Specifications
2-54 Hardware Description
Caution To minimize potential problems, the modem phone line cable should be disconnected
when not in use.
Note The Windows Catalogs are replacing the Hardware Compatibility List (HCL).
Step 1. Go to the Windows Catalogs URL: www.microsoft.com/whdc/hcl/default.mspx.
Step 2. Click on the appropriate link:
• Windows XP devices: Windows Catalog link.
• Windows 2000 Server devices: Windows Server Catalog link.
Step 3. Navigate to the find external analog modems.
Step 4. Select from the products with the strongest compatibility rating(s) (i.e. has all of the
Windows Logo requirements and there is a driver available for download.)
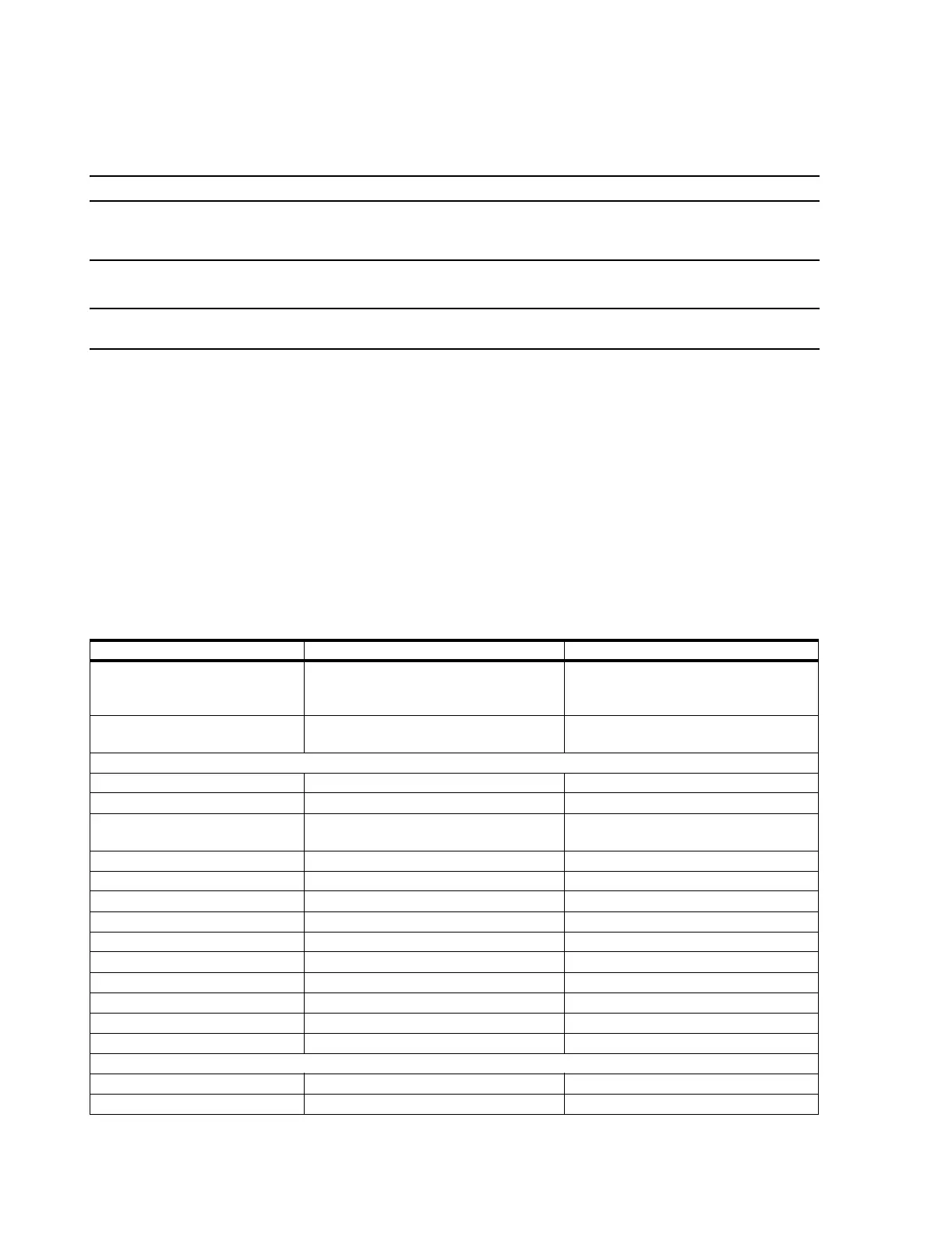
Table 2-8. Requirements for an External Modem
Specification Value Comments
Exact model has a Logo or Compatible
listing for use with Windows 2000 Server
or XP Professional
Follow the modem manufacturer’s
installation procedures for Windows 2000
Server or XP Professional
International Telecommunications
Union (ITU) standardization
e.g. V.34, V.90
Physical Serial B Enable in BIOS Setup
Logical COM 2 OS’s modem preference
Interrupt Request IRQ 3 Default IRQ. Set to Available in BIOS
Setup
Base I/O Address 2F8 Default hex address
Serial port FIFO enabled Yes Default setting
Port Speed 115200 Typical value
Data bits 8 Default value
Parity None Default setting
Stop bits 1 Default value
Use error control Yes, Compress data
Use flow control Yes, Hardware (RTS/CTS)
Modulation type Standard
Record a log file No
External modem-cable connector
Type Female, 9-pin, D-Sub, RS-232C
Pin 1 DCD (Data Carrier Detect)

 Loading...
Loading...