TSP-Link nodes
Each instrument (node) attached to the TSP-Link
®
network must be identified by assigning it a unique
TSP-Link node number.
Commands for remote nodes are stored in the node table. An individual node is accessed as
node[N], where N is the node number assigned to the node.
All TSP-accessible remote commands can be accessed as elements of the specific node. The
following attributes are examples of items you can access:
• node[N].model: The product model number string of the node.
• node[N].revision: The product revision string of the node.
• node[N].serialno: The product serial number string of the node.
You do not need to know the node number of the node that is running a script. The variable
localnode is an alias for the node entry of the node where the script is running. For example, if a
script is running on node 5, you can use the global variable localnode as an alias for node[5]. To
access the product model number for this example, use localnode.model.
Connections
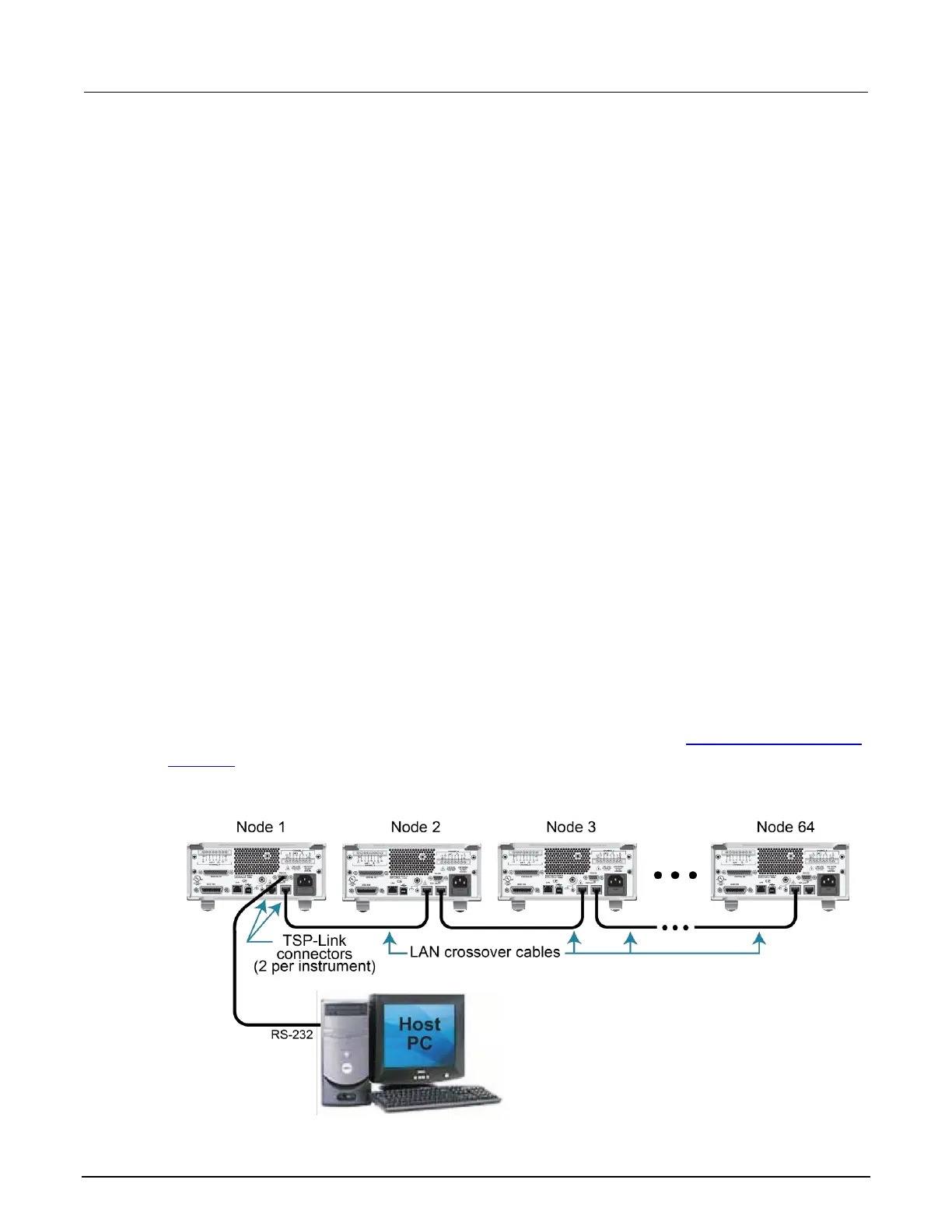
Connections for an expanded system are shown in the following figure. As shown, one instrument is
optionally connected to the computer using the GPIB, LAN, USB, or RS-232 interface.
All the instruments in the system are connected in a sequence (daisy-chained) using LAN
crossover cables. The cables used for TSP-Link connections must be category 5e or higher and less
than three meters between nodes.
Details about these computer communication connections are described in Remote communications
interfaces (on page 8-36). You can use TSP-Link without a host computer.
Figure 107: TSP-Link connections

 Loading...
Loading...











