Display and Analyze your Image
5.2 Basic Image Processing
There are many image processing mechanisms that can make original (raw) data appear to be smooth,
flat, and clean, and reveal more useful information about the sample.
Important
The original, raw acquired data is NEVER overwritten by processing! Any processing
done to this data will cause a copy of the modified data to be saved into the SM4 file. The
user can revert processed data back into its raw data at any time.
5.2.1 Background Removal
As displayed in the previous figure, the raw data of a typical SPM image normally contains different kinds
of background tilt, misalignment, or some offset between scan lines. Such background effects will make
the overall data height distribution to be larger than the actual topographic roughness of the image, and
cause the color maps to have brightness saturation or blurry details. Therefore, the very first processing
operation on your raw data is usually Background Subtraction. The Browser offers a list of algorithms
for Background Subtraction under the Image Processing > Background menu. The Plane/Parabola
Subtraction treats the entire image as a planer or parabolic surface, and flattens the data by removing
the general "tilt" and "bow" of the background, but it is not effective in dealing with an offset between scan
lines, or "steps". Step Flatten is much more effective in dealing with such background offsets. When we
have images with lots of mis-aligned offsets between scan lines, the more aggressive X Offset Subtract
or X Slope Subtract can be used. However, such line-by-line background subtraction could also result in
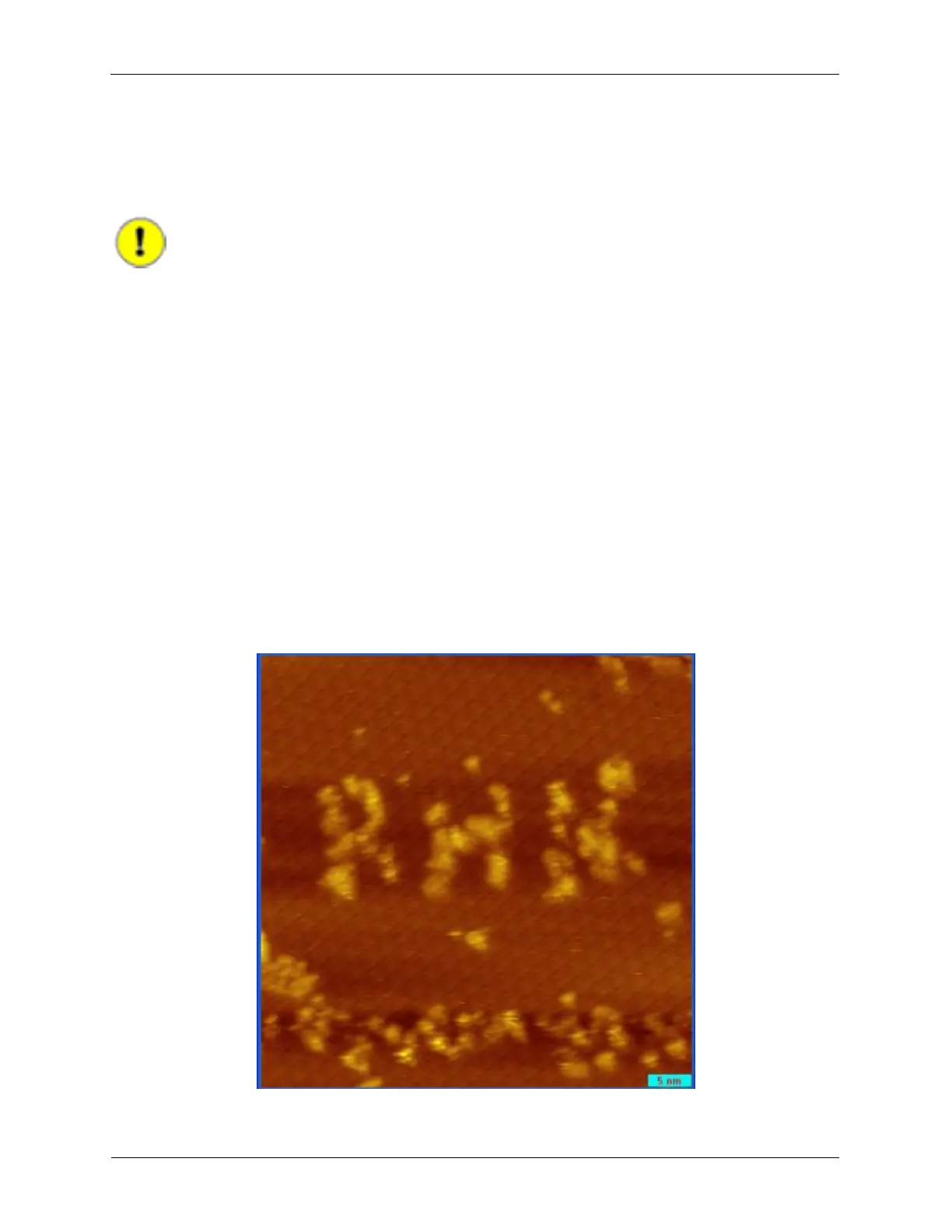
a shadow-like artifact when there are relatively tall features in the image. The following figure shows the
result of such shadow artifact after the image has been processed by X Offset Subtract.
Figure 5.2. Shadow style Artifact from X Offset Subtract
 Loading...
Loading...