3.5 Port Forwarding
Network address translation (NAT) is a method of remapping one IP address space into another by modifying network
address information in Internet Protocol (IP) datagram packet headers while they are in transit across a traffic routing device.
The technique was originally used for ease of rerouting traffic in IP networks without renumbering every host. It has become
a popular and essential tool in conserving global address space allocations in the face of IPv4 address exhaustion. The NTC-
400 Series Router supports NAT. You can disable the NAT function on the [Basic Network]-[WAN & Uplink]-[Internet Setup]-
[WAN Type Configuration] page.
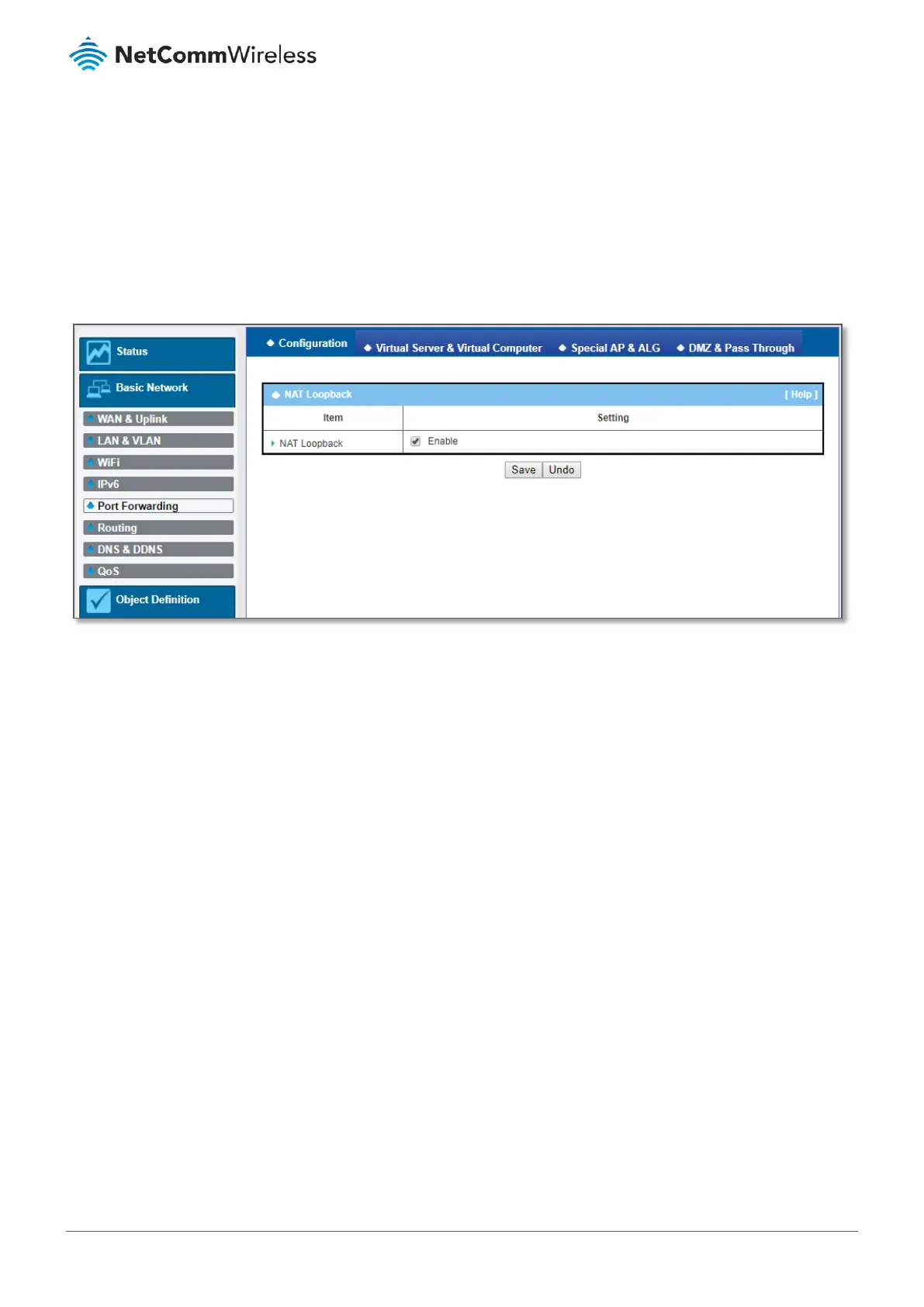
Figure 143 – NAT Loopback
Usually all local hosts or servers behind the corporate gateway are protected by a NAT firewall. The NAT firewall filters out
unrecognized packets to protect your Intranet. All local hosts are invisible to the outside world. Port forwarding or port
mapping is a function that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to an assigned
one. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal)
network available to hosts on the opposite side of the router (external network), by remapping the destination IP address
and port number.
There are several optional Port Forwarding related functions on the NTC-400 Series Router. They are Virtual Server, Virtual
Computer, IP Translation, Special AP & ALG, DMZ, Pass Through, etc.
3.5.1 Configuration
3.5.1.1 NAT Loopback
This feature allows you to access the WAN global IP address from inside your NAT local network. It is useful when you run a
server inside your network. For example, if you set up a mail server on the LAN side, your local devices can access this mail
server through the router’s global IP address when the NAT loopback feature is enabled. Regardless of which side the email
server is being accessed from, the IP address of the mail server does not need to be changed.
3.5.1.2 Configuration Setting
Navigate to the Basic Network > Port Forwarding > Configuration tab. The NAT Loopback feature allows you to access the
WAN IP address from inside your local network.

 Loading...
Loading...