8-49
Configuring Demand Routing for Primary ISDN Modules
Using Demand Routing for ISDN Connections
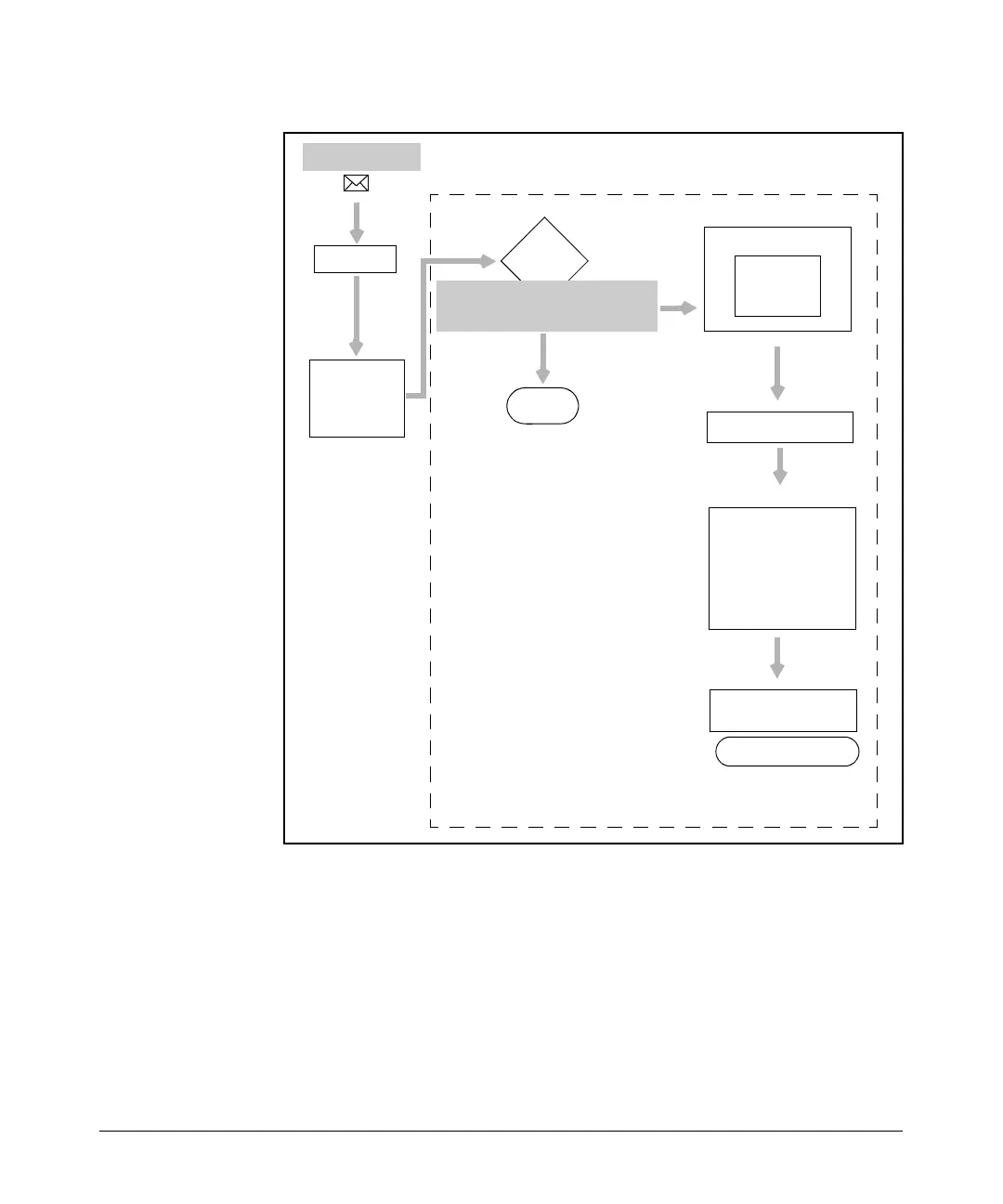
Figure 8-13. Successful Demand Interface Call Setup
When a packet is received on the router, it goes through several processes
before it is finally forwarded across a WAN connection. If fast caching is
enabled, the router takes a moment to check the fast-cache table. In this
example, all traffic to the 192.168.1.0 network has a fast-cache route through
the demand 1 interface. The router matches the incoming packet with this
route and forwards it to the demand interface. (If the packet did not match an
entry in the fast-cache table, the router would match it a route in its standard
routing table.)
Allowed?
connect-
sequence 2
No
ACL Match?
Drop
packet
Yes
Router
permit ip any 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255
permit ip any 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Fast-cache
Table
192.168.1.0/24
demand 1
Resource Pool Pool 1
ISDN group 1
bri 2/1
bri 2/2
Yes int bri 2/1
connect-sequence 2
dial-string 10997161683
forced-ISDN-64k
connect-sequence 4
dial-string 10995555683
forced-ISDN-64k
Successfully Place Call
and Establish Connection
To: 192.168.1.29
connect-mode
either
Resource Available?
Yes
Demand Interface
connect-order?
sequential

 Loading...
Loading...