7-7
ADSL WAN Connections
ADSL Overview
When you configure an ADSL connection, you must configure both the Phys-
ical Layer and the Data Link Layer (which is also called the Logical Layer).
The Physical Layer is, of course, ADSL. The Data Link Layer protocol is
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM).
ADSL Infrastructure
When you purchase an ADSL connection, your company’s premises must be
connected to the public carrier’s nearest CO. All of the telecommunications
infrastructure that is used to connect your company’s premises to the CO is
collectively called the local loop.
ADSL uses modulation to increase the speed at which data can be transmitted
over the plain copper wire that is used for most local loops. Once the ADSL
traffic reaches the public carrier’s CO, it is sent to a DSL Access Multiplexer
(DSLAM) and then routed over the regional broadband, or packet, network.
(See Figure 7-3.) Traffic transmitted over E1- and T1-carrier lines, on the other
hand, is sent to a voice switch before being transmitted through the public
carrier network.
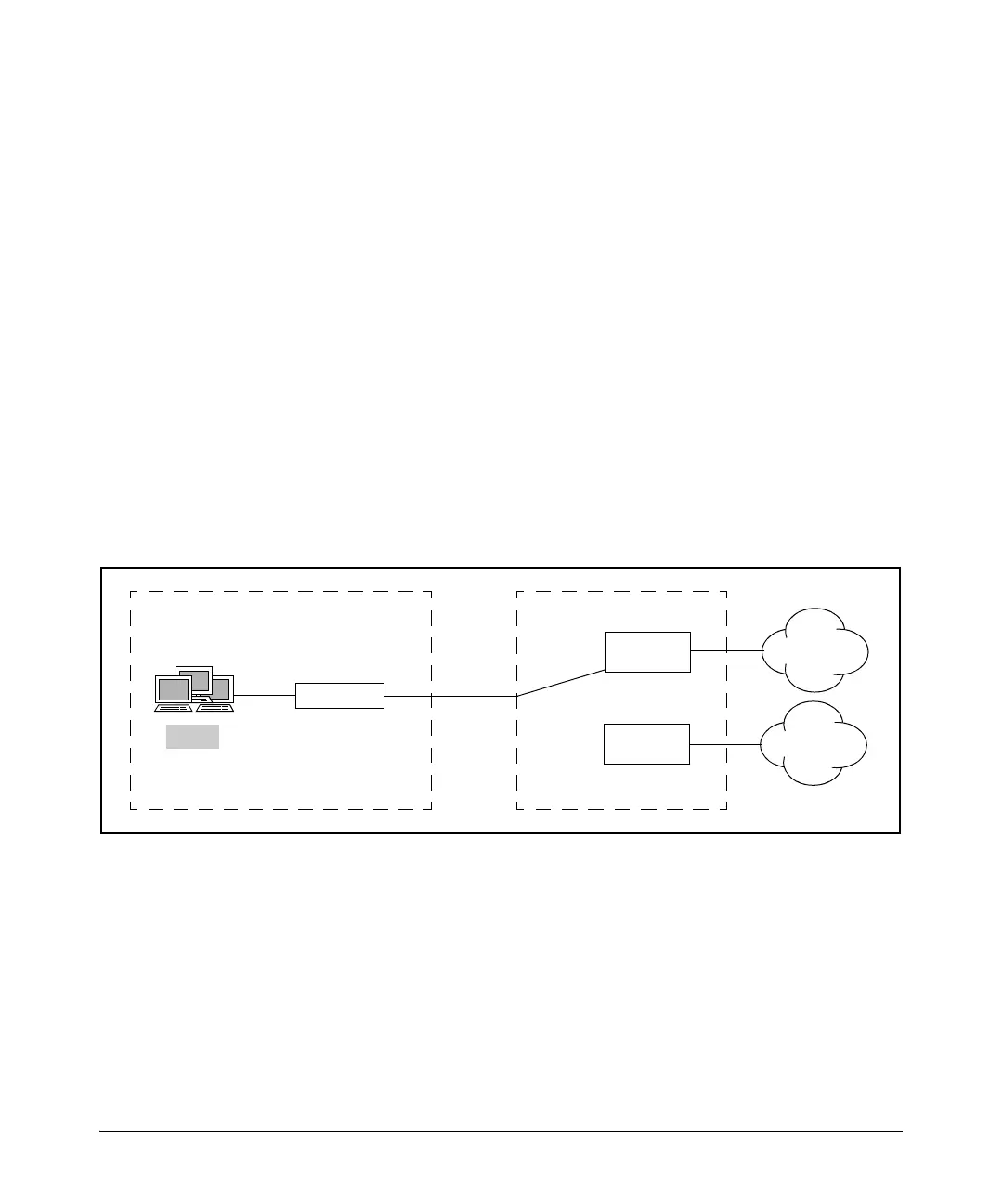
Figure 7-3. The ADSL Network
The regional broadband network is connected to the Internet. (See Figure 7-4.)
Public Carrier’s Central OfficeCustomer’s Premises
WAN router
DSLAM
Local
loop
Regional
broadband
network
Public
carrier
network
LAN
Voice or
ISDN switch
ATM
ATM
ATM

 Loading...
Loading...