LASER EXPOSURE
2-43
SM A229
Detailed
Descriptions
2.4 LASER EXPOSURE
2.4.1 OVERVIEW
This machine uses two laser diodes to produce electrostatic images on an OPC
drum. The laser diode unit converts image data from the SBICU board into laser
pulses, and the optical components direct these pulses to the drum.
Exposure of the drum by the laser beam creates the latent image. The laser beam
makes the main scan while drum rotation controls the sub scan.
The combined strength of both beams is 0.5 mW on the drum surface at a
wavelength of 780 nm.
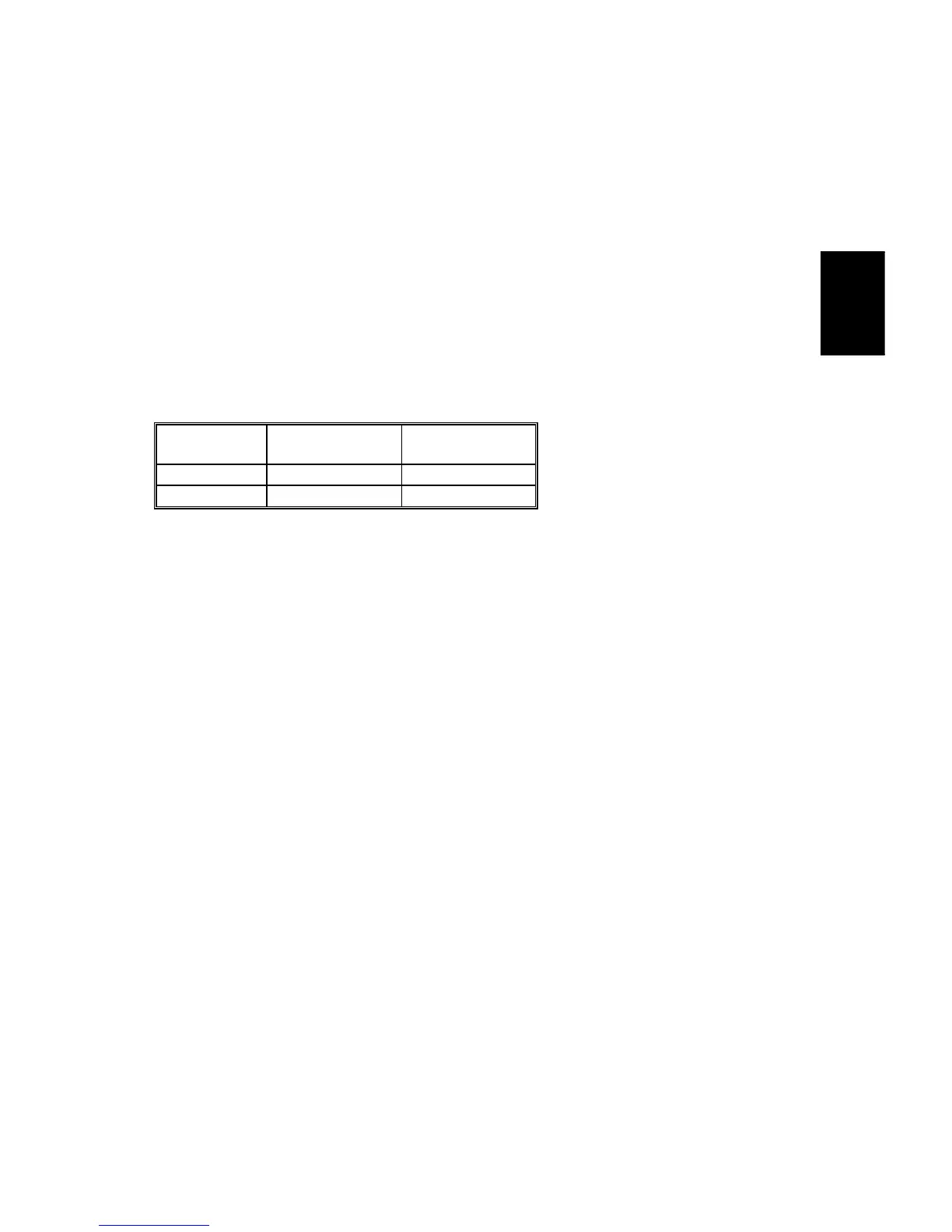
The polygon motor speed is as follows.
Resolution Modes
Motor Speed
(rpm)
400 dpi Copy, Printer Approx. 25984
600 dpi Printer Approx. 38976
There are up to 16 image density levels for each pixel. To realize this, this machine
uses a form of pulse width modulation. In this machine, pulse width modulation
consists of the following processes:
•
Laser diode pulse positioning
•
Laser diode power/pulse width modulation
Laser diode power and pulse width modulation is done by the laser diode drive
board (LDDR). Briefly, the width of the laser pulse for a pixel depends on the output
level (from 0 to 15) required for the pixel.
This machine can also change the laser pulse position (at the left side of the pixel,
at the center, or at the right side) automatically, depending on the location of the
image pixel so that the edges of characters and lines become cleaner. There is no
SP mode adjustment for this, unlike in some earlier models.
 Loading...
Loading...











