Troubleshooting
7-14 Maintenance, Troubleshooting, and Repair
Troubleshooting
Strategy
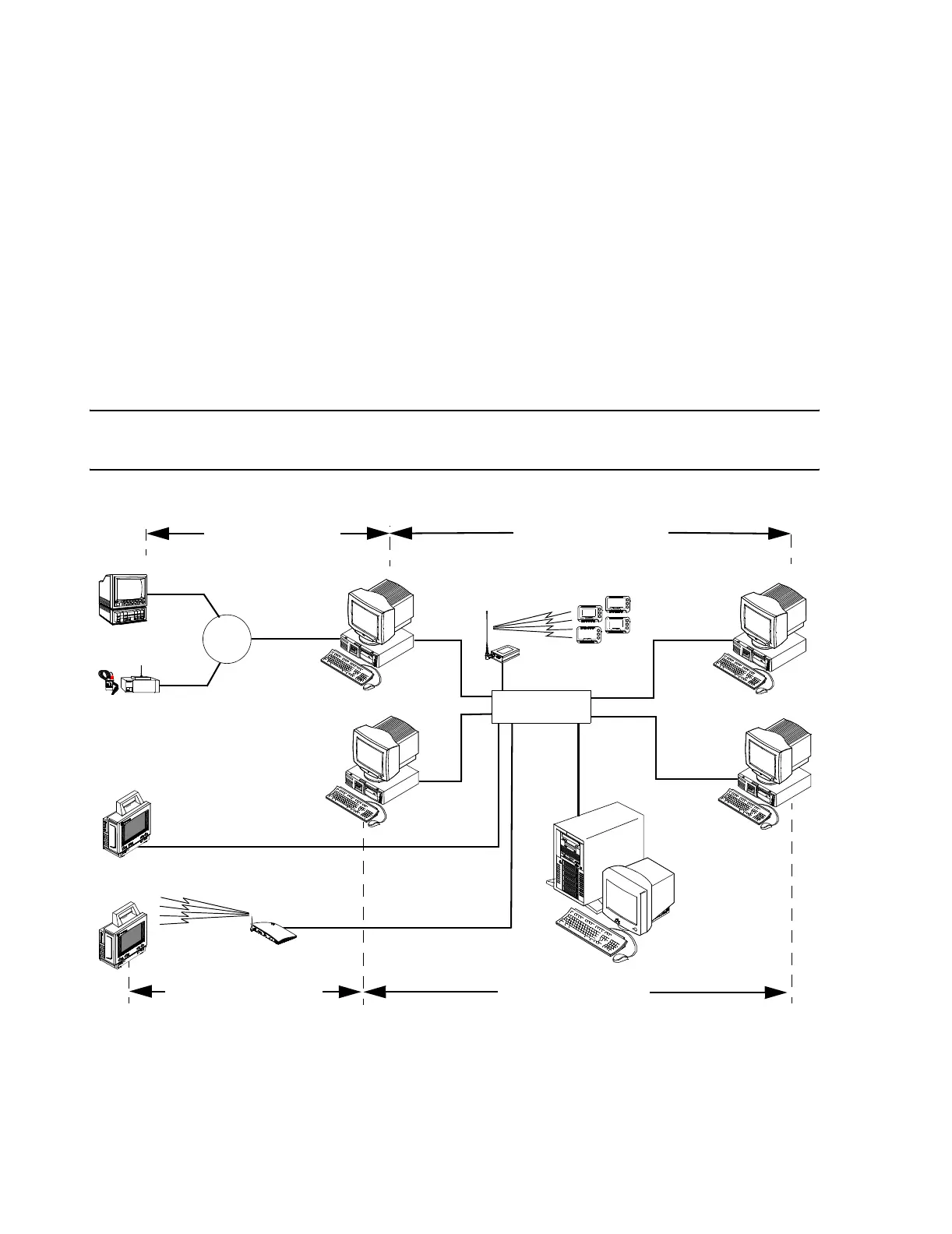
The flow of information in Information Center systems can be divided into 4 major
connectivity components: (See Figure 7-2):
• SDN connectivity - flow of real-time patient monitoring data from patient
monitors through the SDN to Information Centers for display
• Wireless connectivity - flow of real-time patient monitoring data from
wireless Patient monitors via Access Points to Information Centers for display
• Network connectivity - flow of real-time patient data from Information
Centers to Network connected Information Centers and Clients for
overviewing
• Server connectivity - flow of stored patient monitoring data to the Server for
storage and out to Information Centers and Clients for review
Note SDN and Server Connectivity are covered in this manual. Wireless and Network
Connectivity are covered in the Clinical Network Service Manual.
Figure 7-2 Network/Server Connectivity Components
Each connectivity component should be evaluated separately to identify the source of
a problem. The following questions can be asked:
• What devices and functions are working?
Philips Telemetrys
Philips CMSs
Information Centers
Server
Clients
18.5
18.5
18.5
18.5
CareNet
Switch
18.5
Switch
SDN
SDN Connectivity
Network Connectivity
Server Connectivity
Access Point
Wired M2/M3/M4 Monitor
Wireless M3/M4 Monitor
Wireless Connectivity

 Loading...
Loading...