-- Add the source code from the script
-- testScript to the data queue.
node[2].dataqueue.add(testScript.source)
-- Create a new script on the remote node
-- using the source code from testScript.
node[2].execute(testScript.name ..
"= script.new(dataqueue.next(), [[" .. testScript.name .. "]])")
Removing stale values from the reading buffer cache
The node that acquires the data also stores the data for the reading buffer. To optimize data access,
all nodes can cache data from the node that stores the reading buffer data.
When you run Lua code remotely, it can cause reading buffer data that is held in the cache to
become stale. If the values in the reading buffer change while the Lua code runs remotely, another
node can hold stale values. Use the clearcache() command to clear the cache. For additional
detail on the reading buffer cache commands, see bufferVar.cachemode (on page 9-19) and
bufferVar.clearcache() (on page 9-21).
The following example code demonstrates how stale values occur and how to use the clearcache()
command to clear the cache on node 2, which is part of group 7.
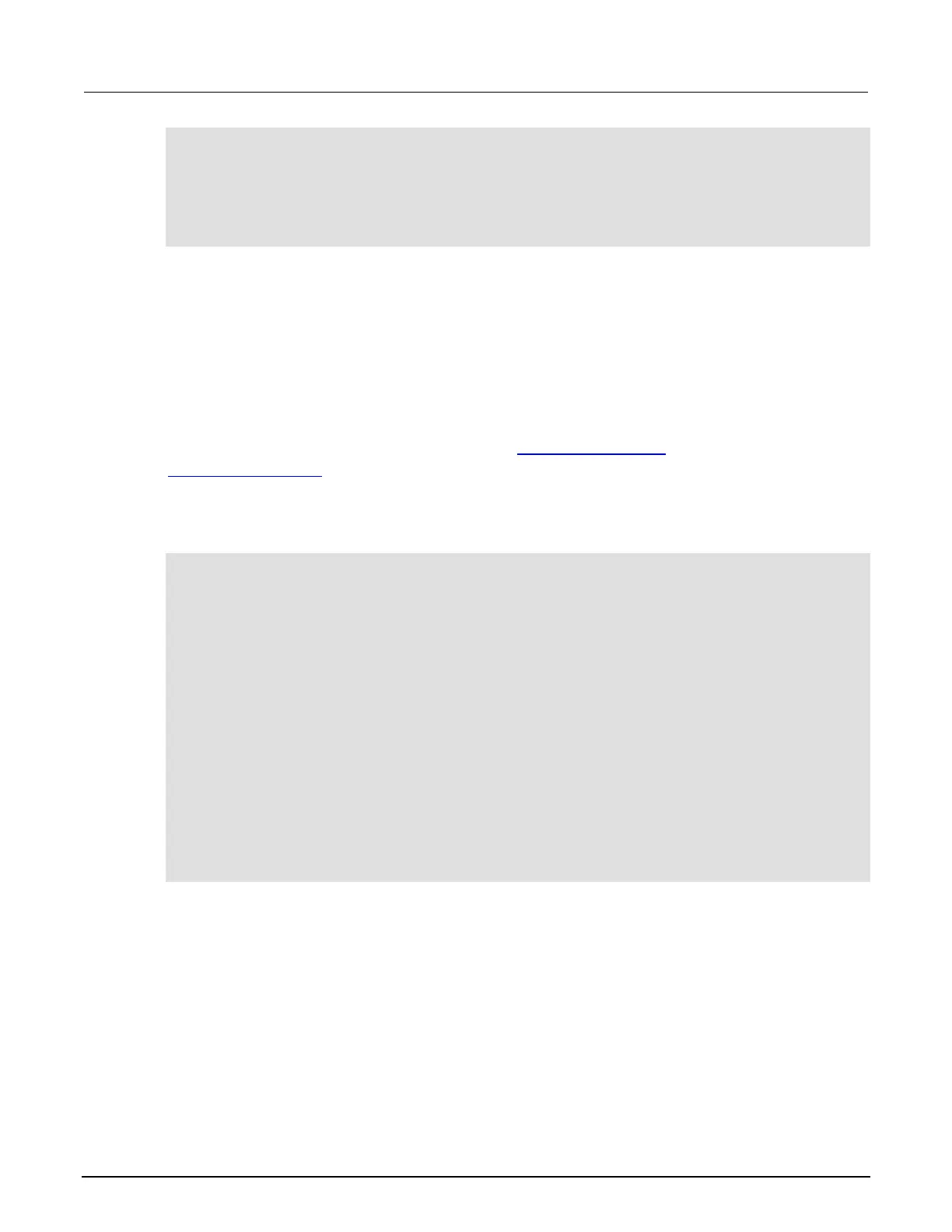
-- Create a reading buffer on a node in a remote group.
node[2].tsplink.group = 7
node[2].execute("rbremote = smua.makebuffer(20)" ..
"smua.measure.count = 20 " ..
"smua.measure.v(rbremote)")
-- Create a variable on the local node to
-- access the reading buffer.
rblocal = node[2].getglobal("rbremote")
-- Access data from the reading buffer.
print(rblocal[1])
-- Run code on the remote node that updates the reading buffer.
node[2].execute("smua.measure.v(rbremote)")
-- Use the clearcache command if the reading buffer contains cached data.
rblocal.clearcache()
-- If you do not use the clearcache command, the data buffer
-- values never update. Every time the print command is
-- issued after the first print command, the same data buffer
-- values print.
print(rblocal[1])

 Loading...
Loading...











