8-17
Configuring Demand Routing for Primary ISDN Modules
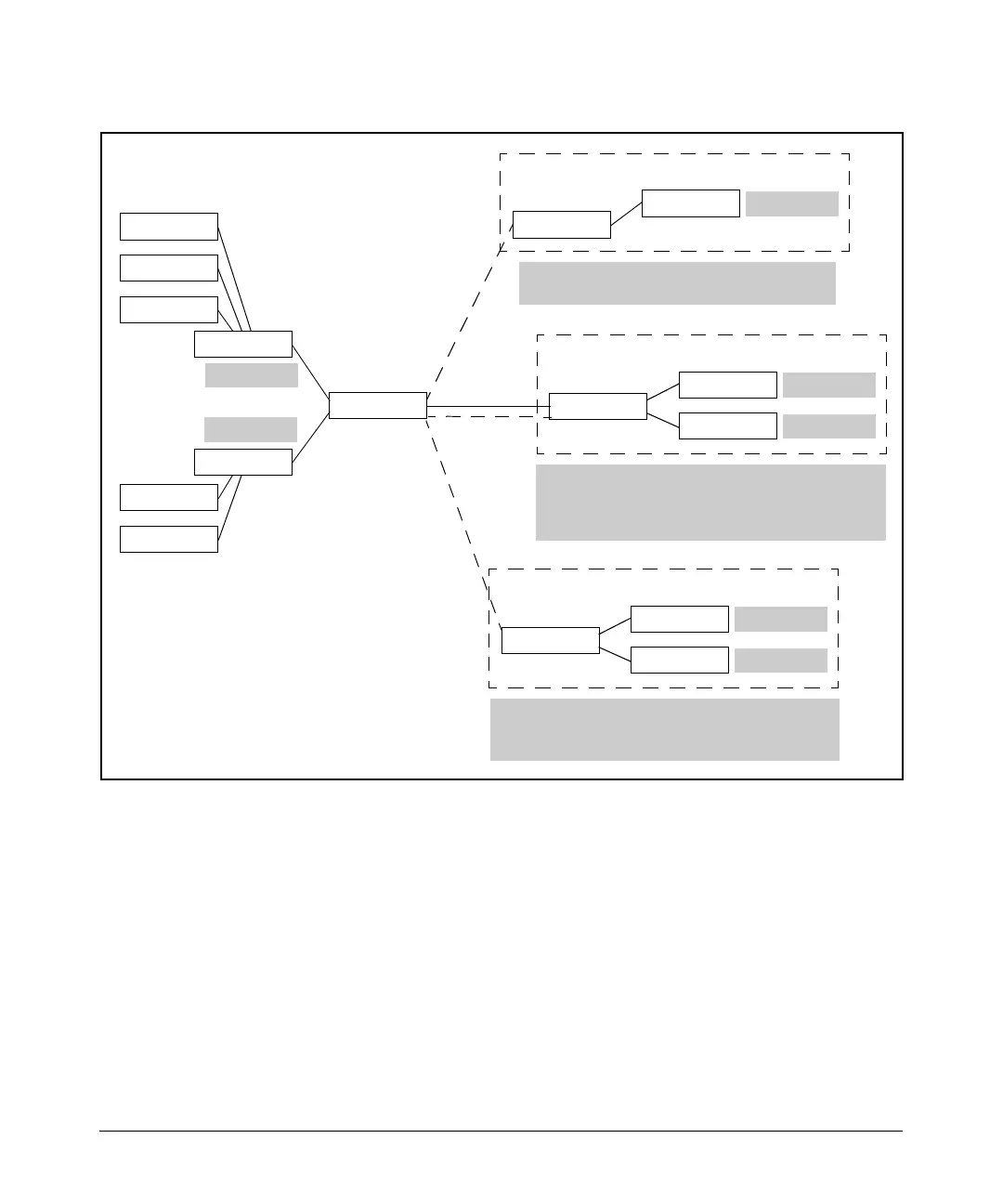
Using Demand Routing for ISDN Connections
Figure 8-5. Using Demand Routing to Establish Dial-Up Connections for Primary
and Backup Interfaces
Demand routing can also be used for backup dial-up connections, ensuring
that they are established only when the primary interface is down and traffic
must be transmitted to another site. (For more information about using
demand routing for backup dial-up connections, see the Advanced Manage-
ment and Configuration Guide, Chapter 3: Configuring Backup WAN
Connections.)
Branch Office C
Branch Office B
Branch Office A
192.168.1.0
ISDN connection to Branch Office A triggered by
traffic with destination address 192.168.4.0 /24
Edge Switch
Edge Switch
Edge Switch
192.168.2.0
Core Switch
Core Switch
Edge Switch
Edge Switch
Main Router
Backup ISDN connection to Branch Office B triggered
only when primary interface goes down and traffic with
destination address 192.168.5.0 /24 or 192.168.6.0 /24 is
forwarded to demand interface
192.168.4.0
Switch
Router A
192.168.5.0
Switch
192.168.6.0
Switch
Router B
ISDN connection to Branch Office C triggered only
when traffic with destination address 192.168.7.0 /24 or
192.168.8.0 /24 is forwarded to demand interface
192.168.7.0
Switch
192.168.8.0
Switch
Router C
Frame Relay
over E1
ISDN
connection
ISDN
connection
Backup
connection

 Loading...
Loading...