1. If the feedback loop is active, the signal should show no variations below the bandwidth cutoff
frequency since the loop is supposed to maintain a constant signal by varying the Z Piezo Signal. This
means low frequency noise will not appear in the Input Signal, but it will be present in the Topography
Signal.
2. If the feedback loop is active, high frequency noise will not appear in the Topography Signal because
the feedback loop will ignore any signal on the input above the bandwidth cutoff frequency and all
spectra above this frequency will be essentially flat.
3. If the feedback loop is disabled, then all noise sources will usually appear in the Input Signal since the
variations of the tip-sample separation will not be corrected. This is usually the preferred method of
looking for noise sources. Noise peaks of concern can be found by measuring the Input Signal with
feedback disabled while the microscope is in feedback range.
4. If the microscope is out of feedback range, the only source of noise in the spectra should be electrical
problems due to ground loops, capacitive coupling, improper shielding, etc.
5. If the microscope is in feedback range, the noise sources will be a combination of electrical and
vibration sources.
K.5. Monitor
Monitor Windows provide additional methods of viewing data channels. Monitors will only display the
data; they are not intended to be used for acquisition. An example use of a Monitor is to display the Input
Signal on a different scale.
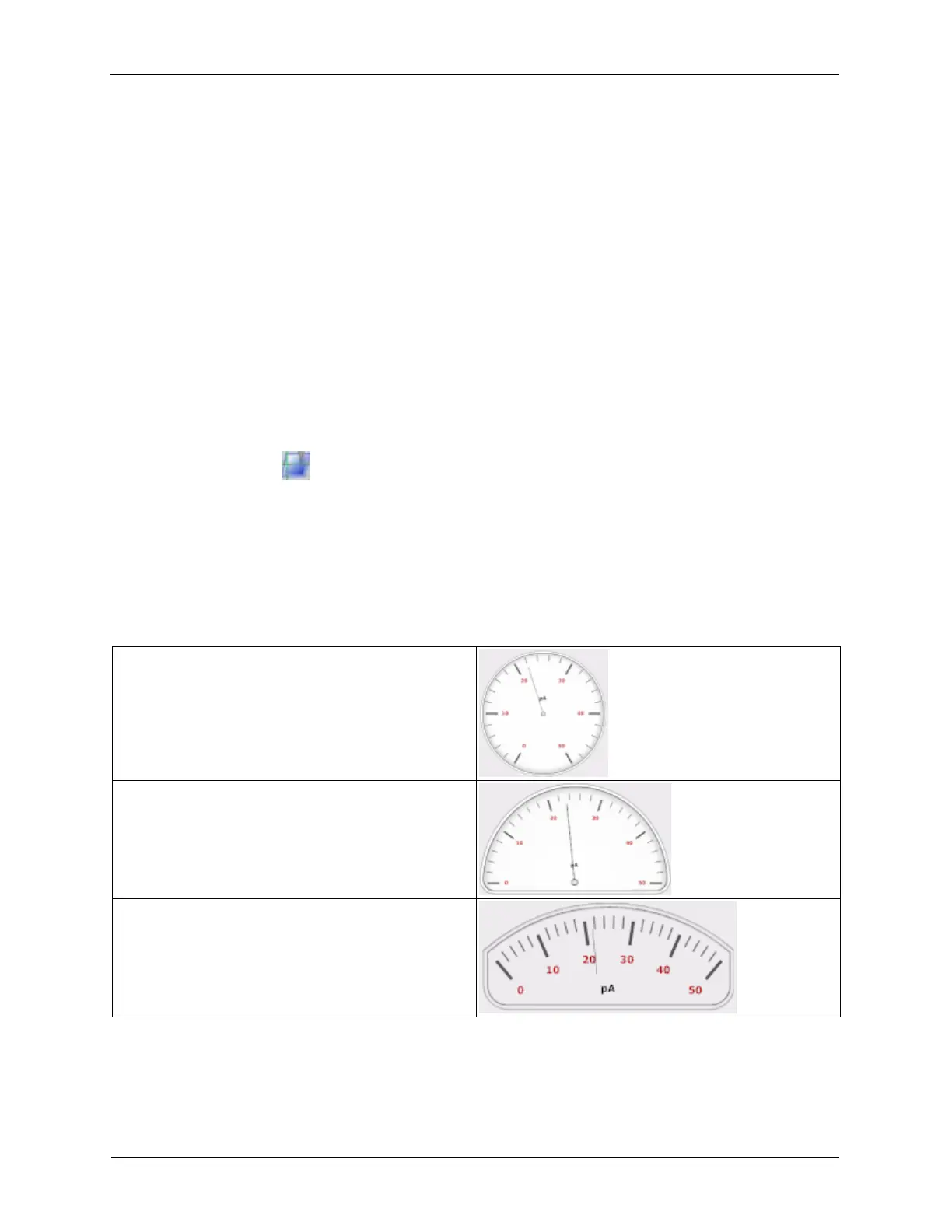
There are several different Monitor visualizations: Circular Full, Circular Half, Circular Wide, Linear
Horizontal, Linear Vertical, and Digital. Below are examples of the different types of Monitors.
Table K.1. Types of Monitors
 Loading...
Loading...