Reference Manual ADuCM356
DIGITAL DIE GENERAL-PURPOSE TIMERS
analog.com Rev. A | 264 of 312
DIGITAL DIE GENERAL-PURPOSE TIMERS
FEATURES
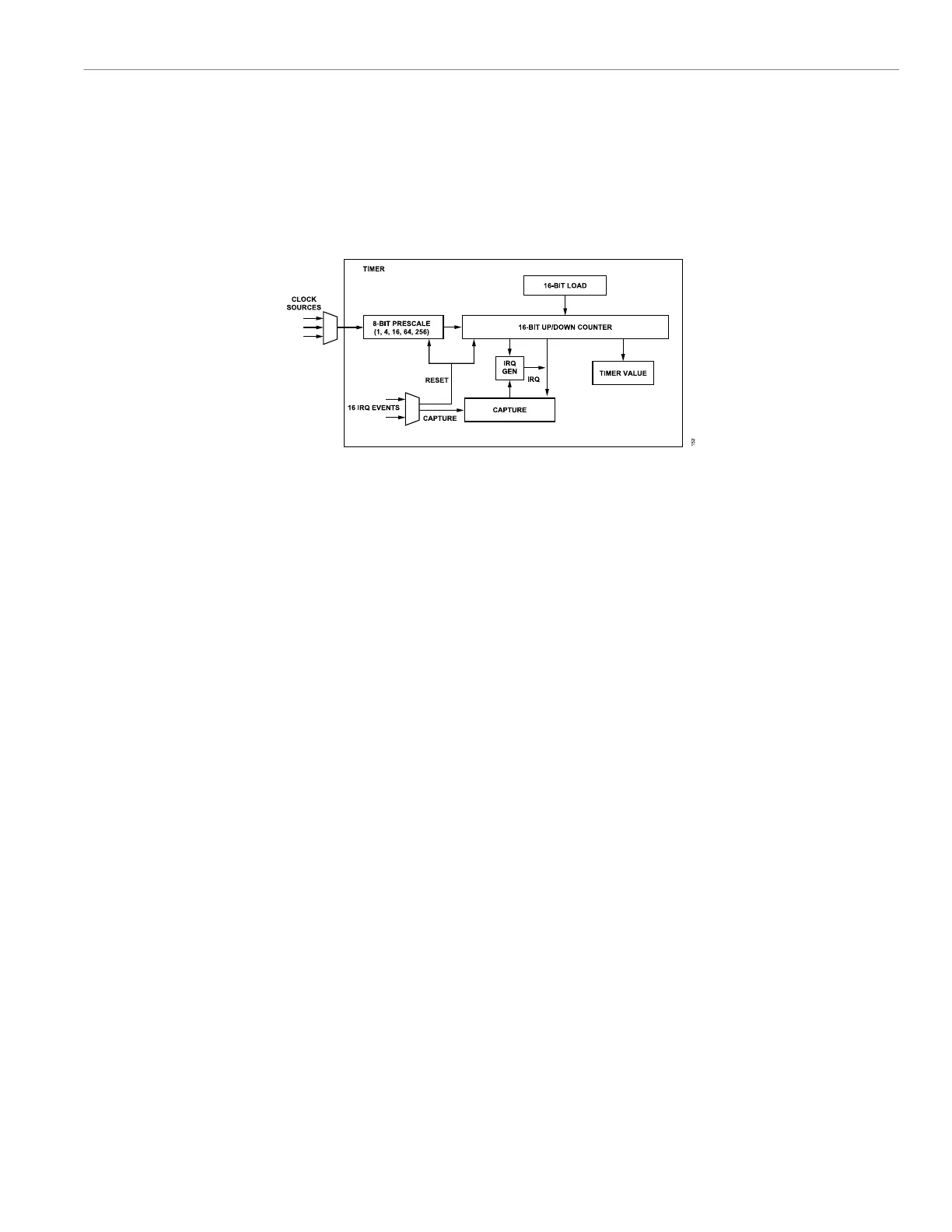
The ADuCM356 digital die integrates three identical general-pur-
pose, 16-bit count up or count down timers: Timer 0, Timer 1, and
Timer 2. These timers can be clocked from the 32 kHz internal
low frequency oscillator, the PCLK, or the internal 26 MHz high
frequency oscillator. Clock sources can be scaled down using a
prescaler to 1, 4, 16, or 256. Free running mode and periodic mode
are available. The timers have a capture events feature, with the
capability to capture 32 different events on each timer. See Figure
64 for an overview of the general-purpose timers.
