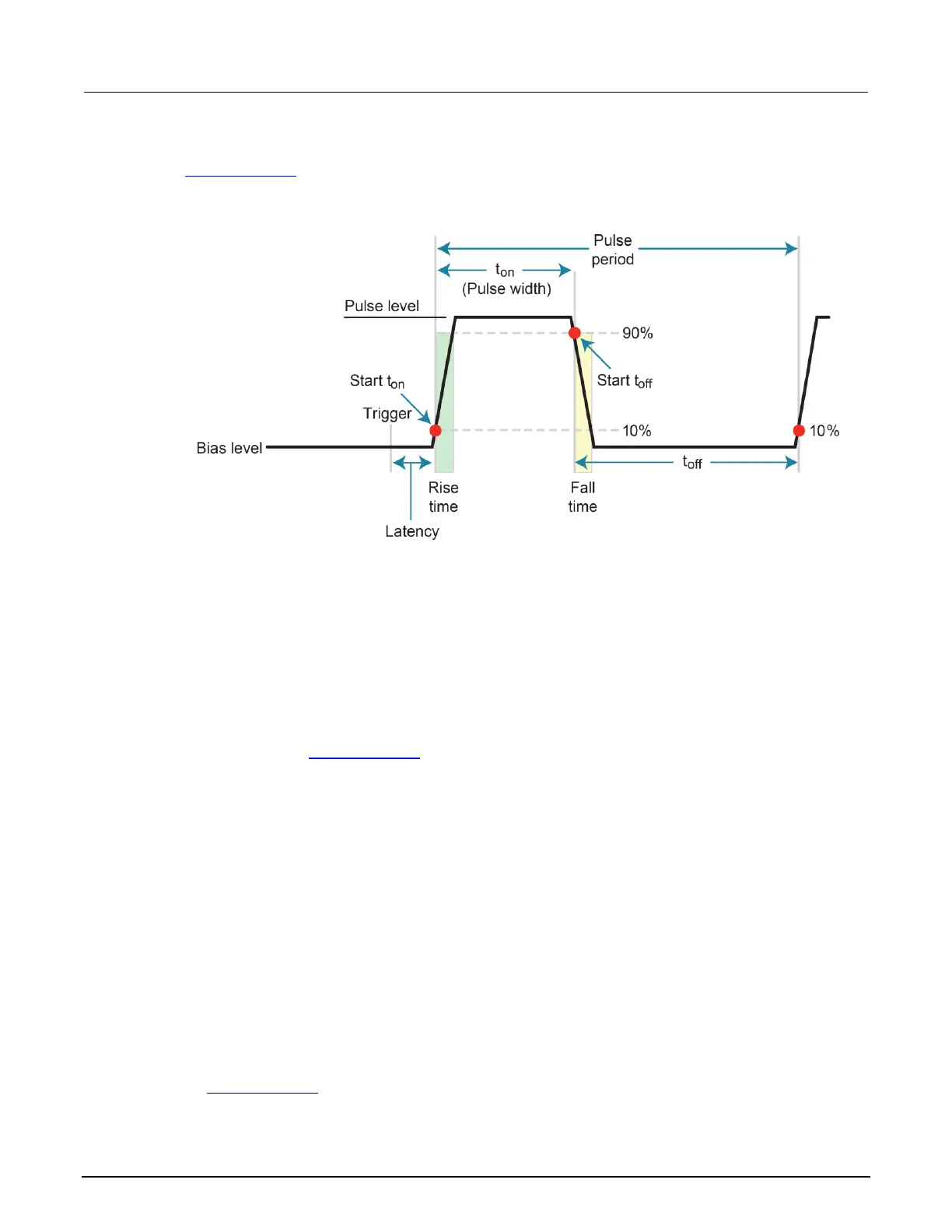
Figure 84: Pulse rise and fall times
Range and pulse settling
Each SMU range has different specifications for source settling times. This causes different rise and
fall time characteristics depending on the set range.
In addition, pulse performance is dependent on the pulse setting as a percent of full scale. For
example, a 100 mA pulse on the 1 A range (which is 10% of full scale) performs differently than a 1 A
pulse on the 1 A range (which is full scale). Refer to the 2600B specifications for details. For the latest
specifications, go to tek.com/keithley.
SMU load and operating mode
Settling times for the current source vary with the resistive load applied. In addition to the load, the
times vary depending on whether the source-measure unit (SMU) is configured as a voltage source or
a current source, and also if the voltage source range is selected.
Pulse width
The pulse width is the interval between 10% on the rising (leading) edge to 90% on the falling (trailing)
edge. Exceeding the specified pulse width limits can result in short pulses. In addition, the jitter of the
pulse width can change the pulse width (this is especially important for short pulse widths). Jitter in
respect to pulse width is the short-term instability of the trailing edge relative to the leading edge.
Review the 2600B specifications for information on source settling time. For the latest specifications,
go to tek.com/keithley.

 Loading...
Loading...











