Reference Manual ADuCM356
HIGH-SPEED DAC CIRCUITS
analog.com Rev. A | 106 of 312
COUPLING AN AC SIGNAL FROM HIGH-SPEED
DAC ONTO THE DC LEVEL SET BY LOW-
POWER DAC
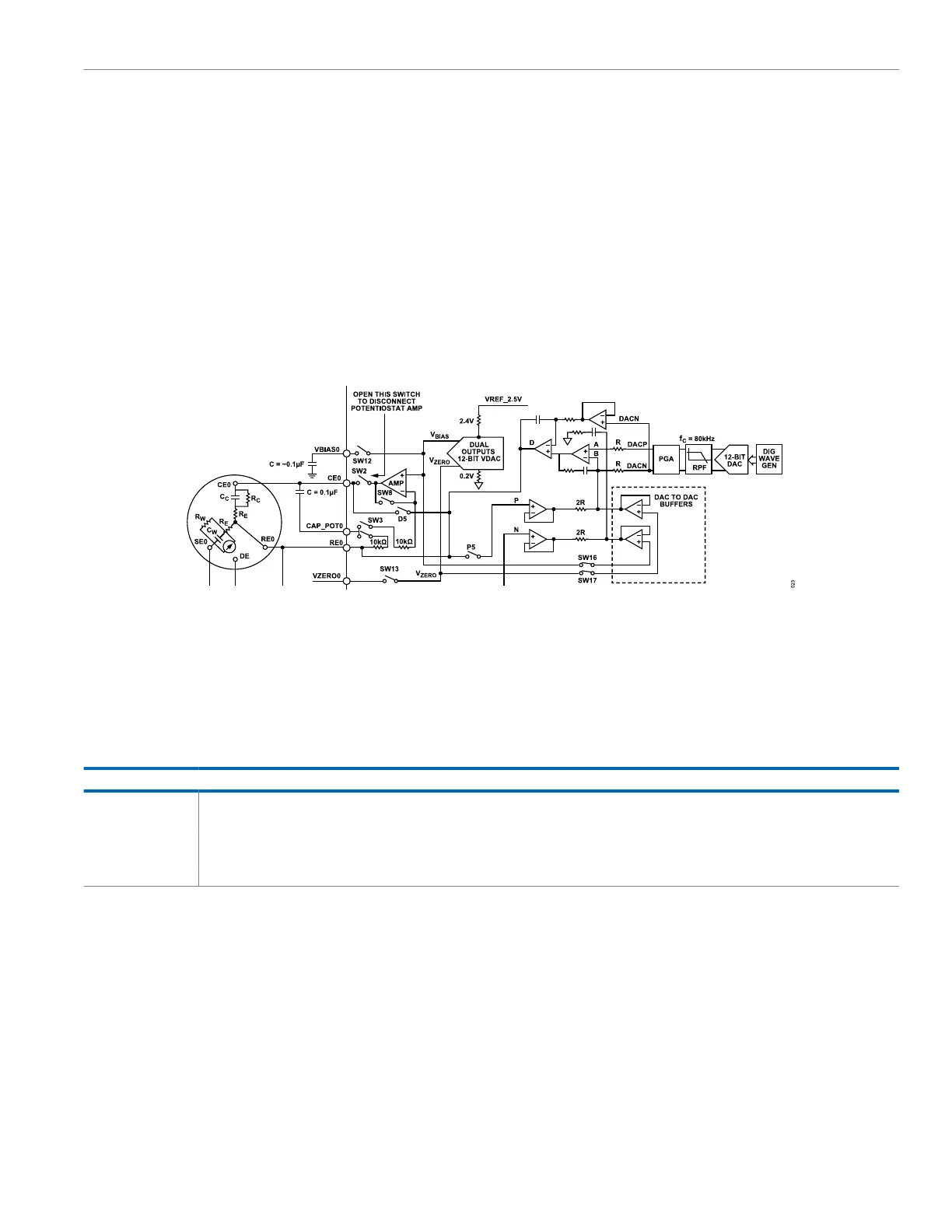
The ADuCM356 contains two independent low-power potentiostat
channels that configure two separate electrochemical sensors. In
normal operation, the bias voltage of the sensor between the
reference electrode and working electrode is set directly by the
low-power DAC outputs, VBIASx and VZEROx. See Figure 15 for
the setup.
In normal operation, the high-speed DAC circuits are not used.
However, to connect an AC signal onto the counter electrode,
the potentiostat amplifier must be disconnected from the sensor
and the whole signal must be applied from the high-speed DAC
excitation amplifier output. The bias voltage setting of the sensor
must also be completed by the high-speed TIA, rather than the
low-power TIA. The AC signal generated by the high-speed DAC
is coupled onto the DC voltage level set by the low-power DAC for
the channel under test. The DACDCBUFCON register, Bit 1 selects
LPDAC0 or LPDAC1 as the DC level voltage source that couples to
the high-speed DAC.
The DAC DC buffers shown in Figure 24 are enabled by setting
AFECON, Bit 21 = 1. This setting feeds the sensor DC bias voltage
to the excitation amplifier. For the appropriate LPDACx channel,
set LPTIASWx, Bits[11:0] = 0x180 to set the low-power TIA and
potentiostat switches for AC impedance measurement mode.
Figure 24. Signal Path for AC Signal Coupled onto DC Level Set by Low-Power DAC
AVOIDING INCOHERENCY ERRORS
BETWEEN EXCITATION AND MEASUREMENT
FREQUENCIES DURING IMPEDANCE
MEASUREMENTS
Table 126 details the recommended settings to avoid incoherency
errors between excitation frequencies and measurement frequen-
cies during impedance measurements.
Table 126. Recommended Settings to Avoid Incoherency Errors
Parameter Recommended Settings
Hanning Window Always on (DFTCON, Bit 0 = 1). Enabling the Hanning window avoids issues due to incoherency. Disabling the Hanning window can result in
degraded performance.
High-Speed DAC
Update Rate
In low-power mode, the typical value is 16 MHz or 27 MHz. (HSDACCON, Bits[8:1] = 0x1B). In high-power mode, the typical value is 32 MHz or 7
MHz. (HSDACCON, Bits[8:1] = 0x7).
ADC Sampling Rate Low-power mode, 800 kSPS, high frequency oscillator = 16 MHz. High-power mode, 1.6 MSPS, high frequency oscillator = 32 MHz.
CALIBRATING THE HIGH-SPEED DAC
The high-speed DAC is not calibrated during production testing.
This section describes the calibration of the high-speed DAC for
all gain settings in low and high-power modes. Calibrate the high-
speed DAC if it is intended to generate an excitation signal to
a sensor. If an offset error exists on the excitation signal, and
a current or voltage output must be measured, the DAC output
voltage can exceed the headroom of the selected TIA or ADC input
buffer and PGA setting.
Calibrate the high-speed DAC with the required HSDACCON, Bit
12 and HSDACCON, Bit 0 settings. For example, if the DAC is
calibrated with HSDACCON, Bit 12 = 0 and HSDACCON, Bit 0
= 0, and the user changes HSDACCON, Bit 12 = 1, an error is
introduced if the DACOFFSET register or DACOFFSETHP register
is not recalibrated for the new output range.
The high-speed DAC is a differential output DAC that swings on
the voltage applied to the excitation N node of the amplifier. Figure
26 shows the connections of the high-speed DAC to the external
calibration resistor (R
CAL
) and internally to the ADC.
To calibrate the offset, ensure that the differential voltage measured
across R
CAL
is 0 V. It is important to ensure the offset error is
calibrated for the chosen high-speed DAC output range and power
mode.

 Loading...
Loading...