Figure 64. General-Purpose Timers Block Diagram
GENERAL-PURPOSE TIMERS OVERVIEW
The timers can either be in free running mode or periodic mode. In
free running mode, the counter decrements from full scale to zero
scale or increments from zero scale to full scale and then restarts.
In periodic mode, the counter decrements or increments from the
value in the load register (GPTx_LOAD, where x is 0 for Timer 0,
1 for Timer 1, and 2 for Timer 2) until zero scale or full scale is
reached. The counter then restarts at the value stored in the load
register.
The value of a counter can be read at any time by access-
ing its value register, GPTx_ACURCNT or GPTx_CURCNT.
GPTx_ACURCNT assumes the timer and the CPU are synchron-
ized (using the same clock source). Do not use GPTx_ACURCNT if
the timer is using a different clock source, such as the low frequen-
cy oscillator. In this case, use GPTx_CURCNT. GPTx_CURCNT
returns a synchronized timer value but has a slightly delayed result
owing to the synchronization period required.
The CON0 register selects the timer mode, configures the clock
source, selects count up or count down, starts the counter, and
controls the event capture function.
An interrupt signal is generated each time the value of the counter
reaches 0 when counting down or each time the counter value
reaches the maximum value when counting up. Clear an IRQ by
writing 1 to the time clear interrupt register of that particular timer
(GPTx_CLRINT).
In addition, Timer 0, Timer 1, and Timer 2 have a capture register
that is triggered by a selected IRQ source initial assertion. When
triggered, the current timer value is copied to the GPTx_CAPTURE
register, and the timer continues to run. This feature determines the
assertion of an event with increased accuracy.
GENERAL-PURPOSE TIMER OPERATIONS
Free Running Mode
In free running mode, the timer is started by setting the enable bit
(GPTx_CTL, Bit 4) to 1 and the mode bit (GPTx_CTL, Bit 3) to 0.
The timer increments from zero scale or full scale to full scale or
zero scale if counting up or down. Full scale is 216, which is 1 or
0xFFFF. Upon reaching full scale or zero scale, a timeout interrupt
occurs and GPTx_STAT, Bit 0 is set. To clear the timer interrupt,
user code must write 1 to GPTx_CLRINT, Bit 0. If GPTx_CTL, Bit 7
is set, the timer keeps counting and reloads when GPTx_CLRINT,
Bit 0 is set to 1.
Periodic Mode
In periodic mode, the initial GPTx_LOAD value must be loaded be-
fore starting the timer by setting the enable bit (GPTx_CTL, Bit 4) to
1. The timer value either increments from the value in GPTx_LOAD
to full scale or decrements from the value in GPTx_LOAD to zero
scale, depending on the GPTx_CTL, Bit 2 settings (count up or
down). Upon reaching full scale or zero scale, the timer generates
an interrupt. GPTx_LOAD is reloaded into GPTx_CURCNT, and the
timer continues counting up or down. The timer must be disabled
prior to changing the GPTx_CTL or GPTx_LOAD register. If the
GPTx_LOAD register is changed while the timer is being loaded,
undefined results can occur. By default, the counter is reloaded
automatically when generating the interrupt signal. If GPTx_CTL,
Bit 7 is set to 1, the counter is also reloaded when user code writes
GPTx_CLRINT, which allows user changes to GPTx_LOAD to take
effect immediately instead of waiting until the next timeout.
The timer interval is calculated as follows:
If the timer is set to count down,

 Loading...
Loading...