Reference Manual ADuCM356
DMA CONTROLLER
analog.com Rev. A | 167 of 312
DMA cycle using the alternate data structure without rearbitrating.
The controller continues to alternate between using the primary and
alternate data structures until the processor configures the alternate
data structure for a basic cycle, or the DMA reads an invalid data
structure.
Table 195 lists the fields of the CHNL_CFG memory location for the
primary data structure, which must be programmed with constant
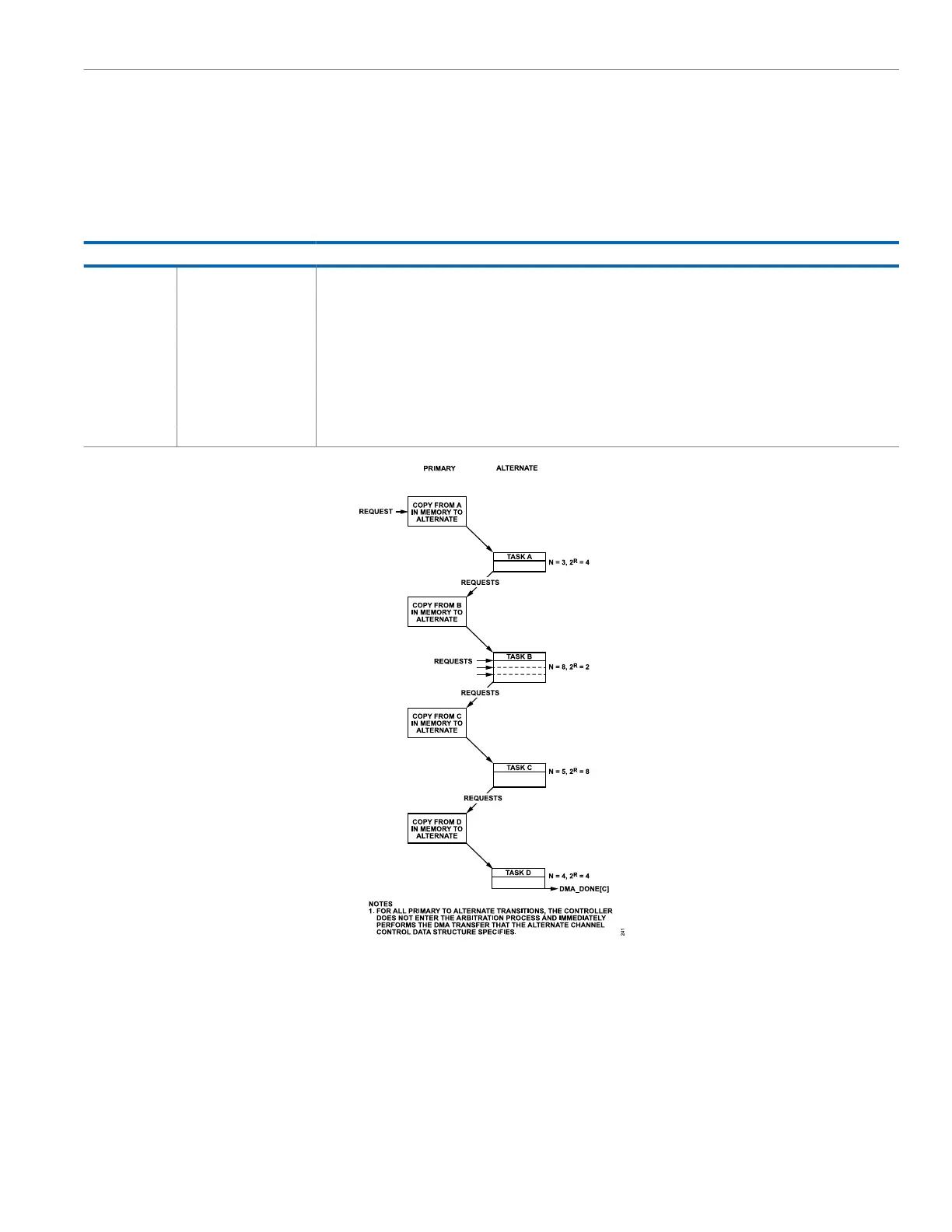
values for the peripheral scatter gather mode. This mode is shown
in Figure 47.
Table 195. CHNL_CFG for Primary Data Structure in Peripheral Scatter Gather Mode, CHNL_CFG, Bits[2:0] = 110
Bit(s) Name Description
[31:30] DST_INC Set to 10, configures the controller to use word increments for the address.
[29:28] Reserved Undefined. Write as 0.
[27:26] SRC_INC Set to 10, configures the controller to use word increments for the address.
[25:24] SRC_SIZE Set to 10, configures the controller to use word transfers.
[23:18] Reserved Undefined. Write as 0.
[17:14] R_POWER Set to 0010, indicates that the DMA controller performed four transfers without rearbitration.
[13:4] N_MINUS_1 Configures the controller to perform N DMA transfers, where N is a multiple of four.
3 Reserved Undefined. Write as 0.
[2:0] CYCLE_CTRL Set to 110, configures the controller to perform a peripheral scatter gather DMA cycle.
Figure 47. Peripheral Scatter Gather DMA Transfer
DMA INTERRUPTS AND EXCEPTIONS
Error Management
The DMA controller generates an error interrupt to the core when
a DMA error occurs. A DMA error can occur due to a bus error
or an invalid descriptor fetch. A bus error can occur when fetching
the descriptor or performing a data transfer. A bus error can occur
when a read from or a write to a reserved address location occurs.
When a bus error occurs, the faulty channel is automatically dis-
abled, and the corresponding status bit in the ERRCHNL_CLR
register is set. If the DMA error is enabled in the NVIC, the
error also generates an interrupt. In addition, the CHNL_CFG data
structure for the corresponding channel is updated with the latest N

 Loading...
Loading...